Sneha Banerjee
Model-agnostic Body Part Relevance Assessment for Pedestrian Detection
Nov 27, 2023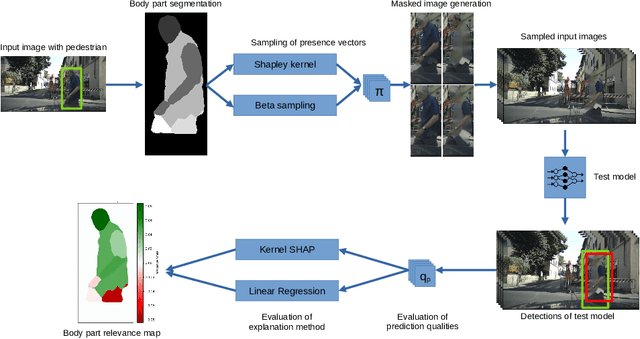

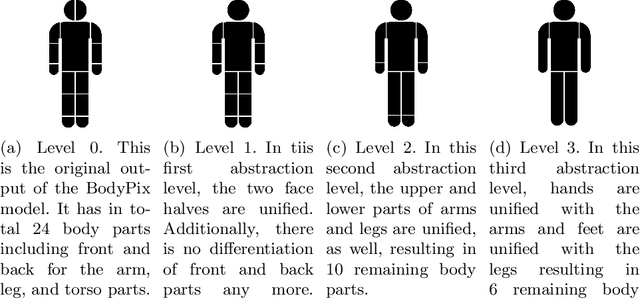
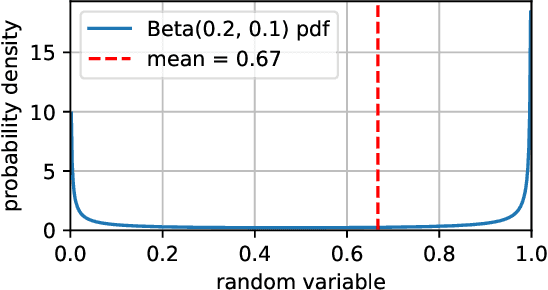
Abstract:Model-agnostic explanation methods for deep learning models are flexible regarding usability and availability. However, due to the fact that they can only manipulate input to see changes in output, they suffer from weak performance when used with complex model architectures. For models with large inputs as, for instance, in object detection, sampling-based methods like KernelSHAP are inefficient due to many computation-heavy forward passes through the model. In this work, we present a framework for using sampling-based explanation models in a computer vision context by body part relevance assessment for pedestrian detection. Furthermore, we introduce a novel sampling-based method similar to KernelSHAP that shows more robustness for lower sampling sizes and, thus, is more efficient for explainability analyses on large-scale datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge