Zelin Dai
Editing Language Model-based Knowledge Graph Embeddings
Jan 25, 2023Abstract:Recently decades have witnessed the empirical success of framing Knowledge Graph (KG) embeddings via language models. However, language model-based KG embeddings are usually deployed as static artifacts, which are challenging to modify without re-training after deployment. To address this issue, we propose a new task of editing language model-based KG embeddings in this paper. The proposed task aims to enable data-efficient and fast updates to KG embeddings without damaging the performance of the rest. We build four new datasets: E-FB15k237, A-FB15k237, E-WN18RR, and A-WN18RR, and evaluate several knowledge editing baselines demonstrating the limited ability of previous models to handle the proposed challenging task. We further propose a simple yet strong baseline dubbed KGEditor, which utilizes additional parametric layers of the hyper network to edit/add facts. Comprehensive experimental results demonstrate that KGEditor can perform better when updating specific facts while not affecting the rest with low training resources. Code and datasets will be available in https://github.com/zjunlp/PromptKG/tree/main/deltaKG.
Commonsense Knowledge Salience Evaluation with a Benchmark Dataset in E-commerce
May 22, 2022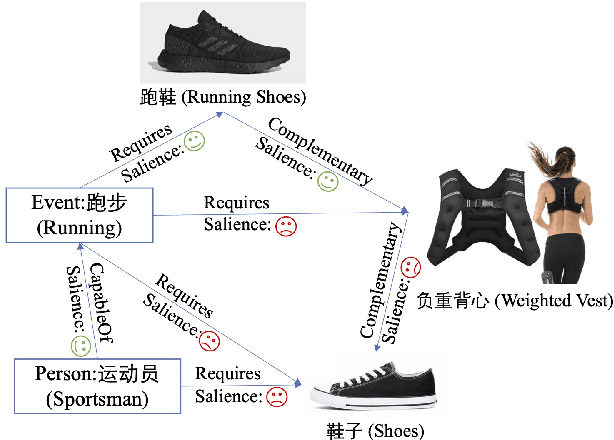
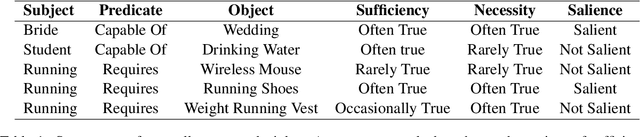

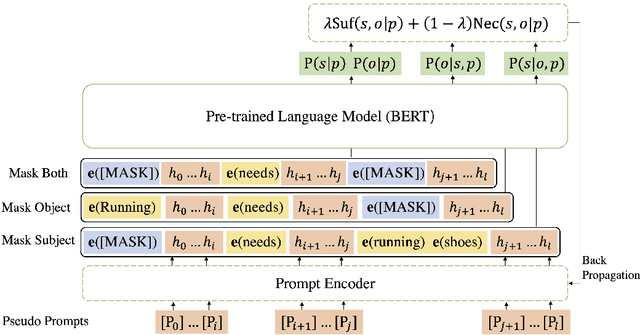
Abstract:In e-commerce, the salience of commonsense knowledge (CSK) is beneficial for widespread applications such as product search and recommendation. For example, when users search for "running" in e-commerce, they would like to find items highly related to running, such as "running shoes" rather than "shoes". However, many existing CSK collections rank statements solely by confidence scores, and there is no information about which ones are salient from a human perspective. In this work, we define the task of supervised salience evaluation, where given a CSK triple, the model is required to learn whether the triple is salient or not. In addition to formulating the new task, we also release a new Benchmark dataset of Salience Evaluation in E-commerce (BSEE) and hope to promote related research on commonsense knowledge salience evaluation. We conduct experiments in the dataset with several representative baseline models. The experimental results show that salience evaluation is a hard task where models perform poorly on our evaluation set. We further propose a simple but effective approach, PMI-tuning, which shows promise for solving this novel problem.
SQUIRE: A Sequence-to-sequence Framework for Multi-hop Knowledge Graph Reasoning
Jan 17, 2022



Abstract:Multi-hop knowledge graph (KG) reasoning has been widely studied in recent years to provide interpretable predictions on missing links. Given a triple query, multi-hop reasoning task aims to give an evidential path that indicates the inference process. Most previous works use reinforcement learning (RL) based method that learns to navigate the path towards the target entity. However, these methods suffer from slow and poor convergence, and they may fail to infer a certain path when there is a missing edge along the path. Here we present SQUIRE, the first Sequence-to-sequence based multi-hop reasoning framework, which utilizes an encoder-decoder structure to translate the query to a path. Our model design brings about two benefits: (1) It can learn and predict in an end-to-end fashion, which gives better and faster convergence; (2) Our model does not rely on existing edges to generate the path, and has the flexibility to complete missing edges along the path, especially in sparse KGs. Experiments on standard and sparse KGs show that our approach yields significant improvement over prior methods, while converging 4x-7x faster.
Interpretable and Low-Resource Entity Matching via Decoupling Feature Learning from Decision Making
Jun 08, 2021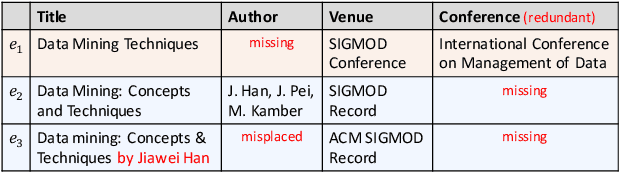
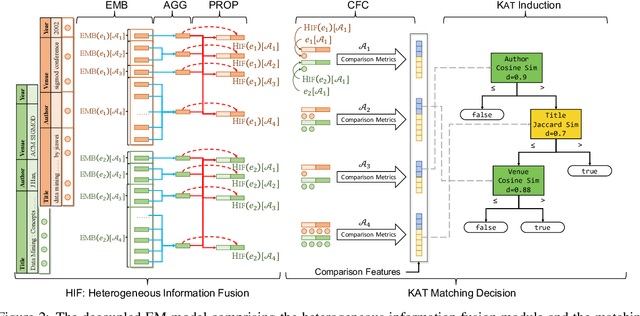
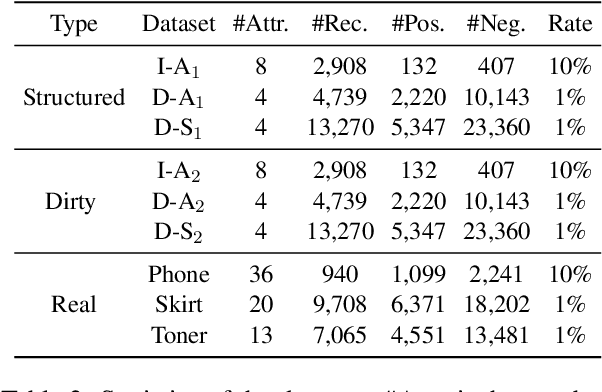
Abstract:Entity Matching (EM) aims at recognizing entity records that denote the same real-world object. Neural EM models learn vector representation of entity descriptions and match entities end-to-end. Though robust, these methods require many resources for training, and lack of interpretability. In this paper, we propose a novel EM framework that consists of Heterogeneous Information Fusion (HIF) and Key Attribute Tree (KAT) Induction to decouple feature representation from matching decision. Using self-supervised learning and mask mechanism in pre-trained language modeling, HIF learns the embeddings of noisy attribute values by inter-attribute attention with unlabeled data. Using a set of comparison features and a limited amount of annotated data, KAT Induction learns an efficient decision tree that can be interpreted by generating entity matching rules whose structure is advocated by domain experts. Experiments on 6 public datasets and 3 industrial datasets show that our method is highly efficient and outperforms SOTA EM models in most cases. Our codes and datasets can be obtained from https://github.com/THU-KEG/HIF-KAT.
Is Multi-Hop Reasoning Really Explainable? Towards Benchmarking Reasoning Interpretability
Apr 14, 2021



Abstract:Multi-hop reasoning has been widely studied in recent years to obtain more interpretable link prediction. However, we find in experiments that many paths given by these models are actually unreasonable, while little works have been done on interpretability evaluation for them. In this paper, we propose a unified framework to quantitatively evaluate the interpretability of multi-hop reasoning models so as to advance their development. In specific, we define three metrics including path recall, local interpretability, and global interpretability for evaluation, and design an approximate strategy to calculate them using the interpretability scores of rules. Furthermore, we manually annotate all possible rules and establish a Benchmark to detect the Interpretability of Multi-hop Reasoning (BIMR). In experiments, we run nine baselines on our benchmark. The experimental results show that the interpretability of current multi-hop reasoning models is less satisfactory and is still far from the upper bound given by our benchmark. Moreover, the rule-based models outperform the multi-hop reasoning models in terms of performance and interpretability, which points to a direction for future research, i.e., we should investigate how to better incorporate rule information into the multi-hop reasoning model. Our codes and datasets can be obtained from https://github.com/THU-KEG/BIMR.
Multiple Generative Models Ensemble for Knowledge-Driven Proactive Human-Computer Dialogue Agent
Jul 08, 2019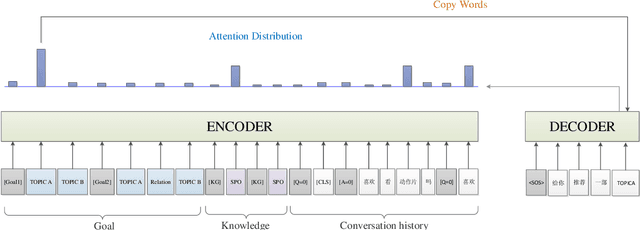
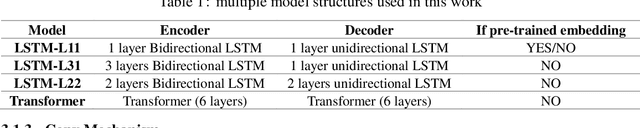
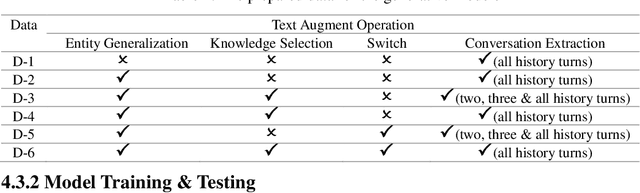
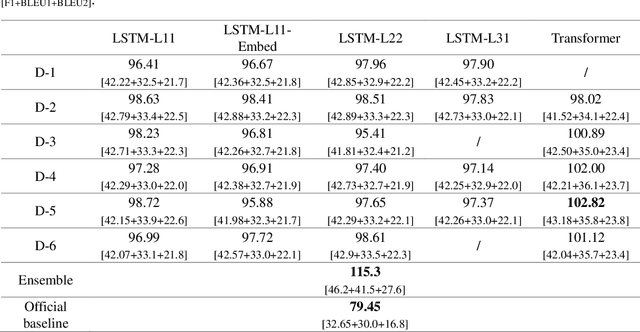
Abstract:Multiple sequence to sequence models were used to establish an end-to-end multi-turns proactive dialogue generation agent, with the aid of data augmentation techniques and variant encoder-decoder structure designs. A rank-based ensemble approach was developed for boosting performance. Results indicate that our single model, in average, makes an obvious improvement in the terms of F1-score and BLEU over the baseline by 18.67% on the DuConv dataset. In particular, the ensemble methods further significantly outperform the baseline by 35.85%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge