Yulun Du
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
Kimi Linear: An Expressive, Efficient Attention Architecture
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:We introduce Kimi Linear, a hybrid linear attention architecture that, for the first time, outperforms full attention under fair comparisons across various scenarios -- including short-context, long-context, and reinforcement learning (RL) scaling regimes. At its core lies Kimi Delta Attention (KDA), an expressive linear attention module that extends Gated DeltaNet with a finer-grained gating mechanism, enabling more effective use of limited finite-state RNN memory. Our bespoke chunkwise algorithm achieves high hardware efficiency through a specialized variant of the Diagonal-Plus-Low-Rank (DPLR) transition matrices, which substantially reduces computation compared to the general DPLR formulation while remaining more consistent with the classical delta rule. We pretrain a Kimi Linear model with 3B activated parameters and 48B total parameters, based on a layerwise hybrid of KDA and Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA). Our experiments show that with an identical training recipe, Kimi Linear outperforms full MLA with a sizeable margin across all evaluated tasks, while reducing KV cache usage by up to 75% and achieving up to 6 times decoding throughput for a 1M context. These results demonstrate that Kimi Linear can be a drop-in replacement for full attention architectures with superior performance and efficiency, including tasks with longer input and output lengths. To support further research, we open-source the KDA kernel and vLLM implementations, and release the pre-trained and instruction-tuned model checkpoints.
Kimi K2: Open Agentic Intelligence
Jul 28, 2025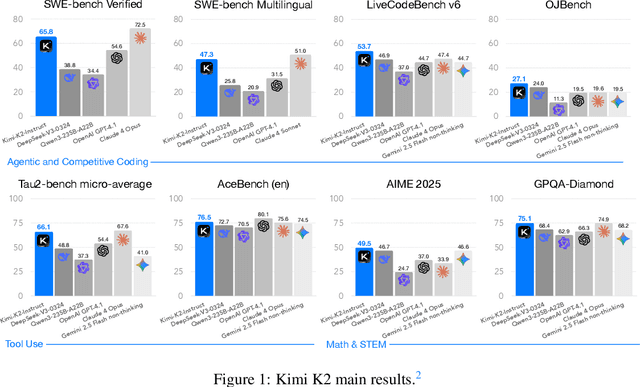
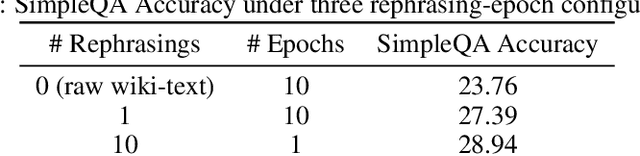
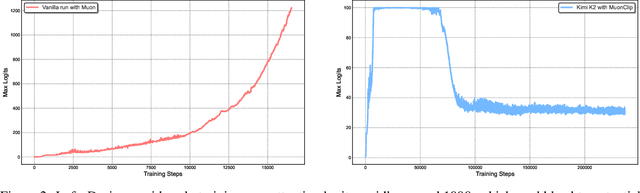
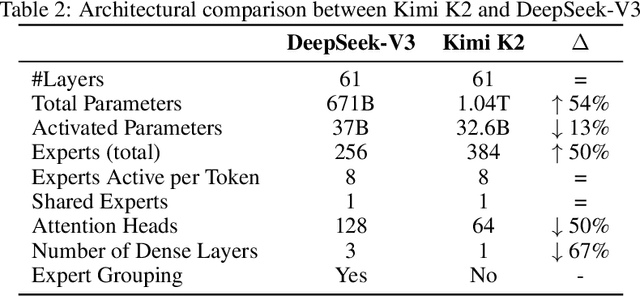
Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) large language model with 32 billion activated parameters and 1 trillion total parameters. We propose the MuonClip optimizer, which improves upon Muon with a novel QK-clip technique to address training instability while enjoying the advanced token efficiency of Muon. Based on MuonClip, K2 was pre-trained on 15.5 trillion tokens with zero loss spike. During post-training, K2 undergoes a multi-stage post-training process, highlighted by a large-scale agentic data synthesis pipeline and a joint reinforcement learning (RL) stage, where the model improves its capabilities through interactions with real and synthetic environments. Kimi K2 achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source non-thinking models, with strengths in agentic capabilities. Notably, K2 obtains 66.1 on Tau2-Bench, 76.5 on ACEBench (En), 65.8 on SWE-Bench Verified, and 47.3 on SWE-Bench Multilingual -- surpassing most open and closed-sourced baselines in non-thinking settings. It also exhibits strong capabilities in coding, mathematics, and reasoning tasks, with a score of 53.7 on LiveCodeBench v6, 49.5 on AIME 2025, 75.1 on GPQA-Diamond, and 27.1 on OJBench, all without extended thinking. These results position Kimi K2 as one of the most capable open-source large language models to date, particularly in software engineering and agentic tasks. We release our base and post-trained model checkpoints to facilitate future research and applications of agentic intelligence.
Kimi-Audio Technical Report
Apr 25, 2025



Abstract:We present Kimi-Audio, an open-source audio foundation model that excels in audio understanding, generation, and conversation. We detail the practices in building Kimi-Audio, including model architecture, data curation, training recipe, inference deployment, and evaluation. Specifically, we leverage a 12.5Hz audio tokenizer, design a novel LLM-based architecture with continuous features as input and discrete tokens as output, and develop a chunk-wise streaming detokenizer based on flow matching. We curate a pre-training dataset that consists of more than 13 million hours of audio data covering a wide range of modalities including speech, sound, and music, and build a pipeline to construct high-quality and diverse post-training data. Initialized from a pre-trained LLM, Kimi-Audio is continual pre-trained on both audio and text data with several carefully designed tasks, and then fine-tuned to support a diverse of audio-related tasks. Extensive evaluation shows that Kimi-Audio achieves state-of-the-art performance on a range of audio benchmarks including speech recognition, audio understanding, audio question answering, and speech conversation. We release the codes, model checkpoints, as well as the evaluation toolkits in https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-Audio.
Kimi-VL Technical Report
Apr 10, 2025
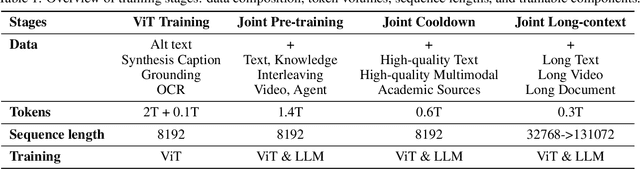
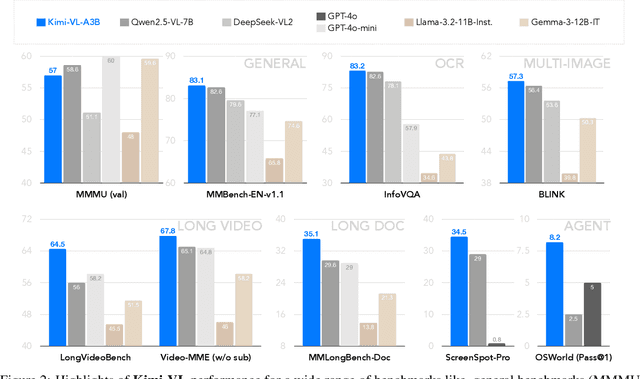
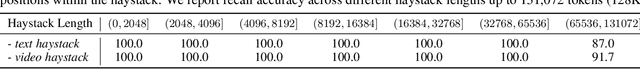
Abstract:We present Kimi-VL, an efficient open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) vision-language model (VLM) that offers advanced multimodal reasoning, long-context understanding, and strong agent capabilities - all while activating only 2.8B parameters in its language decoder (Kimi-VL-A3B). Kimi-VL demonstrates strong performance across challenging domains: as a general-purpose VLM, Kimi-VL excels in multi-turn agent tasks (e.g., OSWorld), matching flagship models. Furthermore, it exhibits remarkable capabilities across diverse challenging vision language tasks, including college-level image and video comprehension, OCR, mathematical reasoning, and multi-image understanding. In comparative evaluations, it effectively competes with cutting-edge efficient VLMs such as GPT-4o-mini, Qwen2.5-VL-7B, and Gemma-3-12B-IT, while surpassing GPT-4o in several key domains. Kimi-VL also advances in processing long contexts and perceiving clearly. With a 128K extended context window, Kimi-VL can process diverse long inputs, achieving impressive scores of 64.5 on LongVideoBench and 35.1 on MMLongBench-Doc. Its native-resolution vision encoder, MoonViT, further allows it to see and understand ultra-high-resolution visual inputs, achieving 83.2 on InfoVQA and 34.5 on ScreenSpot-Pro, while maintaining lower computational cost for common tasks. Building upon Kimi-VL, we introduce an advanced long-thinking variant: Kimi-VL-Thinking. Developed through long chain-of-thought (CoT) supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL), this model exhibits strong long-horizon reasoning capabilities. It achieves scores of 61.7 on MMMU, 36.8 on MathVision, and 71.3 on MathVista while maintaining the compact 2.8B activated LLM parameters, setting a new standard for efficient multimodal thinking models. Code and models are publicly accessible at https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-VL.
Muon is Scalable for LLM Training
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Recently, the Muon optimizer based on matrix orthogonalization has demonstrated strong results in training small-scale language models, but the scalability to larger models has not been proven. We identify two crucial techniques for scaling up Muon: (1) adding weight decay and (2) carefully adjusting the per-parameter update scale. These techniques allow Muon to work out-of-the-box on large-scale training without the need of hyper-parameter tuning. Scaling law experiments indicate that Muon achieves $\sim\!2\times$ computational efficiency compared to AdamW with compute optimal training. Based on these improvements, we introduce Moonlight, a 3B/16B-parameter Mixture-of-Expert (MoE) model trained with 5.7T tokens using Muon. Our model improves the current Pareto frontier, achieving better performance with much fewer training FLOPs compared to prior models. We open-source our distributed Muon implementation that is memory optimal and communication efficient. We also release the pretrained, instruction-tuned, and intermediate checkpoints to support future research.
MoBA: Mixture of Block Attention for Long-Context LLMs
Feb 18, 2025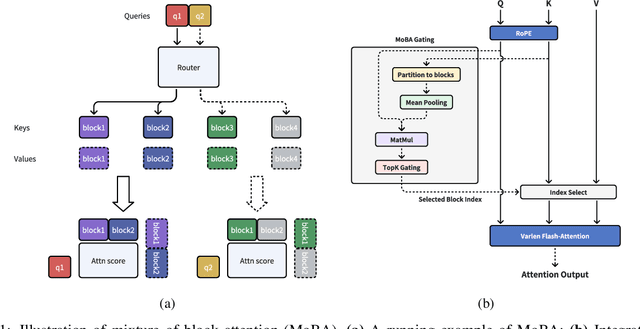
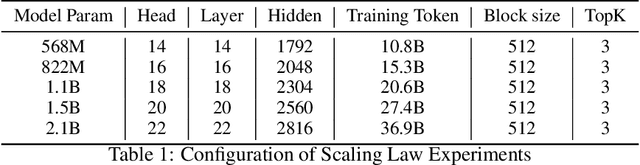
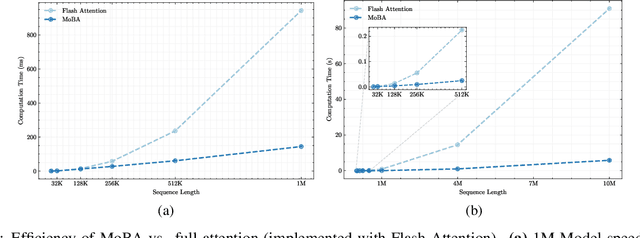
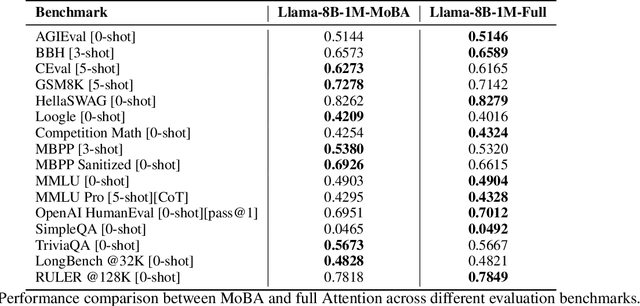
Abstract:Scaling the effective context length is essential for advancing large language models (LLMs) toward artificial general intelligence (AGI). However, the quadratic increase in computational complexity inherent in traditional attention mechanisms presents a prohibitive overhead. Existing approaches either impose strongly biased structures, such as sink or window attention which are task-specific, or radically modify the attention mechanism into linear approximations, whose performance in complex reasoning tasks remains inadequately explored. In this work, we propose a solution that adheres to the ``less structure'' principle, allowing the model to determine where to attend autonomously, rather than introducing predefined biases. We introduce Mixture of Block Attention (MoBA), an innovative approach that applies the principles of Mixture of Experts (MoE) to the attention mechanism. This novel architecture demonstrates superior performance on long-context tasks while offering a key advantage: the ability to seamlessly transition between full and sparse attention, enhancing efficiency without the risk of compromising performance. MoBA has already been deployed to support Kimi's long-context requests and demonstrates significant advancements in efficient attention computation for LLMs. Our code is available at https://github.com/MoonshotAI/MoBA.
STORYWARS: A Dataset and Instruction Tuning Baselines for Collaborative Story Understanding and Generation
May 14, 2023Abstract:Collaborative stories, which are texts created through the collaborative efforts of multiple authors with different writing styles and intentions, pose unique challenges for NLP models. Understanding and generating such stories remains an underexplored area due to the lack of open-domain corpora. To address this, we introduce STORYWARS, a new dataset of over 40,000 collaborative stories written by 9,400 different authors from an online platform. We design 12 task types, comprising 7 understanding and 5 generation task types, on STORYWARS, deriving 101 diverse story-related tasks in total as a multi-task benchmark covering all fully-supervised, few-shot, and zero-shot scenarios. Furthermore, we present our instruction-tuned model, INSTRUCTSTORY, for the story tasks showing that instruction tuning, in addition to achieving superior results in zero-shot and few-shot scenarios, can also obtain the best performance on the fully-supervised tasks in STORYWARS, establishing strong multi-task benchmark performances on STORYWARS.
GPS: Genetic Prompt Search for Efficient Few-shot Learning
Oct 31, 2022



Abstract:Prompt-based techniques have demostrated great potential for improving the few-shot generalization of pretrained language models. However, their performance heavily relies on the manual design of prompts and thus requires a lot of human efforts. In this paper, we introduce Genetic Prompt Search (GPS) to improve few-shot learning with prompts, which utilizes a genetic algorithm to automatically search for high-performing prompts. GPS is gradient-free and requires no update of model parameters but only a small validation set. Experiments on diverse datasets proved the effectiveness of GPS, which outperforms manual prompts by a large margin of 2.6 points. Our method is also better than other parameter-efficient tuning methods such as prompt tuning.
ZeroPrompt: Scaling Prompt-Based Pretraining to 1,000 Tasks Improves Zero-Shot Generalization
Jan 18, 2022



Abstract:We propose a multitask pretraining approach ZeroPrompt for zero-shot generalization, focusing on task scaling and zero-shot prompting. While previous models are trained on only a few dozen tasks, we scale to 1,000 tasks for the first time using real-world data. This leads to a crucial discovery that task scaling can be an efficient alternative to model scaling; i.e., the model size has little impact on performance with an extremely large number of tasks. Our results show that task scaling can substantially improve training efficiency by 30 times in FLOPs. Moreover, we present a prompting method that incorporates a genetic algorithm to automatically search for the best prompt for unseen tasks, along with a few other improvements. Empirically, ZeroPrompt substantially improves both the efficiency and the performance of zero-shot learning across a variety of academic and production datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge