Yuanming Zhang
Decoding Speech Envelopes from Electroencephalogram with a Contrastive Pearson Correlation Coefficient Loss
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in reconstructing speech envelopes from Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals have enabled continuous auditory attention decoding (AAD) in multi-speaker environments. Most Deep Neural Network (DNN)-based envelope reconstruction models are trained to maximize the Pearson correlation coefficients (PCC) between the attended envelope and the reconstructed envelope (attended PCC). While the difference between the attended PCC and the unattended PCC plays an essential role in auditory attention decoding, existing methods often focus on maximizing the attended PCC. We therefore propose a contrastive PCC loss which represents the difference between the attended PCC and the unattended PCC. The proposed approach is evaluated on three public EEG AAD datasets using four DNN architectures. Across many settings, the proposed objective improves envelope separability and AAD accuracy, while also revealing dataset- and architecture-dependent failure cases.
Auditory Attention Decoding from Ear-EEG Signals: A Dataset with Dynamic Attention Switching and Rigorous Cross-Validation
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Recent promising results in auditory attention decoding (AAD) using scalp electroencephalography (EEG) have motivated the exploration of cEEGrid, a flexible and portable ear-EEG system. While prior cEEGrid-based studies have confirmed the feasibility of AAD, they often neglect the dynamic nature of attentional states in real-world contexts. To address this gap, a novel cEEGrid dataset featuring three concurrent speakers distributed across three of five distinct spatial locations is introduced. The novel dataset is designed to probe attentional tracking and switching in realistic scenarios. Nested leave-one-out validation-an approach more rigorous than conventional single-loop leave-one-out validation-is employed to reduce biases stemming from EEG's intricate temporal dynamics. Four rule-based models are evaluated: Wiener filter (WF), canonical component analysis (CCA), common spatial pattern (CSP) and Riemannian Geometry-based classifier (RGC). With a 30-second decision window, WF and CCA models achieve decoding accuracies of 41.5% and 41.4%, respectively, while CSP and RGC models yield 37.8% and 37.6% accuracies using a 10-second window. Notably, both WF and CCA successfully track attentional state switches across all experimental tasks. Additionally, higher decoding accuracies are observed for electrodes positioned at the upper cEEGrid layout and near the listener's right ear. These findings underscore the utility of dynamic, ecologically valid paradigms and rigorous validation in advancing AAD research with cEEGrid.
EduPersona: Benchmarking Subjective Ability Boundaries of Virtual Student Agents
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:As large language models are increasingly integrated into education, virtual student agents are becoming vital for classroom simulation and teacher training. Yet their classroom-oriented subjective abilities remain largely unassessed, limiting understanding of model boundaries and hindering trustworthy deployment. We present EduPersona, a large-scale benchmark spanning two languages, three subjects, and ten persona types based on the Big Five theory. The dataset contains 1,308 authentic classroom dialogue rounds, corresponding to 12,814 teacher-student Q&A turns, and is further expanded through persona stylization into roughly 10 times larger scale (128k turns), providing a solid foundation for evaluation. Building on this resource, we decompose hard-to-quantify subjective performance into three progressive tasks: TASK1 basic coherence (whether behavior, emotion, expression, and voice align with classroom context), TASK2 student realism, and TASK3 long-term persona consistency, thereby establishing an evaluation framework grounded in educational theory and research value. We conduct systematic experiments on three representative LLMs, comparing their original versions with ten persona-fine-tuned variants trained on EduPersona. Results show consistent and significant average improvements across all tasks: TASK1 +33.6%, TASK2 +30.6%, and TASK3 +14.9%. These improvements highlight the dataset's effectiveness and research value, while also revealing the heterogeneous difficulty of persona modeling. In summary, EduPersona delivers the first classroom benchmark centered on subjective abilities, establishes a decoupled and verifiable research paradigm, and we will open-source both the dataset and the framework to support the broader research community in advancing trustworthy and human-like AI for education.
Electroencephalogram-based Multi-class Decoding of Attended Speakers' Direction with Audio Spatial Spectrum
Nov 11, 2024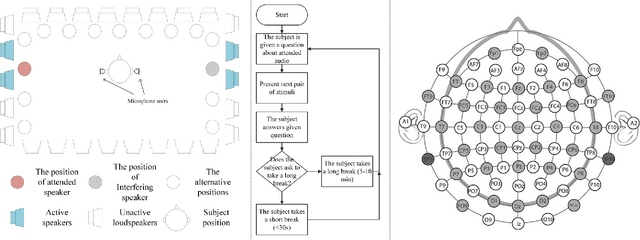
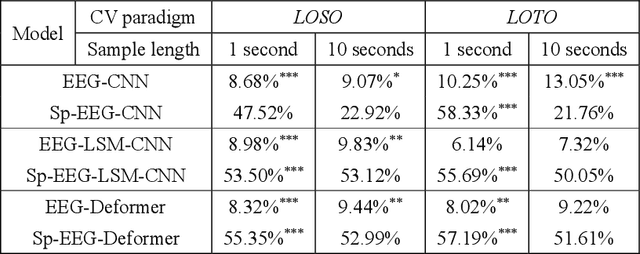
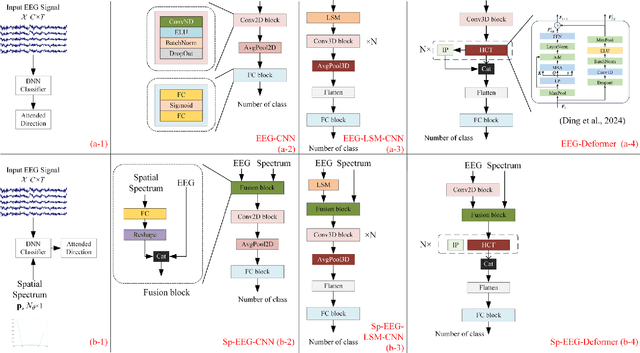
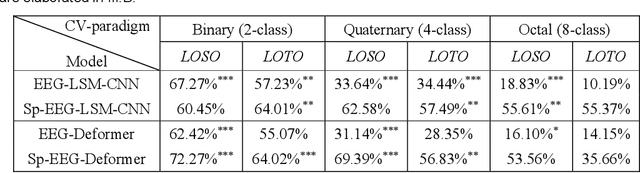
Abstract:Decoding the directional focus of an attended speaker from listeners' electroencephalogram (EEG) signals is essential for developing brain-computer interfaces to improve the quality of life for individuals with hearing impairment. Previous works have concentrated on binary directional focus decoding, i.e., determining whether the attended speaker is on the left or right side of the listener. However, a more precise decoding of the exact direction of the attended speaker is necessary for effective speech processing. Additionally, audio spatial information has not been effectively leveraged, resulting in suboptimal decoding results. In this paper, we observe that, on our recently presented dataset with 15-class directional focus, models relying exclusively on EEG inputs exhibits significantly lower accuracy when decoding the directional focus in both leave-one-subject-out and leave-one-trial-out scenarios. By integrating audio spatial spectra with EEG features, the decoding accuracy can be effectively improved. We employ the CNN, LSM-CNN, and EEG-Deformer models to decode the directional focus from listeners' EEG signals with the auxiliary audio spatial spectra. The proposed Sp-Aux-Deformer model achieves notable 15-class decoding accuracies of 57.48% and 61.83% in leave-one-subject-out and leave-one-trial-out scenarios, respectively.
Fast Gumbel-Max Sketch and its Applications
Feb 10, 2023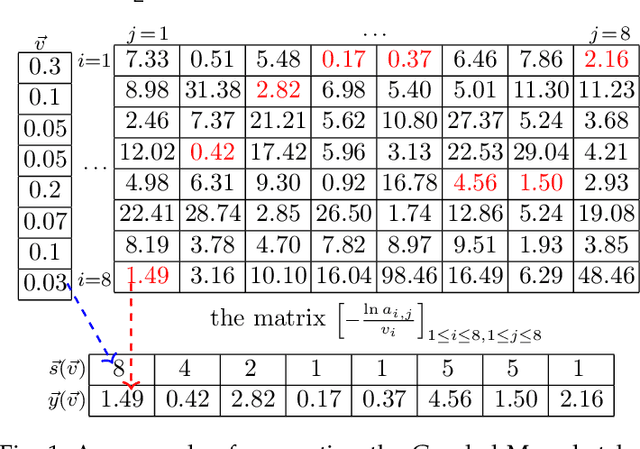
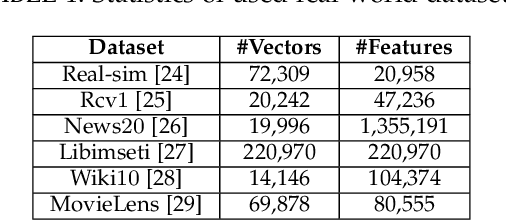
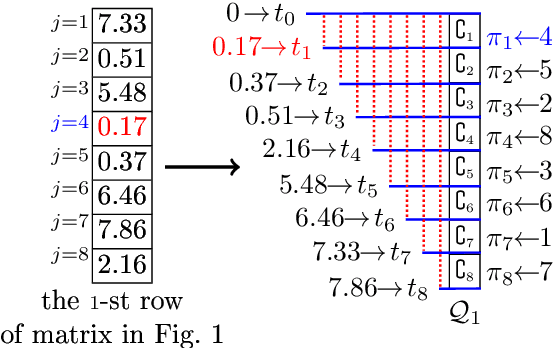
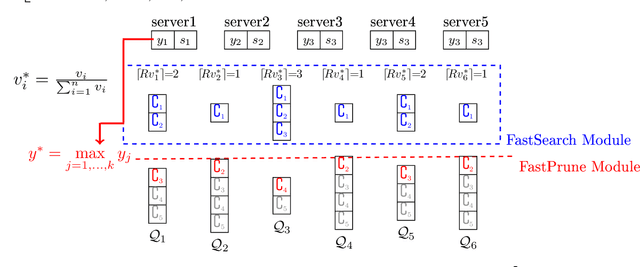
Abstract:The well-known Gumbel-Max Trick for sampling elements from a categorical distribution (or more generally a non-negative vector) and its variants have been widely used in areas such as machine learning and information retrieval. To sample a random element $i$ in proportion to its positive weight $v_i$, the Gumbel-Max Trick first computes a Gumbel random variable $g_i$ for each positive weight element $i$, and then samples the element $i$ with the largest value of $g_i+\ln v_i$. Recently, applications including similarity estimation and weighted cardinality estimation require to generate $k$ independent Gumbel-Max variables from high dimensional vectors. However, it is computationally expensive for a large $k$ (e.g., hundreds or even thousands) when using the traditional Gumbel-Max Trick. To solve this problem, we propose a novel algorithm, FastGM, which reduces the time complexity from $O(kn^+)$ to $O(k \ln k + n^+)$, where $n^+$ is the number of positive elements in the vector of interest. FastGM stops the procedure of Gumbel random variables computing for many elements, especially for those with small weights. We perform experiments on a variety of real-world datasets and the experimental results demonstrate that FastGM is orders of magnitude faster than state-of-the-art methods without sacrificing accuracy or incurring additional expenses.
Pseudo-Data based Self-Supervised Federated Learning for Classification of Histopathological Images
May 31, 2022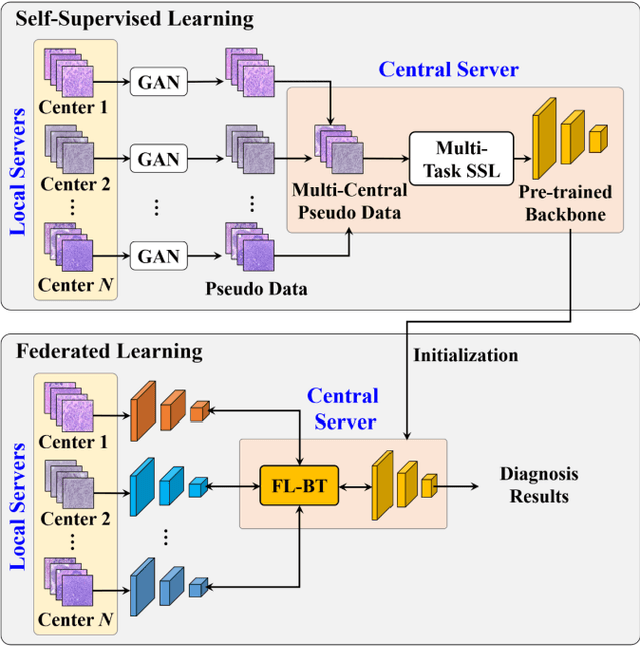
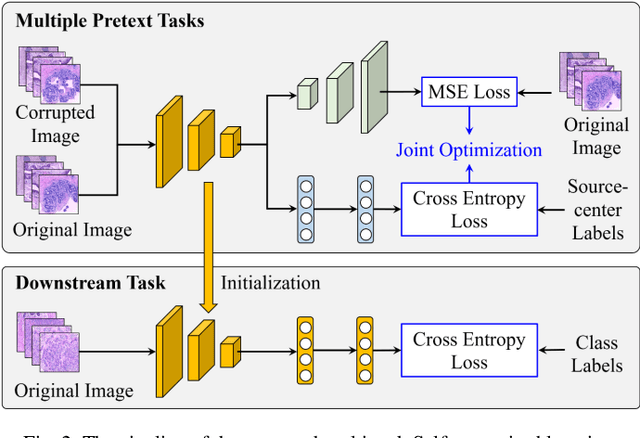
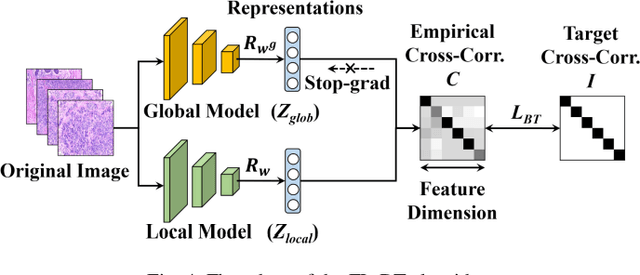
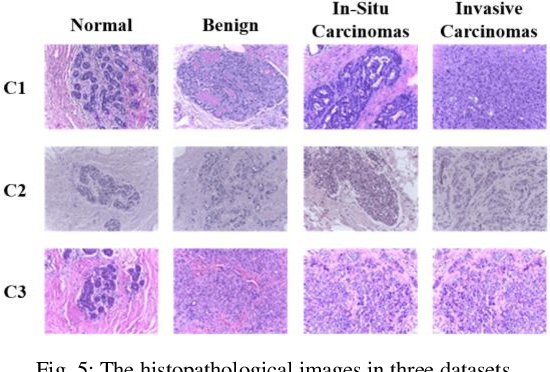
Abstract:Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) can help pathologists improve diagnostic accuracy together with consistency and repeatability for cancers. However, the CAD models trained with the histopathological images only from a single center (hospital) generally suffer from the generalization problem due to the straining inconsistencies among different centers. In this work, we propose a pseudo-data based self-supervised federated learning (FL) framework, named SSL-FT-BT, to improve both the diagnostic accuracy and generalization of CAD models. Specifically, the pseudo histopathological images are generated from each center, which contains inherent and specific properties corresponding to the real images in this center, but does not include the privacy information. These pseudo images are then shared in the central server for self-supervised learning (SSL). A multi-task SSL is then designed to fully learn both the center-specific information and common inherent representation according to the data characteristics. Moreover, a novel Barlow Twins based FL (FL-BT) algorithm is proposed to improve the local training for the CAD model in each center by conducting contrastive learning, which benefits the optimization of the global model in the FL procedure. The experimental results on three public histopathological image datasets indicate the effectiveness of the proposed SSL-FL-BT on both diagnostic accuracy and generalization.
Fast Generating A Large Number of Gumbel-Max Variables
Feb 02, 2020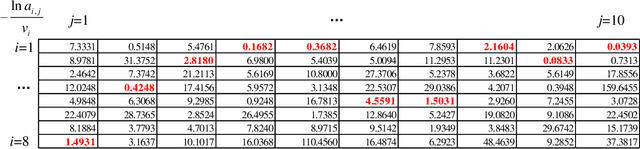
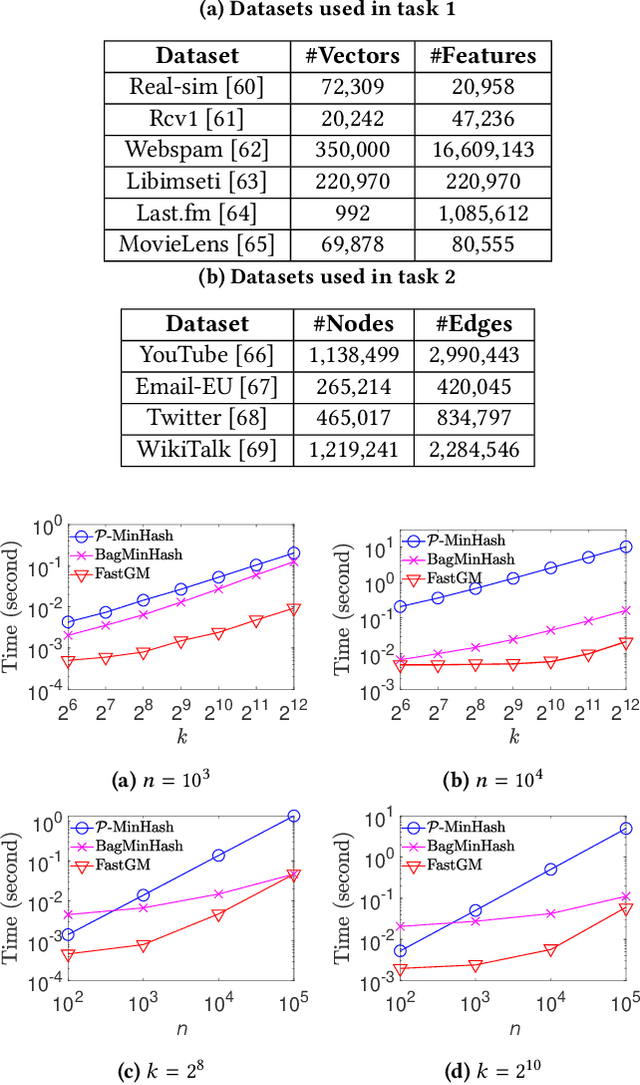
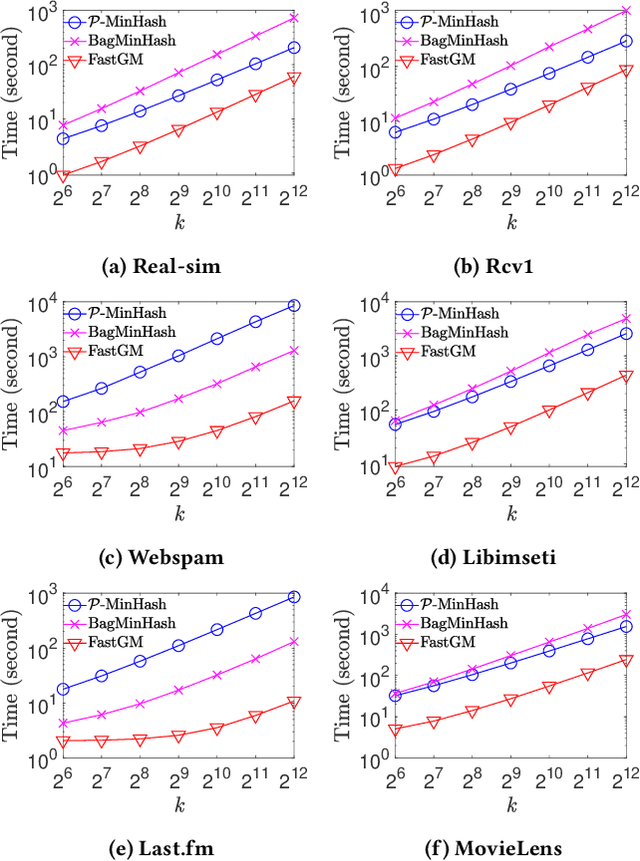
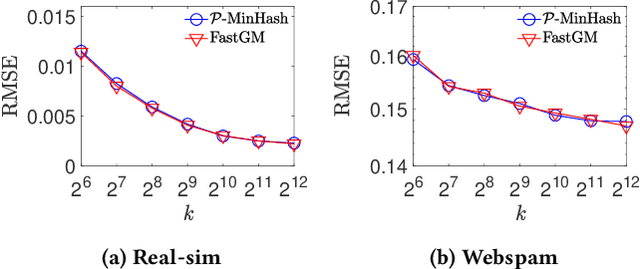
Abstract:The well-known Gumbel-Max Trick for sampling elements from a categorical distribution (or more generally a nonnegative vector) and its variants have been widely used in areas such as machine learning and information retrieval. To sample a random element $i$ (or a Gumbel-Max variable $i$) in proportion to its positive weight $v_i$, the Gumbel-Max Trick first computes a Gumbel random variable $g_i$ for each positive weight element $i$, and then samples the element $i$ with the largest value of $g_i+\ln v_i$. Recently, applications including similarity estimation and graph embedding require to generate $k$ independent Gumbel-Max variables from high dimensional vectors. However, it is computationally expensive for a large $k$ (e.g., hundreds or even thousands) when using the traditional Gumbel-Max Trick. To solve this problem, we propose a novel algorithm, \emph{FastGM}, that reduces the time complexity from $O(kn^+)$ to $O(k \ln k + n^+)$, where $n^+$ is the number of positive elements in the vector of interest. Instead of computing $k$ independent Gumbel random variables directly, we find that there exists a technique to generate these variables in descending order. Using this technique, our method FastGM computes variables $g_i+\ln v_i$ for all positive elements $i$ in descending order. As a result, FastGM significantly reduces the computation time because we can stop the procedure of Gumbel random variables computing for many elements especially for those with small weights. Experiments on a variety of real-world datasets show that FastGM is orders of magnitude faster than state-of-the-art methods without sacrificing accuracy and incurring additional expenses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge