Tiansi Dong
An AI Monkey Gets Grapes for Sure -- Sphere Neural Networks for Reliable Decision-Making
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:This paper compares three methodological categories of neural reasoning: LLM reasoning, supervised learning-based reasoning, and explicit model-based reasoning. LLMs remain unreliable and struggle with simple decision-making that animals can master without extensive corpora training. Through disjunctive syllogistic reasoning testing, we show that reasoning via supervised learning is less appealing than reasoning via explicit model construction. Concretely, we show that an Euler Net trained to achieve 100.00% in classic syllogistic reasoning can be trained to reach 100.00% accuracy in disjunctive syllogistic reasoning. However, the retrained Euler Net suffers severely from catastrophic forgetting (its performance drops to 6.25% on already-learned classic syllogistic reasoning), and its reasoning competence is limited to the pattern level. We propose a new version of Sphere Neural Networks that embeds concepts as circles on the surface of an n-dimensional sphere. These Sphere Neural Networks enable the representation of the negation operator via complement circles and achieve reliable decision-making by filtering out illogical statements that form unsatisfiable circular configurations. We demonstrate that the Sphere Neural Network can master 16 syllogistic reasoning tasks, including rigorous disjunctive syllogistic reasoning, while preserving the rigour of classical syllogistic reasoning. We conclude that neural reasoning with explicit model construction is the most reliable among the three methodological categories of neural reasoning.
Sphere Neural-Networks for Rational Reasoning
Mar 22, 2024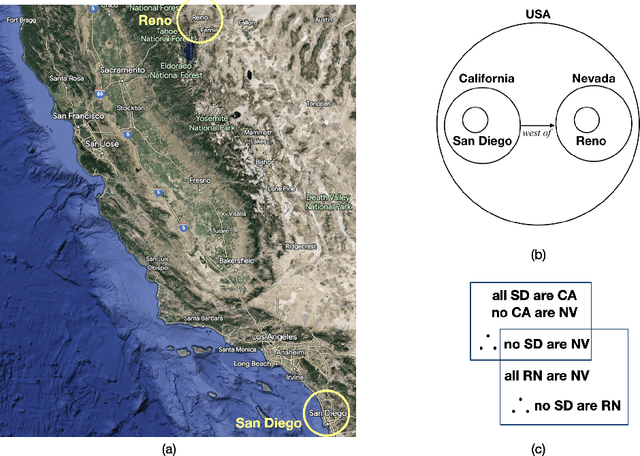
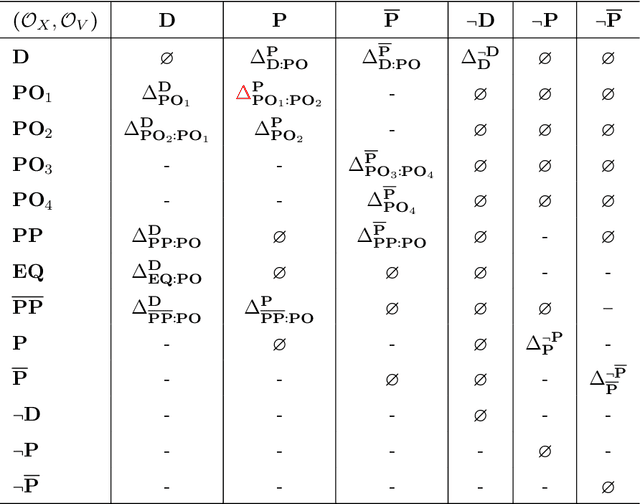
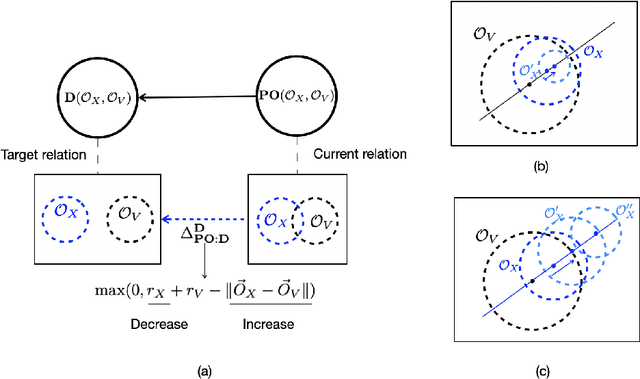
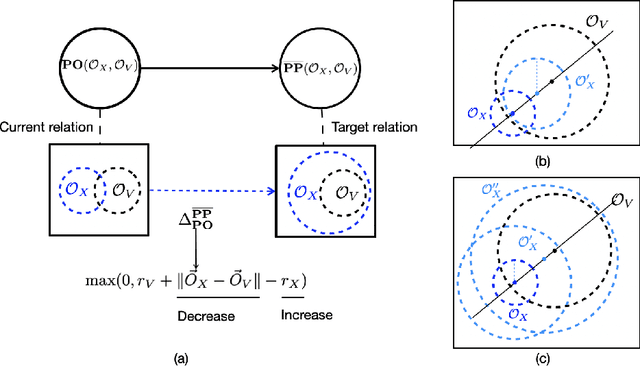
Abstract:The success of Large Language Models (LLMs), e.g., ChatGPT, is witnessed by their planetary popularity, their capability of human-like question-answering, and also by their steadily improved reasoning performance. However, it remains unclear whether LLMs reason. It is an open problem how traditional neural networks can be qualitatively extended to go beyond the statistic paradigm and achieve high-level cognition. Here, we present a minimalist qualitative extension by generalising computational building blocks from vectors to spheres. We propose Sphere Neural Networks (SphNNs) for human-like reasoning through model construction and inspection, and develop SphNN for syllogistic reasoning, a microcosm of human rationality. Instead of training data, SphNN uses a neuro-symbolic transition map of neighbourhood spatial relations to guide transformations from the current sphere configuration towards the target. SphNN is the first neural model that can determine the validity of long-chained syllogistic reasoning in one epoch by constructing sphere configurations as Euler diagrams, with the worst computational complexity of O(N^2). SphNN can evolve into various types of reasoning, such as spatio-temporal reasoning, logical reasoning with negation and disjunction, event reasoning, neuro-symbolic reasoning, and humour understanding (the highest level of cognition). All these suggest a new kind of Herbert A. Simon's scissors with two neural blades. SphNNs will tremendously enhance interdisciplinary collaborations to develop the two neural blades and realise deterministic neural reasoning and human-bounded rationality and elevate LLMs to reliable psychological AI. This work suggests that the non-zero radii of spheres are the missing components that prevent traditional deep-learning systems from reaching the realm of rational reasoning and cause LLMs to be trapped in the swamp of hallucination.
Word Sense Disambiguation as a Game of Neurosymbolic Darts
Jul 25, 2023Abstract:Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) is one of the hardest tasks in natural language understanding and knowledge engineering. The glass ceiling of 80% F1 score is recently achieved through supervised deep-learning, enriched by a variety of knowledge graphs. Here, we propose a novel neurosymbolic methodology that is able to push the F1 score above 90%. The core of our methodology is a neurosymbolic sense embedding, in terms of a configuration of nested balls in n-dimensional space. The centre point of a ball well-preserves word embedding, which partially fix the locations of balls. Inclusion relations among balls precisely encode symbolic hypernym relations among senses, and enable simple logic deduction among sense embeddings, which cannot be realised before. We trained a Transformer to learn the mapping from a contextualized word embedding to its sense ball embedding, just like playing the game of darts (a game of shooting darts into a dartboard). A series of experiments are conducted by utilizing pre-training n-ball embeddings, which have the coverage of around 70% training data and 75% testing data in the benchmark WSD corpus. The F1 scores in experiments range from 90.1% to 100.0% in all six groups of test data-sets (each group has 4 testing data with different sizes of n-ball embeddings). Our novel neurosymbolic methodology has the potential to break the ceiling of deep-learning approaches for WSD. Limitations and extensions of our current works are listed.
Interpretable and Low-Resource Entity Matching via Decoupling Feature Learning from Decision Making
Jun 08, 2021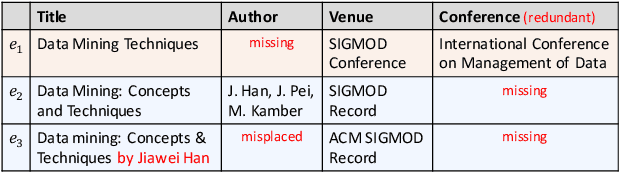
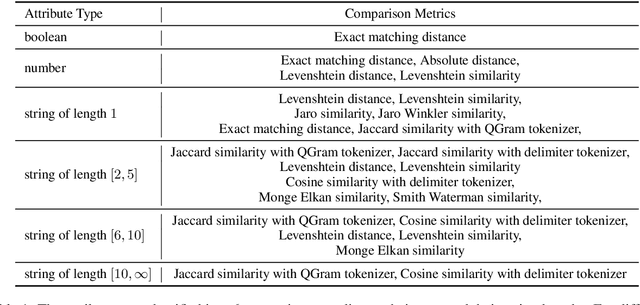
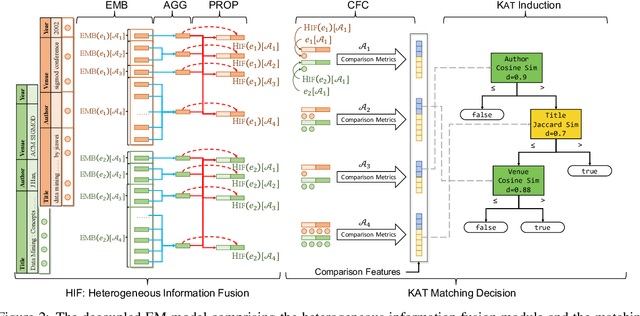
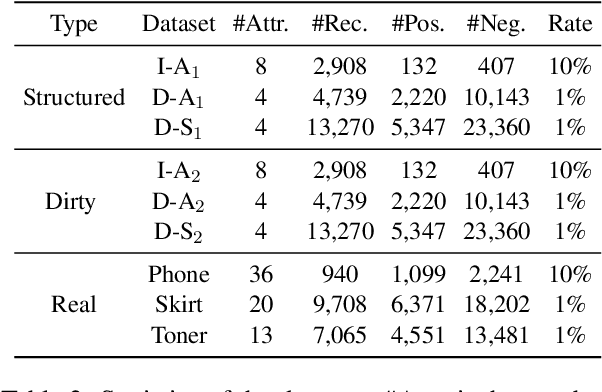
Abstract:Entity Matching (EM) aims at recognizing entity records that denote the same real-world object. Neural EM models learn vector representation of entity descriptions and match entities end-to-end. Though robust, these methods require many resources for training, and lack of interpretability. In this paper, we propose a novel EM framework that consists of Heterogeneous Information Fusion (HIF) and Key Attribute Tree (KAT) Induction to decouple feature representation from matching decision. Using self-supervised learning and mask mechanism in pre-trained language modeling, HIF learns the embeddings of noisy attribute values by inter-attribute attention with unlabeled data. Using a set of comparison features and a limited amount of annotated data, KAT Induction learns an efficient decision tree that can be interpreted by generating entity matching rules whose structure is advocated by domain experts. Experiments on 6 public datasets and 3 industrial datasets show that our method is highly efficient and outperforms SOTA EM models in most cases. Our codes and datasets can be obtained from https://github.com/THU-KEG/HIF-KAT.
Learning Syllogism with Euler Neural-Networks
Jul 20, 2020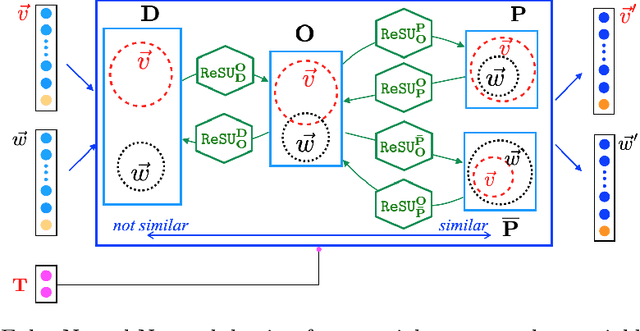
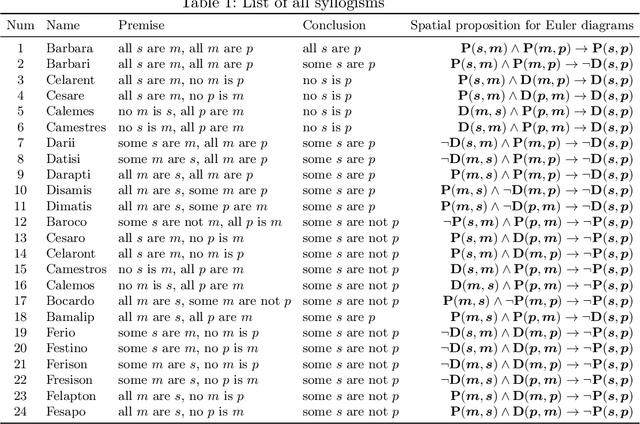
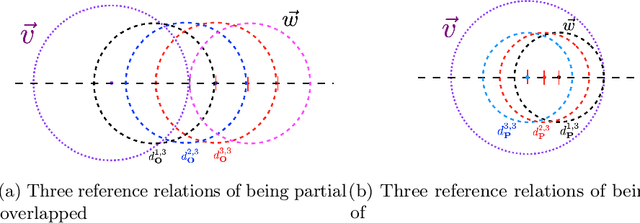
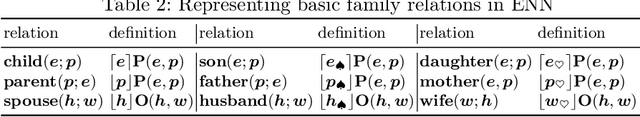
Abstract:Traditional neural networks represent everything as a vector, and are able to approximate a subset of logical reasoning to a certain degree. As basic logic relations are better represented by topological relations between regions, we propose a novel neural network that represents everything as a ball and is able to learn topological configuration as an Euler diagram. So comes the name Euler Neural-Network (ENN). The central vector of a ball is a vector that can inherit representation power of traditional neural network. ENN distinguishes four spatial statuses between balls, namely, being disconnected, being partially overlapped, being part of, being inverse part of. Within each status, ideal values are defined for efficient reasoning. A novel back-propagation algorithm with six Rectified Spatial Units (ReSU) can optimize an Euler diagram representing logical premises, from which logical conclusion can be deduced. In contrast to traditional neural network, ENN can precisely represent all 24 different structures of Syllogism. Two large datasets are created: one extracted from WordNet-3.0 covers all types of Syllogism reasoning, the other extracted all family relations from DBpedia. Experiment results approve the superior power of ENN in logical representation and reasoning. Datasets and source code are available upon request.
Joint Representation Learning of Cross-lingual Words and Entities via Attentive Distant Supervision
Nov 27, 2018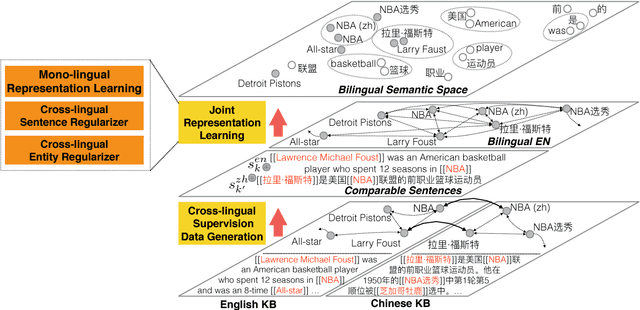
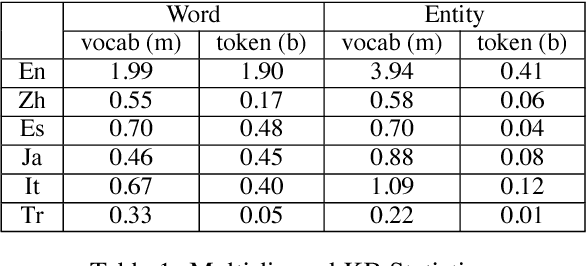
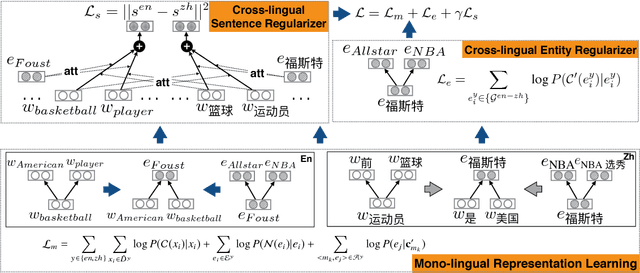
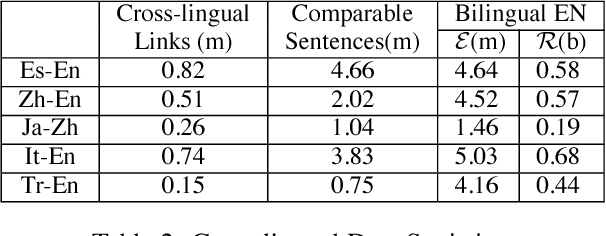
Abstract:Joint representation learning of words and entities benefits many NLP tasks, but has not been well explored in cross-lingual settings. In this paper, we propose a novel method for joint representation learning of cross-lingual words and entities. It captures mutually complementary knowledge, and enables cross-lingual inferences among knowledge bases and texts. Our method does not require parallel corpora, and automatically generates comparable data via distant supervision using multi-lingual knowledge bases. We utilize two types of regularizers to align cross-lingual words and entities, and design knowledge attention and cross-lingual attention to further reduce noises. We conducted a series of experiments on three tasks: word translation, entity relatedness, and cross-lingual entity linking. The results, both qualitatively and quantitatively, demonstrate the significance of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge