Rafet Sifa
Domain-Adaptation through Synthetic Data: Fine-Tuning Large Language Models for German Law
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often struggle in specialized domains such as legal reasoning due to limited expert knowledge, resulting in factually incorrect outputs or hallucinations. This paper presents an effective method for adapting advanced LLMs to German legal question answering through a novel synthetic data generation approach. In contrast to costly human-annotated resources or unreliable synthetic alternatives, our approach systematically produces high-quality, diverse, and legally accurate question-answer pairs directly from authoritative German statutes. Using rigorous automated filtering methods and parameter-efficient fine-tuning techniques, we demonstrate that LLMs adapted with our synthetic dataset significantly outperform their baseline counterparts on German legal question answering tasks. Our results highlight the feasibility of using carefully designed synthetic data as a robust alternative to manual annotation in high-stakes, knowledge-intensive domains.
Generalizing Abstention for Noise-Robust Learning in Medical Image Segmentation
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Label noise is a critical problem in medical image segmentation, often arising from the inherent difficulty of manual annotation. Models trained on noisy data are prone to overfitting, which degrades their generalization performance. While a number of methods and strategies have been proposed to mitigate noisy labels in the segmentation domain, this area remains largely under-explored. The abstention mechanism has proven effective in classification tasks by enhancing the capabilities of Cross Entropy, yet its potential in segmentation remains unverified. In this paper, we address this gap by introducing a universal and modular abstention framework capable of enhancing the noise-robustness of a diverse range of loss functions. Our framework improves upon prior work with two key components: an informed regularization term to guide abstention behaviour, and a more flexible power-law-based auto-tuning algorithm for the abstention penalty. We demonstrate the framework's versatility by systematically integrating it with three distinct loss functions to create three novel, noise-robust variants: GAC, SAC, and ADS. Experiments on the CaDIS and DSAD medical datasets show our methods consistently and significantly outperform their non-abstaining baselines, especially under high noise levels. This work establishes that enabling models to selectively ignore corrupted samples is a powerful and generalizable strategy for building more reliable segmentation models. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/wemous/abstention-for-segmentation.
Benchmark Success, Clinical Failure: When Reinforcement Learning Optimizes for Benchmarks, Not Patients
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Recent Reinforcement Learning (RL) advances for Large Language Models (LLMs) have improved reasoning tasks, yet their resource-constrained application to medical imaging remains underexplored. We introduce ChexReason, a vision-language model trained via R1-style methodology (SFT followed by GRPO) using only 2,000 SFT samples, 1,000 RL samples, and a single A100 GPU. Evaluations on CheXpert and NIH benchmarks reveal a fundamental tension: GRPO recovers in-distribution performance (23% improvement on CheXpert, macro-F1 = 0.346) but degrades cross-dataset transferability (19% drop on NIH). This mirrors high-resource models like NV-Reason-CXR-3B, suggesting the issue stems from the RL paradigm rather than scale. We identify a generalization paradox where the SFT checkpoint uniquely improves on NIH before optimization, indicating teacher-guided reasoning captures more institution-agnostic features. Furthermore, cross-model comparisons show structured reasoning scaffolds benefit general-purpose VLMs but offer minimal gain for medically pre-trained models. Consequently, curated supervised fine-tuning may outperform aggressive RL for clinical deployment requiring robustness across diverse populations.
History Rhymes: Macro-Contextual Retrieval for Robust Financial Forecasting
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Financial markets are inherently non-stationary: structural breaks and macroeconomic regime shifts often cause forecasting models to fail when deployed out of distribution (OOD). Conventional multimodal approaches that simply fuse numerical indicators and textual sentiment rarely adapt to such shifts. We introduce macro-contextual retrieval, a retrieval-augmented forecasting framework that grounds each prediction in historically analogous macroeconomic regimes. The method jointly embeds macro indicators (e.g., CPI, unemployment, yield spread, GDP growth) and financial news sentiment in a shared similarity space, enabling causal retrieval of precedent periods during inference without retraining. Trained on seventeen years of S&P 500 data (2007-2023) and evaluated OOD on AAPL (2024) and XOM (2024), the framework consistently narrows the CV to OOD performance gap. Macro-conditioned retrieval achieves the only positive out-of-sample trading outcomes (AAPL: PF=1.18, Sharpe=0.95; XOM: PF=1.16, Sharpe=0.61), while static numeric, text-only, and naive multimodal baselines collapse under regime shifts. Beyond metric gains, retrieved neighbors form interpretable evidence chains that correspond to recognizable macro contexts, such as inflationary or yield-curve inversion phases, supporting causal interpretability and transparency. By operationalizing the principle that "financial history may not repeat, but it often rhymes," this work demonstrates that macro-aware retrieval yields robust, explainable forecasts under distributional change. All datasets, models, and source code are publicly available.
From Retinal Pixels to Patients: Evolution of Deep Learning Research in Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
Nov 14, 2025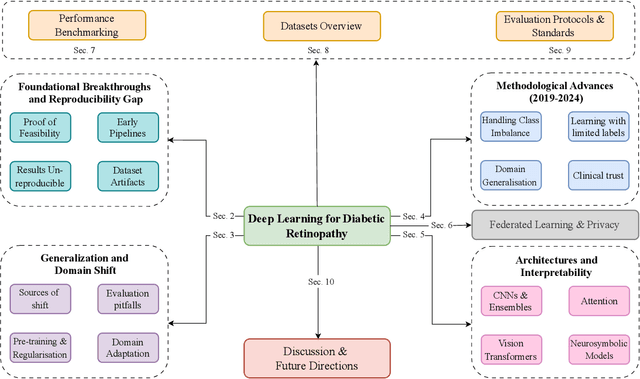

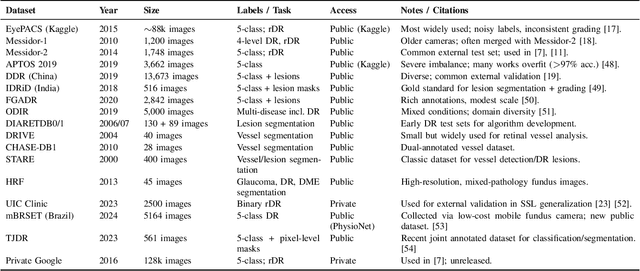
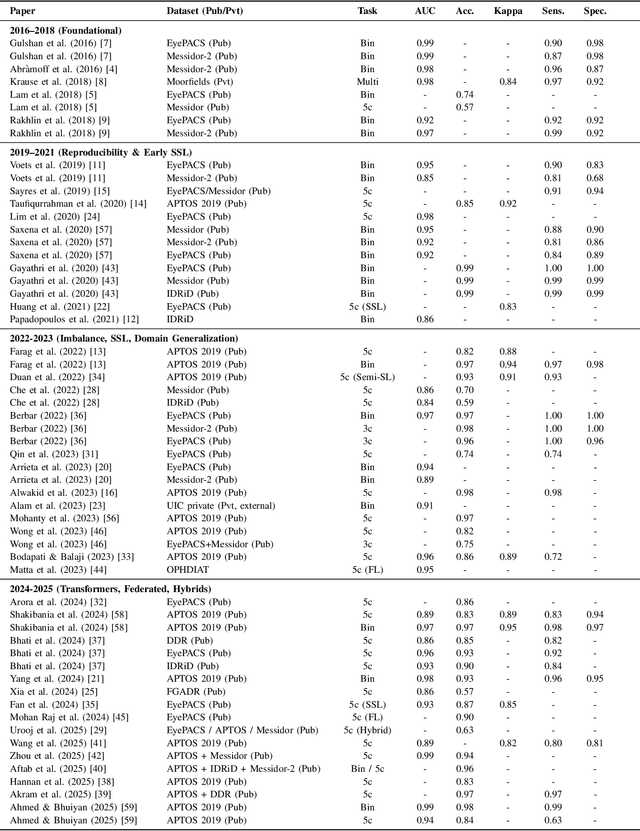
Abstract:Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) remains a leading cause of preventable blindness, with early detection critical for reducing vision loss worldwide. Over the past decade, deep learning has transformed DR screening, progressing from early convolutional neural networks trained on private datasets to advanced pipelines addressing class imbalance, label scarcity, domain shift, and interpretability. This survey provides the first systematic synthesis of DR research spanning 2016-2025, consolidating results from 50+ studies and over 20 datasets. We critically examine methodological advances, including self- and semi-supervised learning, domain generalization, federated training, and hybrid neuro-symbolic models, alongside evaluation protocols, reporting standards, and reproducibility challenges. Benchmark tables contextualize performance across datasets, while discussion highlights open gaps in multi-center validation and clinical trust. By linking technical progress with translational barriers, this work outlines a practical agenda for reproducible, privacy-preserving, and clinically deployable DR AI. Beyond DR, many of the surveyed innovations extend broadly to medical imaging at scale.
How Small Can You Go? Compact Language Models for On-Device Critical Error Detection in Machine Translation
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at evaluating machine translation (MT), but their scale and cost hinder deployment on edge devices and in privacy-sensitive workflows. We ask: how small can you get while still detecting meaning-altering translation errors? Focusing on English->German Critical Error Detection (CED), we benchmark sub-2B models (LFM2-350M, Qwen-3-0.6B/1.7B, Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct, Gemma-3-1B) across WMT21, WMT22, and SynCED-EnDe-2025. Our framework standardizes prompts, applies lightweight logit-bias calibration and majority voting, and reports both semantic quality (MCC, F1-ERR/F1-NOT) and compute metrics (VRAM, latency, throughput). Results reveal a clear sweet spot around one billion parameters: Gemma-3-1B provides the best quality-efficiency trade-off, reaching MCC=0.77 with F1-ERR=0.98 on SynCED-EnDe-2025 after merged-weights fine-tuning, while maintaining 400 ms single-sample latency on a MacBook Pro M4 Pro (24 GB). At larger scale, Qwen-3-1.7B attains the highest absolute MCC (+0.11 over Gemma) but with higher compute cost. In contrast, ultra-small models (0.6B) remain usable with few-shot calibration yet under-detect entity and number errors. Overall, compact, instruction-tuned LLMs augmented with lightweight calibration and small-sample supervision can deliver trustworthy, on-device CED for MT, enabling private, low-cost error screening in real-world translation pipelines. All datasets, prompts, and scripts are publicly available at our GitHub repository.
A Survey on Current Trends and Recent Advances in Text Anonymization
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:The proliferation of textual data containing sensitive personal information across various domains requires robust anonymization techniques to protect privacy and comply with regulations, while preserving data usability for diverse and crucial downstream tasks. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of current trends and recent advances in text anonymization techniques. We begin by discussing foundational approaches, primarily centered on Named Entity Recognition, before examining the transformative impact of Large Language Models, detailing their dual role as sophisticated anonymizers and potent de-anonymization threats. The survey further explores domain-specific challenges and tailored solutions in critical sectors such as healthcare, law, finance, and education. We investigate advanced methodologies incorporating formal privacy models and risk-aware frameworks, and address the specialized subfield of authorship anonymization. Additionally, we review evaluation frameworks, comprehensive metrics, benchmarks, and practical toolkits for real-world deployment of anonymization solutions. This review consolidates current knowledge, identifies emerging trends and persistent challenges, including the evolving privacy-utility trade-off, the need to address quasi-identifiers, and the implications of LLM capabilities, and aims to guide future research directions for both academics and practitioners in this field.
Reasoning LLMs in the Medical Domain: A Literature Survey
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The emergence of advanced reasoning capabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs) marks a transformative development in healthcare applications. Beyond merely expanding functional capabilities, these reasoning mechanisms enhance decision transparency and explainability-critical requirements in medical contexts. This survey examines the transformation of medical LLMs from basic information retrieval tools to sophisticated clinical reasoning systems capable of supporting complex healthcare decisions. We provide a thorough analysis of the enabling technological foundations, with a particular focus on specialized prompting techniques like Chain-of-Thought and recent breakthroughs in Reinforcement Learning exemplified by DeepSeek-R1. Our investigation evaluates purpose-built medical frameworks while also examining emerging paradigms such as multi-agent collaborative systems and innovative prompting architectures. The survey critically assesses current evaluation methodologies for medical validation and addresses persistent challenges in field interpretation limitations, bias mitigation strategies, patient safety frameworks, and integration of multimodal clinical data. Through this survey, we seek to establish a roadmap for developing reliable LLMs that can serve as effective partners in clinical practice and medical research.
Interpretable Topic Extraction and Word Embedding Learning using row-stochastic DEDICOM
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:The DEDICOM algorithm provides a uniquely interpretable matrix factorization method for symmetric and asymmetric square matrices. We employ a new row-stochastic variation of DEDICOM on the pointwise mutual information matrices of text corpora to identify latent topic clusters within the vocabulary and simultaneously learn interpretable word embeddings. We introduce a method to efficiently train a constrained DEDICOM algorithm and a qualitative evaluation of its topic modeling and word embedding performance.
* Accepted and published at CD-MAKE 2020, 20 pages, 8 tables, 8 figures
Advancing Risk and Quality Assurance: A RAG Chatbot for Improved Regulatory Compliance
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Risk and Quality (R&Q) assurance in highly regulated industries requires constant navigation of complex regulatory frameworks, with employees handling numerous daily queries demanding accurate policy interpretation. Traditional methods relying on specialized experts create operational bottlenecks and limit scalability. We present a novel Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) system leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs), hybrid search and relevance boosting to enhance R&Q query processing. Evaluated on 124 expert-annotated real-world queries, our actively deployed system demonstrates substantial improvements over traditional RAG approaches. Additionally, we perform an extensive hyperparameter analysis to compare and evaluate multiple configuration setups, delivering valuable insights to practitioners.
* Accepted and published at BigData 2024, 3 pages, 3 tables, 2 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge