Yongtao Liu
RFAssigner: A Generic Label Assignment Strategy for Dense Object Detection
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Label assignment is a critical component in training dense object detectors. State-of-the-art methods typically assign each training sample a positive and a negative weight, optimizing the assignment scheme during training. However, these strategies often assign an insufficient number of positive samples to small objects, leading to a scale imbalance during training. To address this limitation, we introduce RFAssigner, a novel assignment strategy designed to enhance the multi-scale learning capabilities of dense detectors. RFAssigner first establishes an initial set of positive samples using a point-based prior. It then leverages a Gaussian Receptive Field (GRF) distance to measure the similarity between the GRFs of unassigned candidate locations and the ground-truth objects. Based on this metric, RFAssigner adaptively selects supplementary positive samples from the unassigned pool, promoting a more balanced learning process across object scales. Comprehensive experiments on three datasets with distinct object scale distributions validate the effectiveness and generalizability of our method. Notably, a single FCOS-ResNet-50 detector equipped with RFAssigner achieves state-of-the-art performance across all object scales, consistently outperforming existing strategies without requiring auxiliary modules or heuristics.
Human-AI collaborative autonomous synthesis with pulsed laser deposition for remote epitaxy
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Autonomous laboratories typically rely on data-driven decision-making, occasionally with human-in-the-loop oversight to inject domain expertise. Fully leveraging AI agents, however, requires tightly coupled, collaborative workflows spanning hypothesis generation, experimental planning, execution, and interpretation. To address this, we develop and deploy a human-AI collaborative (HAIC) workflow that integrates large language models for hypothesis generation and analysis, with collaborative policy updates driving autonomous pulsed laser deposition (PLD) experiments for remote epitaxy of BaTiO$_3$/graphene. HAIC accelerated the hypothesis formation and experimental design and efficiently mapped the growth space to graphene-damage. In situ Raman spectroscopy reveals that chemistry drives degradation while the highest energy plume components seed defects, identifying a low-O$_2$ pressure low-temperature synthesis window that preserves graphene but is incompatible with optimal BaTiO$_3$ growth. Thus, we show a two-step Ar/O$_2$ deposition is required to exfoliate ferroelectric BaTiO$_3$ while maintaining a monolayer graphene interlayer. HAIC stages human insight with AI reasoning between autonomous batches to drive rapid scientific progress, providing an evolution to many existing human-in-the-loop autonomous workflows.
Gaussian Combined Distance: A Generic Metric for Object Detection
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:In object detection, a well-defined similarity metric can significantly enhance model performance. Currently, the IoU-based similarity metric is the most commonly preferred choice for detectors. However, detectors using IoU as a similarity metric often perform poorly when detecting small objects because of their sensitivity to minor positional deviations. To address this issue, recent studies have proposed the Wasserstein Distance as an alternative to IoU for measuring the similarity of Gaussian-distributed bounding boxes. However, we have observed that the Wasserstein Distance lacks scale invariance, which negatively impacts the model's generalization capability. Additionally, when used as a loss function, its independent optimization of the center attributes leads to slow model convergence and unsatisfactory detection precision. To address these challenges, we introduce the Gaussian Combined Distance (GCD). Through analytical examination of GCD and its gradient, we demonstrate that GCD not only possesses scale invariance but also facilitates joint optimization, which enhances model localization performance. Extensive experiments on the AI-TOD-v2 dataset for tiny object detection show that GCD, as a bounding box regression loss function and label assignment metric, achieves state-of-the-art performance across various detectors. We further validated the generalizability of GCD on the MS-COCO-2017 and Visdrone-2019 datasets, where it outperforms the Wasserstein Distance across diverse scales of datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/MArKkwanGuan/mmdet-GCD.
Mic-hackathon 2024: Hackathon on Machine Learning for Electron and Scanning Probe Microscopy
Jun 10, 2025
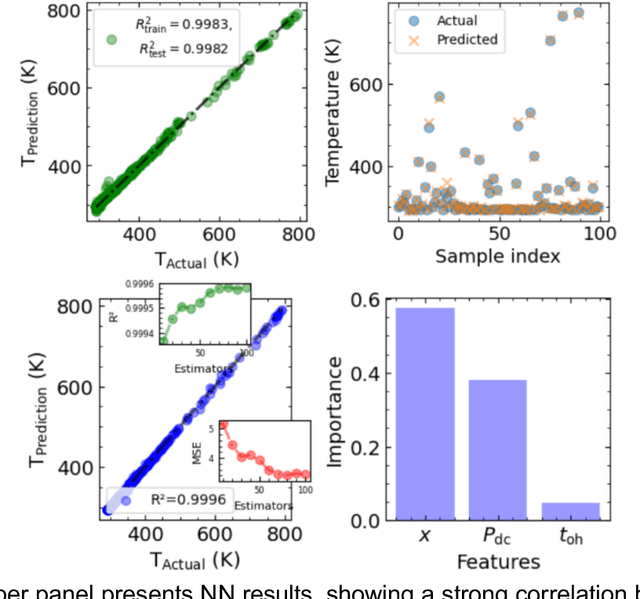
Abstract:Microscopy is a primary source of information on materials structure and functionality at nanometer and atomic scales. The data generated is often well-structured, enriched with metadata and sample histories, though not always consistent in detail or format. The adoption of Data Management Plans (DMPs) by major funding agencies promotes preservation and access. However, deriving insights remains difficult due to the lack of standardized code ecosystems, benchmarks, and integration strategies. As a result, data usage is inefficient and analysis time is extensive. In addition to post-acquisition analysis, new APIs from major microscope manufacturers enable real-time, ML-based analytics for automated decision-making and ML-agent-controlled microscope operation. Yet, a gap remains between the ML and microscopy communities, limiting the impact of these methods on physics, materials discovery, and optimization. Hackathons help bridge this divide by fostering collaboration between ML researchers and microscopy experts. They encourage the development of novel solutions that apply ML to microscopy, while preparing a future workforce for instrumentation, materials science, and applied ML. This hackathon produced benchmark datasets and digital twins of microscopes to support community growth and standardized workflows. All related code is available at GitHub: https://github.com/KalininGroup/Mic-hackathon-2024-codes-publication/tree/1.0.0.1
Curiosity Driven Exploration to Optimize Structure-Property Learning in Microscopy
Apr 28, 2025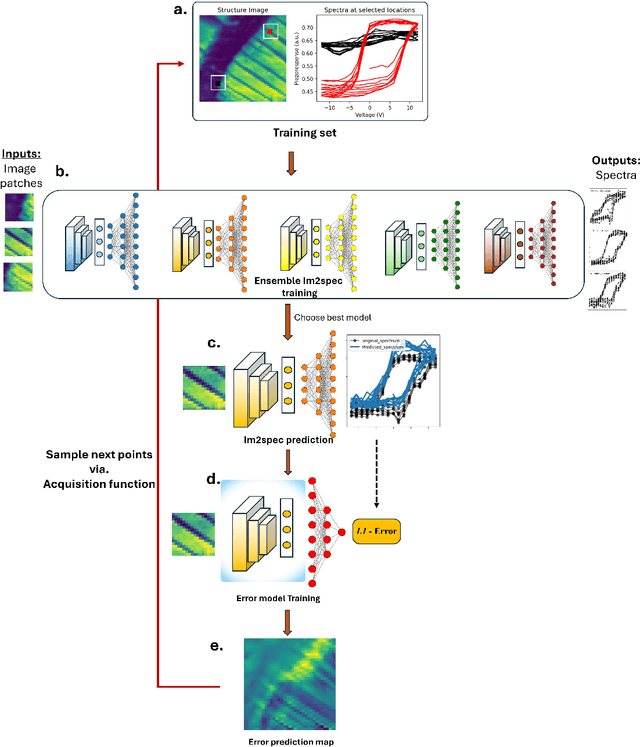
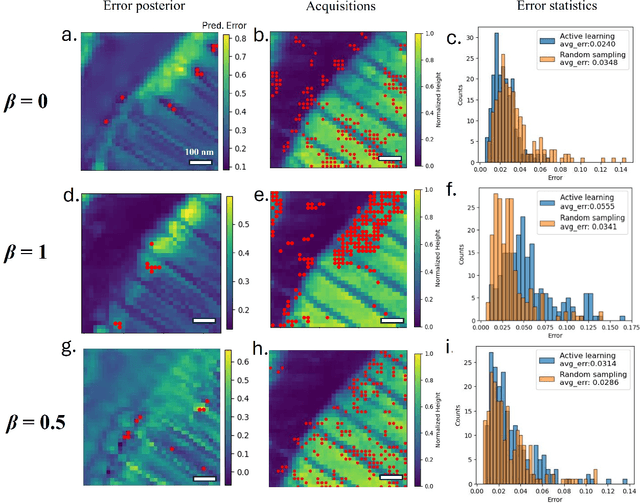
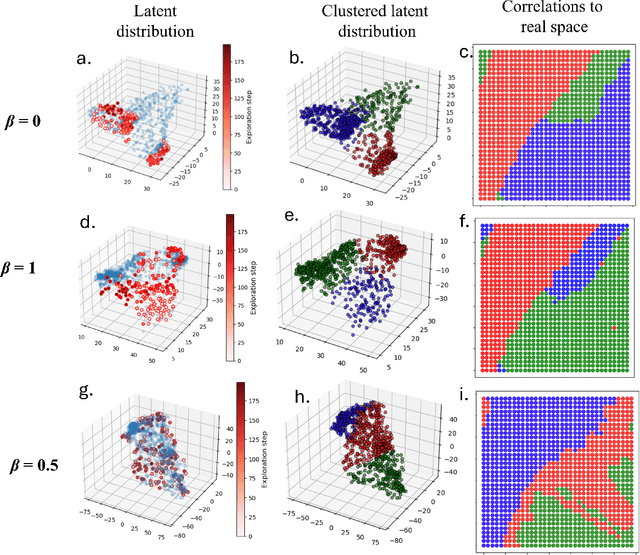
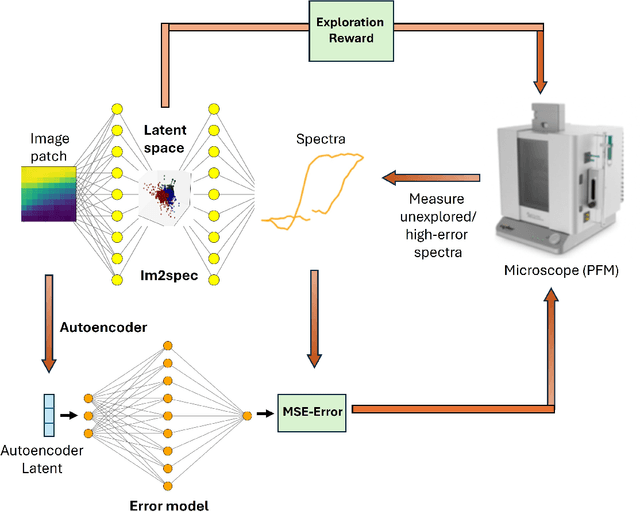
Abstract:Rapidly determining structure-property correlations in materials is an important challenge in better understanding fundamental mechanisms and greatly assists in materials design. In microscopy, imaging data provides a direct measurement of the local structure, while spectroscopic measurements provide relevant functional property information. Deep kernel active learning approaches have been utilized to rapidly map local structure to functional properties in microscopy experiments, but are computationally expensive for multi-dimensional and correlated output spaces. Here, we present an alternative lightweight curiosity algorithm which actively samples regions with unexplored structure-property relations, utilizing a deep-learning based surrogate model for error prediction. We show that the algorithm outperforms random sampling for predicting properties from structures, and provides a convenient tool for efficient mapping of structure-property relationships in materials science.
Invariant Discovery of Features Across Multiple Length Scales: Applications in Microscopy and Autonomous Materials Characterization
Aug 01, 2024Abstract:Physical imaging is a foundational characterization method in areas from condensed matter physics and chemistry to astronomy and spans length scales from atomic to universe. Images encapsulate crucial data regarding atomic bonding, materials microstructures, and dynamic phenomena such as microstructural evolution and turbulence, among other phenomena. The challenge lies in effectively extracting and interpreting this information. Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) have emerged as powerful tools for identifying underlying factors of variation in image data, providing a systematic approach to distilling meaningful patterns from complex datasets. However, a significant hurdle in their application is the definition and selection of appropriate descriptors reflecting local structure. Here we introduce the scale-invariant VAE approach (SI-VAE) based on the progressive training of the VAE with the descriptors sampled at different length scales. The SI-VAE allows the discovery of the length scale dependent factors of variation in the system. Here, we illustrate this approach using the ferroelectric domain images and generalize it to the movies of the electron-beam induced phenomena in graphene and topography evolution across combinatorial libraries. This approach can further be used to initialize the decision making in automated experiments including structure-property discovery and can be applied across a broad range of imaging methods. This approach is universal and can be applied to any spatially resolved data including both experimental imaging studies and simulations, and can be particularly useful for exploration of phenomena such as turbulence, scale-invariant transformation fronts, etc.
Bayesian Co-navigation: Dynamic Designing of the Materials Digital Twins via Active Learning
Apr 19, 2024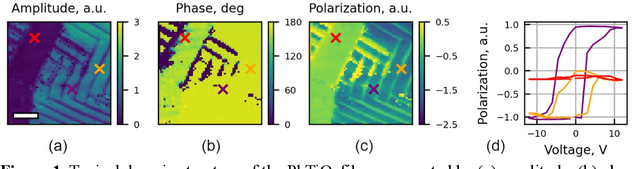



Abstract:Scientific advancement is universally based on the dynamic interplay between theoretical insights, modelling, and experimental discoveries. However, this feedback loop is often slow, including delayed community interactions and the gradual integration of experimental data into theoretical frameworks. This challenge is particularly exacerbated in domains dealing with high-dimensional object spaces, such as molecules and complex microstructures. Hence, the integration of theory within automated and autonomous experimental setups, or theory in the loop automated experiment, is emerging as a crucial objective for accelerating scientific research. The critical aspect is not only to use theory but also on-the-fly theory updates during the experiment. Here, we introduce a method for integrating theory into the loop through Bayesian co-navigation of theoretical model space and experimentation. Our approach leverages the concurrent development of surrogate models for both simulation and experimental domains at the rates determined by latencies and costs of experiments and computation, alongside the adjustment of control parameters within theoretical models to minimize epistemic uncertainty over the experimental object spaces. This methodology facilitates the creation of digital twins of material structures, encompassing both the surrogate model of behavior that includes the correlative part and the theoretical model itself. While demonstrated here within the context of functional responses in ferroelectric materials, our approach holds promise for broader applications, the exploration of optical properties in nanoclusters, microstructure-dependent properties in complex materials, and properties of molecular systems. The analysis code that supports the funding is publicly available at https://github.com/Slautin/2024_Co-navigation/tree/main
Multimodal Co-orchestration for Exploring Structure-Property Relationships in Combinatorial Libraries via Multi-Task Bayesian Optimization
Feb 03, 2024Abstract:The rapid growth of automated and autonomous instrumentations brings forth an opportunity for the co-orchestration of multimodal tools, equipped with multiple sequential detection methods, or several characterization tools to explore identical samples. This can be exemplified by the combinatorial libraries that can be explored in multiple locations by multiple tools simultaneously, or downstream characterization in automated synthesis systems. In the co-orchestration approaches, information gained in one modality should accelerate the discovery of other modalities. Correspondingly, the orchestrating agent should select the measurement modality based on the anticipated knowledge gain and measurement cost. Here, we propose and implement a co-orchestration approach for conducting measurements with complex observables such as spectra or images. The method relies on combining dimensionality reduction by variational autoencoders with representation learning for control over the latent space structure, and integrated into iterative workflow via multi-task Gaussian Processes (GP). This approach further allows for the native incorporation of the system's physics via a probabilistic model as a mean function of the GP. We illustrated this method for different modalities of piezoresponse force microscopy and micro-Raman on combinatorial $Sm-BiFeO_3$ library. However, the proposed framework is general and can be extended to multiple measurement modalities and arbitrary dimensionality of measured signals. The analysis code that supports the funding is publicly available at https://github.com/Slautin/2024_Co-orchestration.
Unraveling the Impact of Initial Choices and In-Loop Interventions on Learning Dynamics in Autonomous Scanning Probe Microscopy
Jan 30, 2024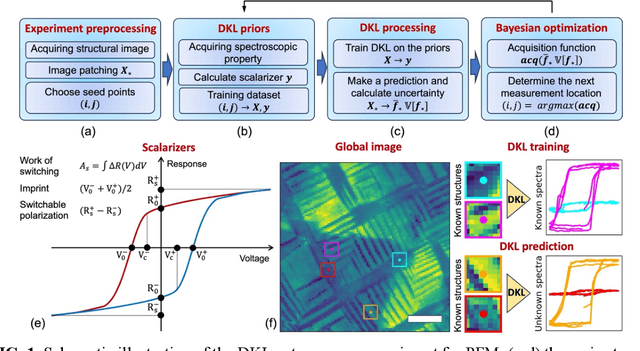
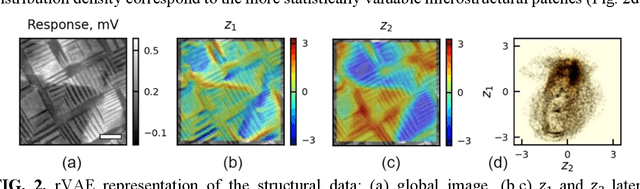
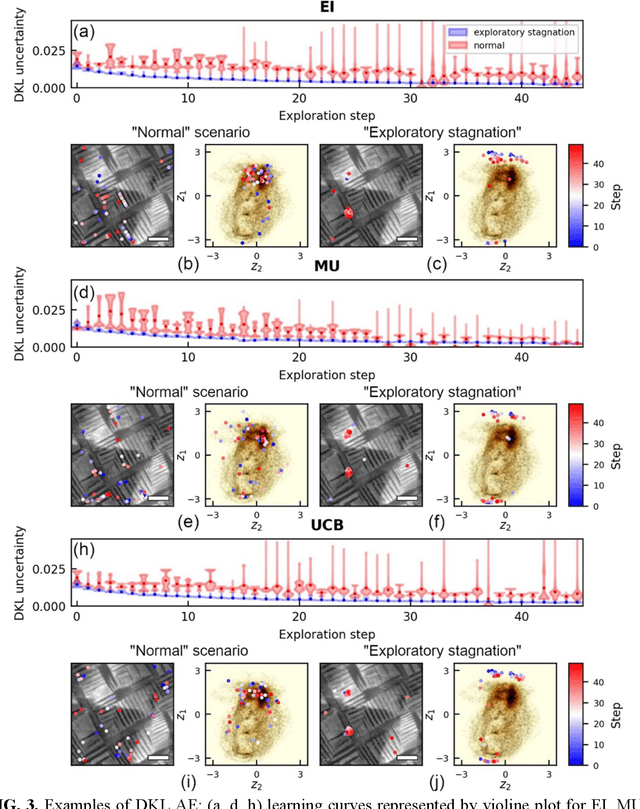
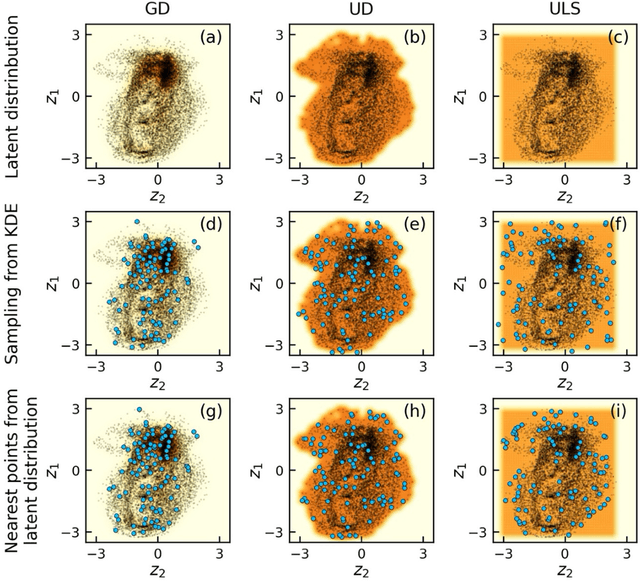
Abstract:The current focus in Autonomous Experimentation (AE) is on developing robust workflows to conduct the AE effectively. This entails the need for well-defined approaches to guide the AE process, including strategies for hyperparameter tuning and high-level human interventions within the workflow loop. This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the influence of initial experimental conditions and in-loop interventions on the learning dynamics of Deep Kernel Learning (DKL) within the realm of AE in Scanning Probe Microscopy. We explore the concept of 'seed effect', where the initial experiment setup has a substantial impact on the subsequent learning trajectory. Additionally, we introduce an approach of the seed point interventions in AE allowing the operator to influence the exploration process. Using a dataset from Piezoresponse Force Microscopy (PFM) on PbTiO3 thin films, we illustrate the impact of the 'seed effect' and in-loop seed interventions on the effectiveness of DKL in predicting material properties. The study highlights the importance of initial choices and adaptive interventions in optimizing learning rates and enhancing the efficiency of automated material characterization. This work offers valuable insights into designing more robust and effective AE workflows in microscopy with potential applications across various characterization techniques. The analysis code that supports the funding is publicly available at https://github.com/Slautin/2024_Seed_effect_DKL_BO.
Human-in-the-loop: The future of Machine Learning in Automated Electron Microscopy
Oct 08, 2023Abstract:Machine learning methods are progressively gaining acceptance in the electron microscopy community for de-noising, semantic segmentation, and dimensionality reduction of data post-acquisition. The introduction of the APIs by major instrument manufacturers now allows the deployment of ML workflows in microscopes, not only for data analytics but also for real-time decision-making and feedback for microscope operation. However, the number of use cases for real-time ML remains remarkably small. Here, we discuss some considerations in designing ML-based active experiments and pose that the likely strategy for the next several years will be human-in-the-loop automated experiments (hAE). In this paradigm, the ML learning agent directly controls beam position and image and spectroscopy acquisition functions, and human operator monitors experiment progression in real- and feature space of the system and tunes the policies of the ML agent to steer the experiment towards specific objectives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge