Sergei V. Kalinin
Mic-hackathon 2024: Hackathon on Machine Learning for Electron and Scanning Probe Microscopy
Jun 10, 2025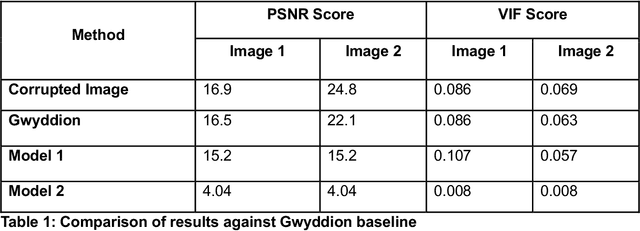
Abstract:Microscopy is a primary source of information on materials structure and functionality at nanometer and atomic scales. The data generated is often well-structured, enriched with metadata and sample histories, though not always consistent in detail or format. The adoption of Data Management Plans (DMPs) by major funding agencies promotes preservation and access. However, deriving insights remains difficult due to the lack of standardized code ecosystems, benchmarks, and integration strategies. As a result, data usage is inefficient and analysis time is extensive. In addition to post-acquisition analysis, new APIs from major microscope manufacturers enable real-time, ML-based analytics for automated decision-making and ML-agent-controlled microscope operation. Yet, a gap remains between the ML and microscopy communities, limiting the impact of these methods on physics, materials discovery, and optimization. Hackathons help bridge this divide by fostering collaboration between ML researchers and microscopy experts. They encourage the development of novel solutions that apply ML to microscopy, while preparing a future workforce for instrumentation, materials science, and applied ML. This hackathon produced benchmark datasets and digital twins of microscopes to support community growth and standardized workflows. All related code is available at GitHub: https://github.com/KalininGroup/Mic-hackathon-2024-codes-publication/tree/1.0.0.1
Domain Switching on the Pareto Front: Multi-Objective Deep Kernel Learning in Automated Piezoresponse Force Microscopy
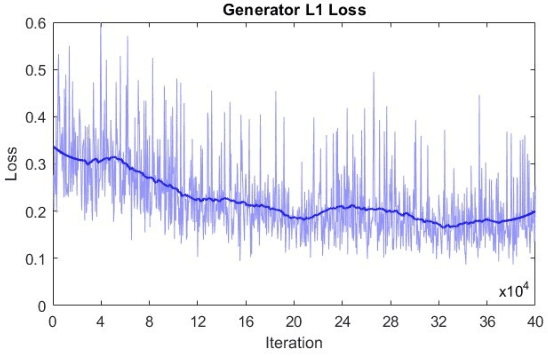
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Ferroelectric polarization switching underpins the functional performance of a wide range of materials and devices, yet its dependence on complex local microstructural features renders systematic exploration by manual or grid-based spectroscopic measurements impractical. Here, we introduce a multi-objective kernel-learning workflow that infers the microstructural rules governing switching behavior directly from high-resolution imaging data. Applied to automated piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM) experiments, our framework efficiently identifies the key relationships between domain-wall configurations and local switching kinetics, revealing how specific wall geometries and defect distributions modulate polarization reversal. Post-experiment analysis projects abstract reward functions, such as switching ease and domain symmetry, onto physically interpretable descriptors including domain configuration and proximity to boundaries. This enables not only high-throughput active learning, but also mechanistic insight into the microstructural control of switching phenomena. While demonstrated for ferroelectric domain switching, our approach provides a powerful, generalizable tool for navigating complex, non-differentiable design spaces, from structure-property correlations in molecular discovery to combinatorial optimization across diverse imaging modalities.
Exploring Domain Wall Pinning in Ferroelectrics via Automated High Throughput AFM
May 29, 2025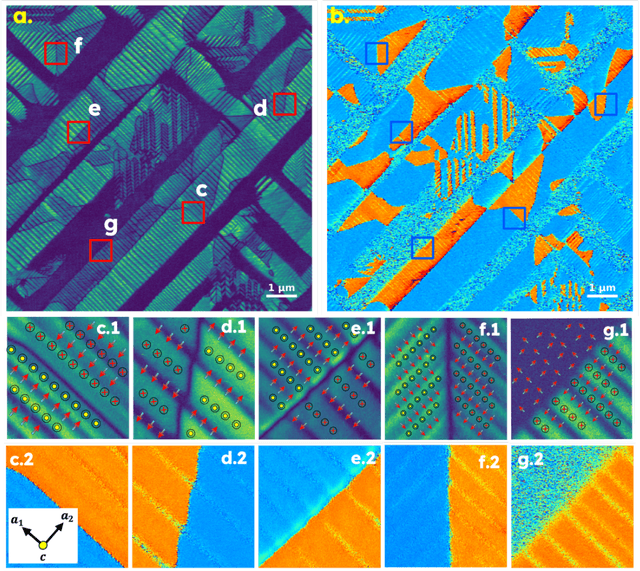
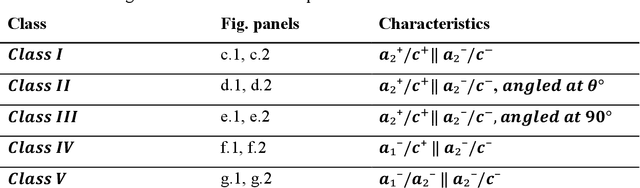
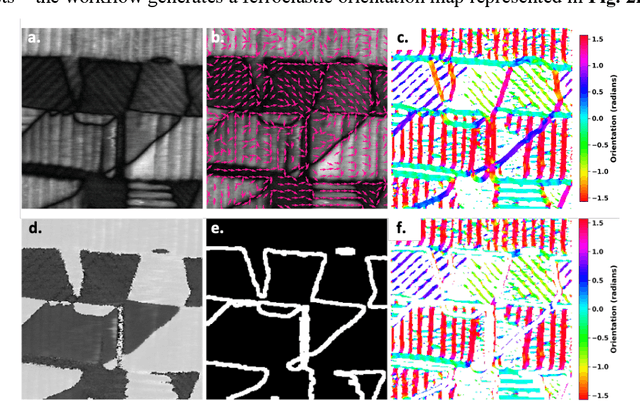
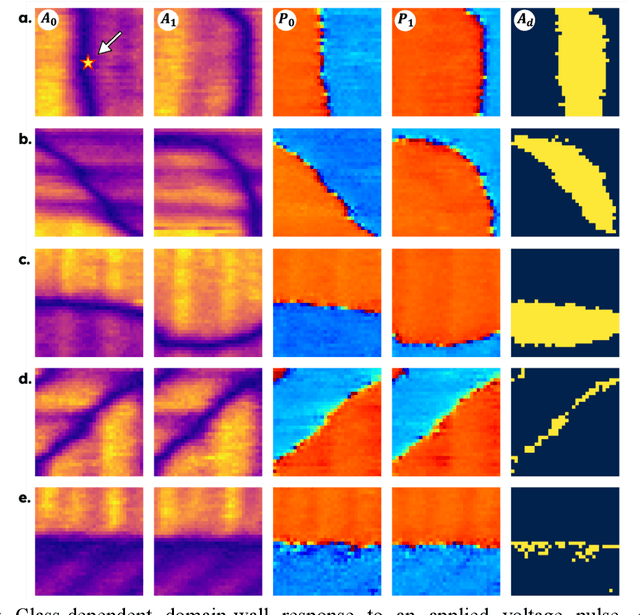
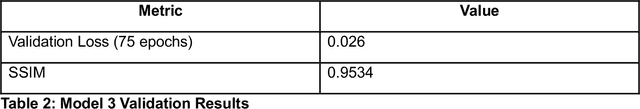
Abstract:Domain-wall dynamics in ferroelectric materials are strongly position-dependent since each polar interface is locked into a unique local microstructure. This necessitates spatially resolved studies of the wall-pinning using scanning-probe microscopy techniques. The pinning centers and preexisting domain walls are usually sparse within image plane, precluding the use of dense hyperspectral imaging modes and requiring time-consuming human experimentation. Here, a large area epitaxial PbTiO$_3$ film on cubic KTaO$_3$ were investigated to quantify the electric field driven dynamics of the polar-strain domain structures using ML-controlled automated Piezoresponse Force Microscopy. Analysis of 1500 switching events reveals that domain wall displacement depends not only on field parameters but also on the local ferroelectric-ferroelastic configuration. For example, twin boundaries in polydomains regions like a$_1^-$/$c^+$ $\parallel$ a$_2^-$/$c^-$ stay pinned up to a certain level of bias magnitude and change only marginally as the bias increases from 20V to 30V, whereas single variant boundaries like a$_2^+$/$c^+$ $\parallel$ a$_2^-$/$c^-$ stack are already activated at 20V. These statistics on the possible ferroelectric and ferroelastic wall orientations, together with the automated, high-throughput AFM workflow, can be distilled into a predictive map that links domain configurations to pulse parameters. This microstructure-specific rule set forms the foundation for designing ferroelectric memories.
The Power of the Pareto Front: Balancing Uncertain Rewards for Adaptive Experimentation in scanning probe microscopy
Apr 09, 2025



Abstract:Automated experimentation has the potential to revolutionize scientific discovery, but its effectiveness depends on well-defined optimization targets, which are often uncertain or probabilistic in real-world settings. In this work, we demonstrate the application of Multi-Objective Bayesian Optimization (MOBO) to balance multiple, competing rewards in autonomous experimentation. Using scanning probe microscopy (SPM) imaging, one of the most widely used and foundational SPM modes, we show that MOBO can optimize imaging parameters to enhance measurement quality, reproducibility, and efficiency. A key advantage of this approach is the ability to compute and analyze the Pareto front, which not only guides optimization but also provides physical insights into the trade-offs between different objectives. Additionally, MOBO offers a natural framework for human-in-the-loop decision-making, enabling researchers to fine-tune experimental trade-offs based on domain expertise. By standardizing high-quality, reproducible measurements and integrating human input into AI-driven optimization, this work highlights MOBO as a powerful tool for advancing autonomous scientific discovery.
Causal Discovery from Data Assisted by Large Language Models
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Knowledge driven discovery of novel materials necessitates the development of the causal models for the property emergence. While in classical physical paradigm the causal relationships are deduced based on the physical principles or via experiment, rapid accumulation of observational data necessitates learning causal relationships between dissimilar aspects of materials structure and functionalities based on observations. For this, it is essential to integrate experimental data with prior domain knowledge. Here we demonstrate this approach by combining high-resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) data with insights derived from large language models (LLMs). By fine-tuning ChatGPT on domain-specific literature, such as arXiv papers on ferroelectrics, and combining obtained information with data-driven causal discovery, we construct adjacency matrices for Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) that map the causal relationships between structural, chemical, and polarization degrees of freedom in Sm-doped BiFeO3 (SmBFO). This approach enables us to hypothesize how synthesis conditions influence material properties, particularly the coercive field (E0), and guides experimental validation. The ultimate objective of this work is to develop a unified framework that integrates LLM-driven literature analysis with data-driven discovery, facilitating the precise engineering of ferroelectric materials by establishing clear connections between synthesis conditions and their resulting material properties.
Integrating Predictive and Generative Capabilities by Latent Space Design via the DKL-VAE Model
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:We introduce a Deep Kernel Learning Variational Autoencoder (VAE-DKL) framework that integrates the generative power of a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) with the predictive nature of Deep Kernel Learning (DKL). The VAE learns a latent representation of high-dimensional data, enabling the generation of novel structures, while DKL refines this latent space by structuring it in alignment with target properties through Gaussian Process (GP) regression. This approach preserves the generative capabilities of the VAE while enhancing its latent space for GP-based property prediction. We evaluate the framework on two datasets: a structured card dataset with predefined variational factors and the QM9 molecular dataset, where enthalpy serves as the target function for optimization. The model demonstrates high-precision property prediction and enables the generation of novel out-of-training subset structures with desired characteristics. The VAE-DKL framework offers a promising approach for high-throughput material discovery and molecular design, balancing structured latent space organization with generative flexibility.
Rewards-based image analysis in microscopy
Feb 23, 2025



Abstract:Analyzing imaging and hyperspectral data is crucial across scientific fields, including biology, medicine, chemistry, and physics. The primary goal is to transform high-resolution or high-dimensional data into an interpretable format to generate actionable insights, aiding decision-making and advancing knowledge. Currently, this task relies on complex, human-designed workflows comprising iterative steps such as denoising, spatial sampling, keypoint detection, feature generation, clustering, dimensionality reduction, and physics-based deconvolutions. The introduction of machine learning over the past decade has accelerated tasks like image segmentation and object detection via supervised learning, and dimensionality reduction via unsupervised methods. However, both classical and NN-based approaches still require human input, whether for hyperparameter tuning, data labeling, or both. The growing use of automated imaging tools, from atomically resolved imaging to biological applications, demands unsupervised methods that optimize data representation for human decision-making or autonomous experimentation. Here, we discuss advances in reward-based workflows, which adopt expert decision-making principles and demonstrate strong transfer learning across diverse tasks. We represent image analysis as a decision-making process over possible operations and identify desiderata and their mappings to classical decision-making frameworks. Reward-driven workflows enable a shift from supervised, black-box models sensitive to distribution shifts to explainable, unsupervised, and robust optimization in image analysis. They can function as wrappers over classical and DCNN-based methods, making them applicable to both unsupervised and supervised workflows (e.g., classification, regression for structure-property mapping) across imaging and hyperspectral data.
Automated Materials Discovery Platform Realized: Scanning Probe Microscopy of Combinatorial Libraries
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Combinatorial libraries are a powerful approach for exploring the evolution of physical properties across binary and ternary cross-sections in multicomponent phase diagrams. Although the synthesis of these libraries has been developed since the 1960s and expedited with advanced laboratory automation, the broader application of combinatorial libraries relies on fast, reliable measurements of concentration-dependent structures and functionalities. Scanning Probe Microscopies (SPM), including piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM), offer significant potential for quantitative, functionally relevant combi-library readouts. Here we demonstrate the implementation of fully automated SPM to explore the evolution of ferroelectric properties in combinatorial libraries, focusing on Sm-doped BiFeO3 and ZnxMg1-xO systems. We also present and compare Gaussian Process-based Bayesian Optimization models for fully automated exploration, emphasizing local reproducibility (effective noise) as an essential factor in optimal experiment workflows. Automated SPM, when coupled with upstream synthesis controls, plays a pivotal role in bridging materials synthesis and characterization.
Reward driven workflows for unsupervised explainable analysis of phases and ferroic variants from atomically resolved imaging data
Nov 19, 2024
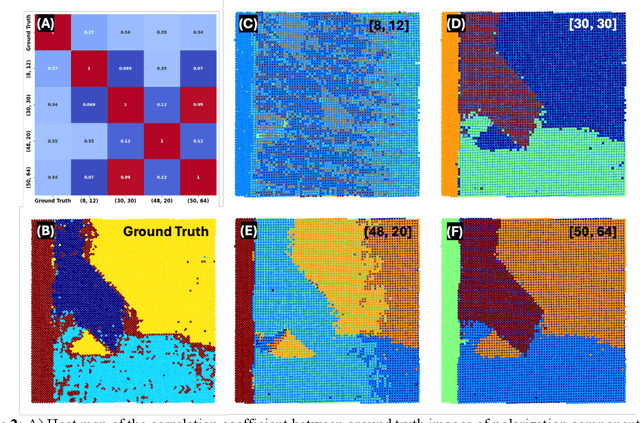


Abstract:Rapid progress in aberration corrected electron microscopy necessitates development of robust methods for the identification of phases, ferroic variants, and other pertinent aspects of materials structure from imaging data. While unsupervised methods for clustering and classification are widely used for these tasks, their performance can be sensitive to hyperparameter selection in the analysis workflow. In this study, we explore the effects of descriptors and hyperparameters on the capability of unsupervised ML methods to distill local structural information, exemplified by discovery of polarization and lattice distortion in Sm doped BiFeO3 (BFO) thin films. We demonstrate that a reward-driven approach can be used to optimize these key hyperparameters across the full workflow, where rewards were designed to reflect domain wall continuity and straightness, ensuring that the analysis aligns with the material's physical behavior. This approach allows us to discover local descriptors that are best aligned with the specific physical behavior, providing insight into the fundamental physics of materials. We further extend the reward driven workflows to disentangle structural factors of variation via optimized variational autoencoder (VAE). Finally, the importance of well-defined rewards was explored as a quantifiable measure of success of the workflow.
Predicting Battery Capacity Fade Using Probabilistic Machine Learning Models With and Without Pre-Trained Priors
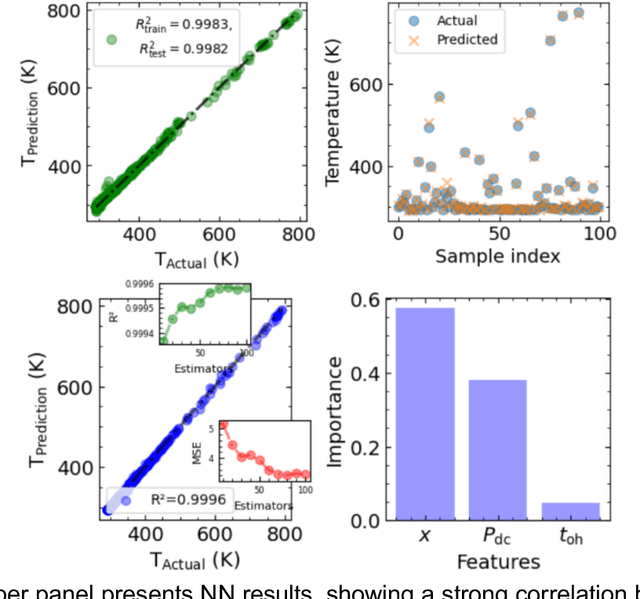
Oct 08, 2024Abstract:Lithium-ion batteries are a key energy storage technology driving revolutions in mobile electronics, electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. Capacity retention is a vital performance measure that is frequently utilized to assess whether these batteries have approached their end-of-life. Machine learning (ML) offers a powerful tool for predicting capacity degradation based on past data, and, potentially, prior physical knowledge, but the degree to which an ML prediction can be trusted is of significant practical importance in situations where consequential decisions must be made based on battery state of health. This study explores the efficacy of fully Bayesian machine learning in forecasting battery health with the quantification of uncertainty in its predictions. Specifically, we implemented three probabilistic ML approaches and evaluated the accuracy of their predictions and uncertainty estimates: a standard Gaussian process (GP), a structured Gaussian process (sGP), and a fully Bayesian neural network (BNN). In typical applications of GP and sGP, their hyperparameters are learned from a single sample while, in contrast, BNNs are typically pre-trained on an existing dataset to learn the weight distributions before being used for inference. This difference in methodology gives the BNN an advantage in learning global trends in a dataset and makes BNNs a good choice when training data is available. However, we show that pre-training can also be leveraged for GP and sGP approaches to learn the prior distributions of the hyperparameters and that in the case of the pre-trained sGP, similar accuracy and improved uncertainty estimation compared to the BNN can be achieved. This approach offers a framework for a broad range of probabilistic machine learning scenarios where past data is available and can be used to learn priors for (hyper)parameters of probabilistic ML models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge