Tobias Deußer
for the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
A Survey on Current Trends and Recent Advances in Text Anonymization
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:The proliferation of textual data containing sensitive personal information across various domains requires robust anonymization techniques to protect privacy and comply with regulations, while preserving data usability for diverse and crucial downstream tasks. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of current trends and recent advances in text anonymization techniques. We begin by discussing foundational approaches, primarily centered on Named Entity Recognition, before examining the transformative impact of Large Language Models, detailing their dual role as sophisticated anonymizers and potent de-anonymization threats. The survey further explores domain-specific challenges and tailored solutions in critical sectors such as healthcare, law, finance, and education. We investigate advanced methodologies incorporating formal privacy models and risk-aware frameworks, and address the specialized subfield of authorship anonymization. Additionally, we review evaluation frameworks, comprehensive metrics, benchmarks, and practical toolkits for real-world deployment of anonymization solutions. This review consolidates current knowledge, identifies emerging trends and persistent challenges, including the evolving privacy-utility trade-off, the need to address quasi-identifiers, and the implications of LLM capabilities, and aims to guide future research directions for both academics and practitioners in this field.
Towards Automated Regulatory Compliance Verification in Financial Auditing with Large Language Models
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:The auditing of financial documents, historically a labor-intensive process, stands on the precipice of transformation. AI-driven solutions have made inroads into streamlining this process by recommending pertinent text passages from financial reports to align with the legal requirements of accounting standards. However, a glaring limitation remains: these systems commonly fall short in verifying if the recommended excerpts indeed comply with the specific legal mandates. Hence, in this paper, we probe the efficiency of publicly available Large Language Models (LLMs) in the realm of regulatory compliance across different model configurations. We place particular emphasis on comparing cutting-edge open-source LLMs, such as Llama-2, with their proprietary counterparts like OpenAI's GPT models. This comparative analysis leverages two custom datasets provided by our partner PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) Germany. We find that the open-source Llama-2 70 billion model demonstrates outstanding performance in detecting non-compliance or true negative occurrences, beating all their proprietary counterparts. Nevertheless, proprietary models such as GPT-4 perform the best in a broad variety of scenarios, particularly in non-English contexts.
* Accepted and published at BigData 2023, 10 pages, 3 figures, 5 tables
Translating the future: Image-to-image translation for the prediction of future brain metabolism
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder leading to cognitive decline. [$^{18}$F]-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography ([$^{18}$F]-FDG PET) is used to monitor brain metabolism, aiding in the diagnosis and assessment of AD over time. However, the feasibility of multi-time point [$^{18}$F]-FDG PET scans for diagnosis is limited due to radiation exposure, cost, and patient burden. To address this, we have developed a predictive image-to-image translation (I2I) model to forecast future [$^{18}$F]-FDG PET scans using baseline and year-one data. The proposed model employs a convolutional neural network architecture with long-short term memory and was trained on [$^{18}$F]-FDG PET data from 161 individuals from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Our I2I network showed high accuracy in predicting year-two [18F]-FDG PET scans, with a mean absolute error of 0.031 and a structural similarity index of 0.961. Furthermore, the model successfully predicted PET scans up to seven years post-baseline. Notably, the predicted [$^{18}$F]-FDG PET signal in an AD-susceptible meta-region was highly accurate for individuals with mild cognitive impairment across years. In contrast, a linear model was sufficient for predicting brain metabolism in cognitively normal and dementia subjects. In conclusion, both the I2I network and the linear model could offer valuable prognostic insights, guiding early intervention strategies to preemptively address anticipated declines in brain metabolism and potentially to monitor treatment effects.
Controlled Randomness Improves the Performance of Transformer Models
Oct 20, 2023

Abstract:During the pre-training step of natural language models, the main objective is to learn a general representation of the pre-training dataset, usually requiring large amounts of textual data to capture the complexity and diversity of natural language. Contrasting this, in most cases, the size of the data available to solve the specific downstream task is often dwarfed by the aforementioned pre-training dataset, especially in domains where data is scarce. We introduce controlled randomness, i.e. noise, into the training process to improve fine-tuning language models and explore the performance of targeted noise in addition to the parameters of these models. We find that adding such noise can improve the performance in our two downstream tasks of joint named entity recognition and relation extraction and text summarization.
Informed Named Entity Recognition Decoding for Generative Language Models
Aug 15, 2023



Abstract:Ever-larger language models with ever-increasing capabilities are by now well-established text processing tools. Alas, information extraction tasks such as named entity recognition are still largely unaffected by this progress as they are primarily based on the previous generation of encoder-only transformer models. Here, we propose a simple yet effective approach, Informed Named Entity Recognition Decoding (iNERD), which treats named entity recognition as a generative process. It leverages the language understanding capabilities of recent generative models in a future-proof manner and employs an informed decoding scheme incorporating the restricted nature of information extraction into open-ended text generation, improving performance and eliminating any risk of hallucinations. We coarse-tune our model on a merged named entity corpus to strengthen its performance, evaluate five generative language models on eight named entity recognition datasets, and achieve remarkable results, especially in an environment with an unknown entity class set, demonstrating the adaptability of the approach.
Improving Zero-Shot Text Matching for Financial Auditing with Large Language Models
Aug 14, 2023


Abstract:Auditing financial documents is a very tedious and time-consuming process. As of today, it can already be simplified by employing AI-based solutions to recommend relevant text passages from a report for each legal requirement of rigorous accounting standards. However, these methods need to be fine-tuned regularly, and they require abundant annotated data, which is often lacking in industrial environments. Hence, we present ZeroShotALI, a novel recommender system that leverages a state-of-the-art large language model (LLM) in conjunction with a domain-specifically optimized transformer-based text-matching solution. We find that a two-step approach of first retrieving a number of best matching document sections per legal requirement with a custom BERT-based model and second filtering these selections using an LLM yields significant performance improvements over existing approaches.
sustain.AI: a Recommender System to analyze Sustainability Reports
May 26, 2023



Abstract:We present sustainAI, an intelligent, context-aware recommender system that assists auditors and financial investors as well as the general public to efficiently analyze companies' sustainability reports. The tool leverages an end-to-end trainable architecture that couples a BERT-based encoding module with a multi-label classification head to match relevant text passages from sustainability reports to their respective law regulations from the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) standards. We evaluate our model on two novel German sustainability reporting data sets and consistently achieve a significantly higher recommendation performance compared to multiple strong baselines. Furthermore, sustainAI is publicly available for everyone at https://sustain.ki.nrw/.
Towards automating Numerical Consistency Checks in Financial Reports
Nov 11, 2022



Abstract:We introduce KPI-Check, a novel system that automatically identifies and cross-checks semantically equivalent key performance indicators (KPIs), e.g. "revenue" or "total costs", in real-world German financial reports. It combines a financial named entity and relation extraction module with a BERT-based filtering and text pair classification component to extract KPIs from unstructured sentences before linking them to synonymous occurrences in the balance sheet and profit & loss statement. The tool achieves a high matching performance of $73.00$% micro F$_1$ on a hold out test set and is currently being deployed for a globally operating major auditing firm to assist the auditing procedure of financial statements.
A Linguistic Investigation of Machine Learning based Contradiction Detection Models: An Empirical Analysis and Future Perspectives
Oct 19, 2022
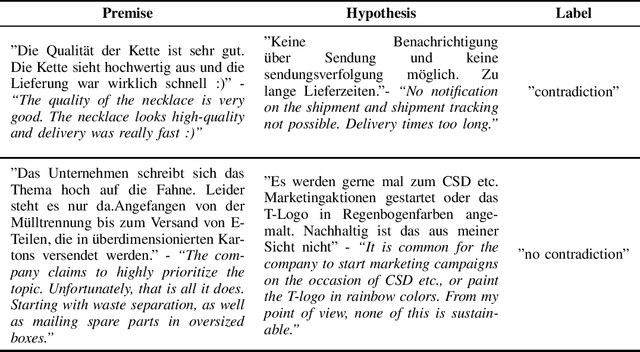
Abstract:We analyze two Natural Language Inference data sets with respect to their linguistic features. The goal is to identify those syntactic and semantic properties that are particularly hard to comprehend for a machine learning model. To this end, we also investigate the differences between a crowd-sourced, machine-translated data set (SNLI) and a collection of text pairs from internet sources. Our main findings are, that the model has difficulty recognizing the semantic importance of prepositions and verbs, emphasizing the importance of linguistically aware pre-training tasks. Furthermore, it often does not comprehend antonyms and homonyms, especially if those are depending on the context. Incomplete sentences are another problem, as well as longer paragraphs and rare words or phrases. The study shows that automated language understanding requires a more informed approach, utilizing as much external knowledge as possible throughout the training process.
KPI-EDGAR: A Novel Dataset and Accompanying Metric for Relation Extraction from Financial Documents
Oct 17, 2022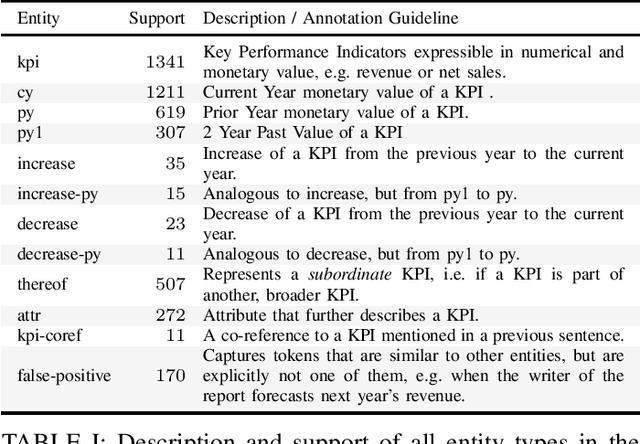
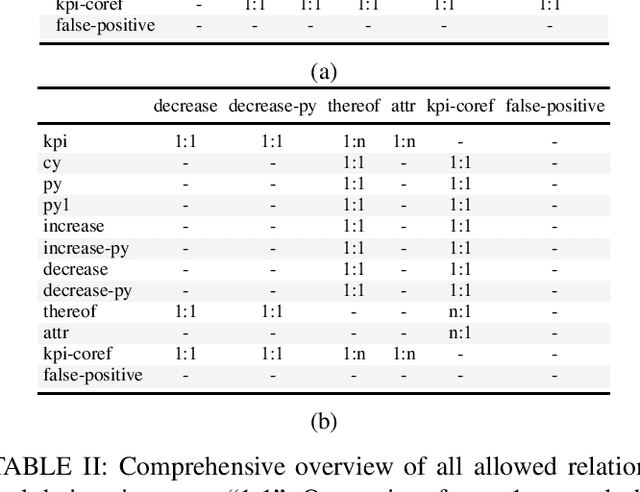
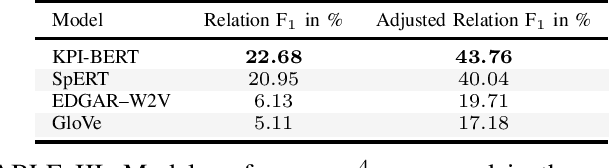
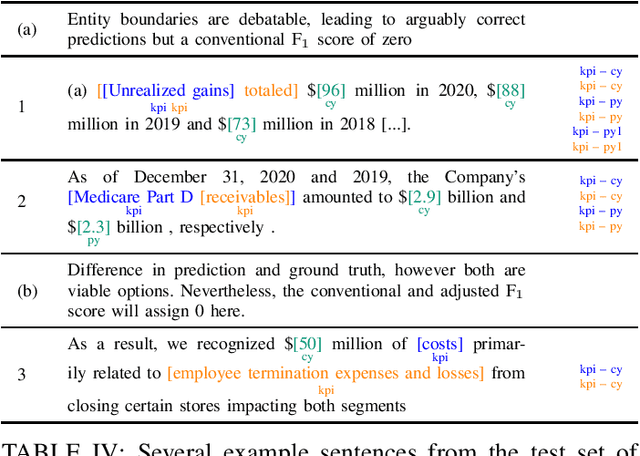
Abstract:We introduce KPI-EDGAR, a novel dataset for Joint Named Entity Recognition and Relation Extraction building on financial reports uploaded to the Electronic Data Gathering, Analysis, and Retrieval (EDGAR) system, where the main objective is to extract Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) from financial documents and link them to their numerical values and other attributes. We further provide four accompanying baselines for benchmarking potential future research. Additionally, we propose a new way of measuring the success of said extraction process by incorporating a word-level weighting scheme into the conventional F1 score to better model the inherently fuzzy borders of the entity pairs of a relation in this domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge