Yu-Ping Ruan
Parameter-Efficient Tuning on Layer Normalization for Pre-trained Language Models
Dec 09, 2022



Abstract:Conventional fine-tuning encounters increasing difficulties given the size of current Pre-trained Language Models, which makes parameter-efficient tuning become the focal point of frontier research. Previous methods in this field add tunable adapters into MHA or/and FFN of Transformer blocks to enable PLMs achieve transferability. However, as an important part of Transformer architecture, the power of layer normalization for parameter-efficent tuning is ignored. In this paper, we first propose LN-tuning, by tuning the gain and bias term of Layer Normalization module with only 0.03\% parameters, which is of high time-efficency and significantly superior to baselines which are less than 0.1\% tunable parameters. Further, we study the unified framework of combining LN-tuning with previous ones and we find that: (1) the unified framework of combining prefix-tuning, the adapter-based method working on MHA, and LN-tuning achieves SOTA performance. (2) unified framework which tunes MHA and LayerNorm simultaneously can get performance improvement but those which tune FFN and LayerNorm simultaneous will cause performance decrease. Ablation study validates LN-tuning is of no abundant parameters and gives a further understanding of it.
Fast sensor placement by enlarging principle submatrix for large-scale linear inverse problems
Oct 07, 2021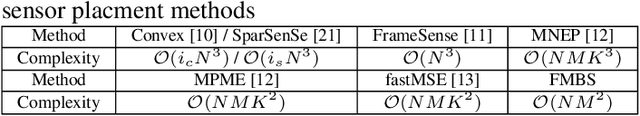
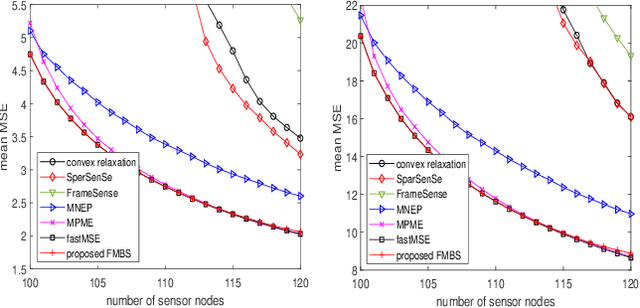
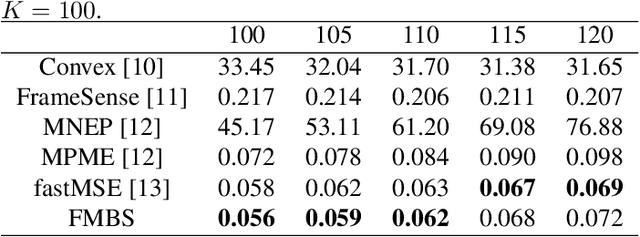
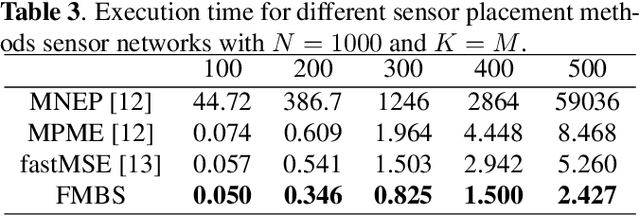
Abstract:Sensor placement for linear inverse problems is the selection of locations to assign sensors so that the entire physical signal can be well recovered from partial observations. In this paper, we propose a fast sampling algorithm to place sensors. Specifically, assuming that the field signal $\mathbf{f}$ is represented by a linear model $\mathbf{f}=\pmb{\phi}\mathbf{g}$, it can be estimated from partial noisy samples via an unbiased least-squares (LS) method, whose expected mean square error (MSE) depends on chosen samples. First, we formulate an approximate MSE problem, and then prove it is equivalent to a problem related to a principle submatrix of $\pmb{\phi}\pmb{\phi}^\top$ indexed by sample set. To solve the formulated problem, we devise a fast greedy algorithm with simple matrix-vector multiplications, leveraging a matrix inverse formula. To further reduce complexity, we reuse results in the previous greedy step for warm start, so that candidates can be evaluated via lightweight vector-vector multiplications. Extensive experiments show that our proposed sensor placement method achieved the lowest sensor sampling time and the best performance compared to state-of-the-art schemes.
SemEval-2021 Task 4: Reading Comprehension of Abstract Meaning
Jun 01, 2021

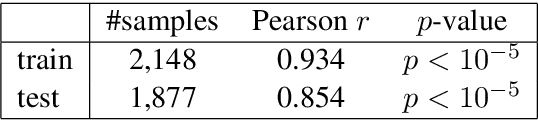
Abstract:This paper introduces the SemEval-2021 shared task 4: Reading Comprehension of Abstract Meaning (ReCAM). This shared task is designed to help evaluate the ability of machines in representing and understanding abstract concepts. Given a passage and the corresponding question, a participating system is expected to choose the correct answer from five candidates of abstract concepts in a cloze-style machine reading comprehension setup. Based on two typical definitions of abstractness, i.e., the imperceptibility and nonspecificity, our task provides three subtasks to evaluate the participating models. Specifically, Subtask 1 aims to evaluate how well a system can model concepts that cannot be directly perceived in the physical world. Subtask 2 focuses on models' ability in comprehending nonspecific concepts located high in a hypernym hierarchy given the context of a passage. Subtask 3 aims to provide some insights into models' generalizability over the two types of abstractness. During the SemEval-2021 official evaluation period, we received 23 submissions to Subtask 1 and 28 to Subtask 2. The participating teams additionally made 29 submissions to Subtask 3. The leaderboard and competition website can be found at https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/26153. The data and baseline code are available at https://github.com/boyuanzheng010/SemEval2021-Reading-Comprehension-of-Abstract-Meaning.
Emotion-Regularized Conditional Variational Autoencoder for Emotional Response Generation
Apr 18, 2021



Abstract:This paper presents an emotion-regularized conditional variational autoencoder (Emo-CVAE) model for generating emotional conversation responses. In conventional CVAE-based emotional response generation, emotion labels are simply used as additional conditions in prior, posterior and decoder networks. Considering that emotion styles are naturally entangled with semantic contents in the language space, the Emo-CVAE model utilizes emotion labels to regularize the CVAE latent space by introducing an extra emotion prediction network. In the training stage, the estimated latent variables are required to predict the emotion labels and token sequences of the input responses simultaneously. Experimental results show that our Emo-CVAE model can learn a more informative and structured latent space than a conventional CVAE model and output responses with better content and emotion performance than baseline CVAE and sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) models.
Pre-Trained and Attention-Based Neural Networks for Building Noetic Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems
Apr 04, 2020
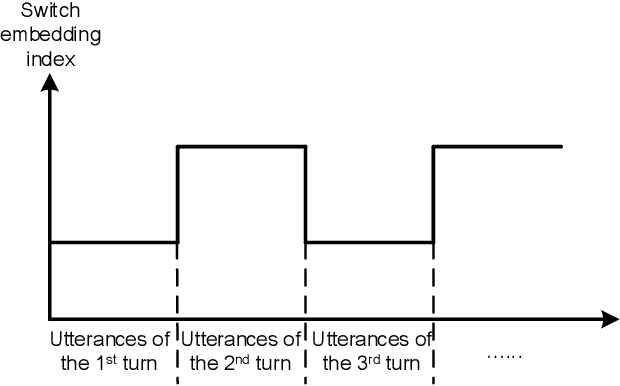
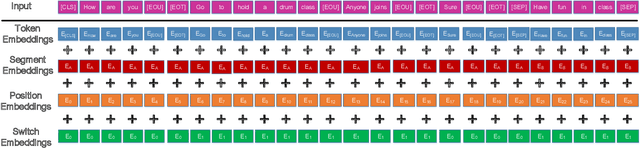
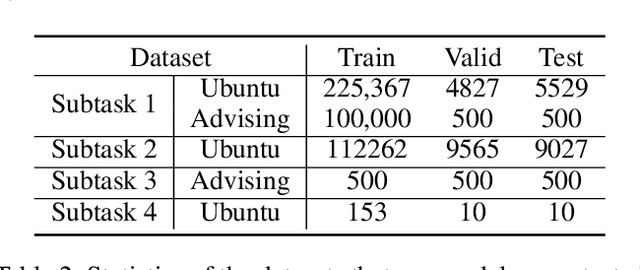
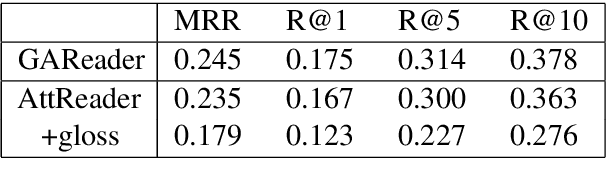
Abstract:The NOESIS II challenge, as the Track 2 of the 8th Dialogue System Technology Challenges (DSTC 8), is the extension of DSTC 7. This track incorporates new elements that are vital for the creation of a deployed task-oriented dialogue system. This paper describes our systems that are evaluated on all subtasks under this challenge. We study the problem of employing pre-trained attention-based network for multi-turn dialogue systems. Meanwhile, several adaptation methods are proposed to adapt the pre-trained language models for multi-turn dialogue systems, in order to keep the intrinsic property of dialogue systems. In the released evaluation results of Track 2 of DSTC 8, our proposed models ranked fourth in subtask 1, third in subtask 2, and first in subtask 3 and subtask 4 respectively.
Fine-Tuning BERT for Schema-Guided Zero-Shot Dialogue State Tracking
Feb 01, 2020



Abstract:We present our work on Track 4 in the Dialogue System Technology Challenges 8 (DSTC8). The DSTC8-Track 4 aims to perform dialogue state tracking (DST) under the zero-shot settings, in which the model needs to generalize on unseen service APIs given a schema definition of these target APIs. Serving as the core for many virtual assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, the DST keeps track of the user's goal and what happened in the dialogue history, mainly including intent prediction, slot filling, and user state tracking, which tests models' ability of natural language understanding. Recently, the pretrained language models have achieved state-of-the-art results and shown impressive generalization ability on various NLP tasks, which provide a promising way to perform zero-shot learning for language understanding. Based on this, we propose a schema-guided paradigm for zero-shot dialogue state tracking (SGP-DST) by fine-tuning BERT, one of the most popular pretrained language models. The SGP-DST system contains four modules for intent prediction, slot prediction, slot transfer prediction, and user state summarizing respectively. According to the official evaluation results, our SGP-DST (team12) ranked 3rd on the joint goal accuracy (primary evaluation metric for ranking submissions) and 1st on the requsted slots F1 among 25 participant teams.
Condition-Transforming Variational AutoEncoder for Conversation Response Generation
Apr 24, 2019



Abstract:This paper proposes a new model, called condition-transforming variational autoencoder (CTVAE), to improve the performance of conversation response generation using conditional variational autoencoders (CVAEs). In conventional CVAEs , the prior distribution of latent variable z follows a multivariate Gaussian distribution with mean and variance modulated by the input conditions. Previous work found that this distribution tends to become condition independent in practical application. In our proposed CTVAE model, the latent variable z is sampled by performing a non-lineartransformation on the combination of the input conditions and the samples from a condition-independent prior distribution N (0; I). In our objective evaluations, the CTVAE model outperforms the CVAE model on fluency metrics and surpasses a sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) model on diversity metrics. In subjective preference tests, our proposed CTVAE model performs significantly better than CVAE and Seq2Seq models on generating fluency, informative and topic relevant responses.
Exploring Unsupervised Pretraining and Sentence Structure Modelling for Winograd Schema Challenge
Apr 22, 2019



Abstract:Winograd Schema Challenge (WSC) was proposed as an AI-hard problem in testing computers' intelligence on common sense representation and reasoning. This paper presents the new state-of-theart on WSC, achieving an accuracy of 71.1%. We demonstrate that the leading performance benefits from jointly modelling sentence structures, utilizing knowledge learned from cutting-edge pretraining models, and performing fine-tuning. We conduct detailed analyses, showing that fine-tuning is critical for achieving the performance, but it helps more on the simpler associative problems. Modelling sentence dependency structures, however, consistently helps on the harder non-associative subset of WSC. Analysis also shows that larger fine-tuning datasets yield better performances, suggesting the potential benefit of future work on annotating more Winograd schema sentences.
Promoting Diversity for End-to-End Conversation Response Generation
Jan 30, 2019



Abstract:We present our work on Track 2 in the Dialog System Technology Challenges 7 (DSTC7). The DSTC7-Track 2 aims to evaluate the response generation of fully data-driven conversation models in knowledge-grounded settings, which provides the contextual-relevant factual texts. The Sequenceto-Sequence models have been widely used for end-to-end generative conversation modelling and achieved impressive results. However, they tend to output dull and repeated responses in previous studies. Our work aims to promote the diversity for end-to-end conversation response generation, which follows a two-stage pipeline: 1) Generate multiple responses. At this stage, two different models are proposed, i.e., a variational generative (VariGen) model and a retrieval based (Retrieval) model. 2) Rank and return the most related response by training a topic coherence discrimination (TCD) model for the ranking process. According to the official evaluation results, our proposed Retrieval and VariGen systems ranked first and second respectively on objective diversity metrics, i.e., Entropy, among all participant systems. And the VariGen system ranked second on NIST and METEOR metrics.
Building Sequential Inference Models for End-to-End Response Selection
Dec 03, 2018



Abstract:This paper presents an end-to-end response selection model for Track 1 of the 7th Dialogue System Technology Challenges (DSTC7). This task focuses on selecting the correct next utterance from a set of candidates given a partial conversation. We propose an end-to-end neural network based on enhanced sequential inference model (ESIM) for this task. Our proposed model differs from the original ESIM model in the following four aspects. First, a new word representation method which combines the general pre-trained word embeddings with those estimated on the task-specific training set is adopted in order to address the challenge of out-of-vocabulary (OOV) words. Second, an attentive hierarchical recurrent encoder (AHRE) is designed which is capable to encode sentences hierarchically and generate more descriptive representations by aggregation. Third, a new pooling method which combines multi-dimensional pooling and last-state pooling is used instead of the simple combination of max pooling and average pooling in the original ESIM. Last, a modification layer is added before the softmax layer to emphasize the importance of the last utterance in the context for response selection. In the released evaluation results of DSTC7, our proposed method ranked second on the Ubuntu dataset and third on the Advising dataset in subtask 1 of Track 1.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge