Yifan Qiao
SERL: Self-Examining Reinforcement Learning on Open-Domain
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) has been shown to improve the capabilities of large language models (LLMs). However, applying RL to open-domain tasks faces two key challenges: (1) the inherent subjectivity of these tasks prevents the verifiable rewards as required by Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR); (2) Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) relies on external reward mechanisms. To overcome these limitations, we propose Self-Examining Reinforcement Learning (SERL), a novel self-improving framework where the LLM serves as both Actor and Judge. SERL introduces two synergistic reward mechanisms without any external signals. On the one hand, to improve the Actor's capability, we derive rewards from Copeland-style pairwise comparison judgments across a group of generated responses. On the other hand, a self-consistency reward that encourages coherent judgments is proposed to improve the Judge's reliability. This process refines the Judge's capability, which in turn provides a more robust reward for Actor. Experiments show that our method outperforms existing self-improvement training methods. SERL improves the LC win rate of Qwen3-8B on AlpacaEval 2 from 52.37% to 59.90%. To the best of our knowledge, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance among self-improving approaches. Furthermore, it achieves a performance comparable to significantly larger models like Qwen3-32B, demonstrating superior effectiveness and robustness on open-domain tasks.
Balancing Signal and Variance: Adaptive Offline RL Post-Training for VLA Flow Models
Sep 04, 2025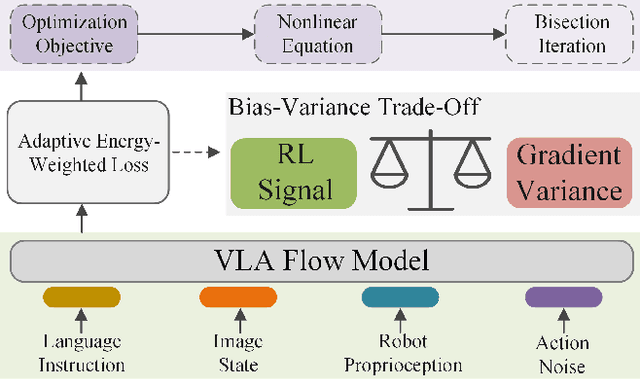
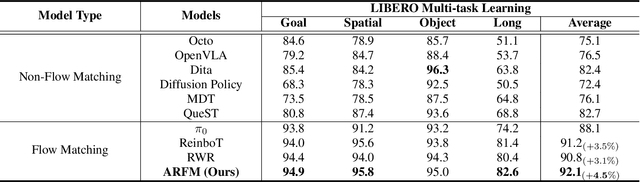
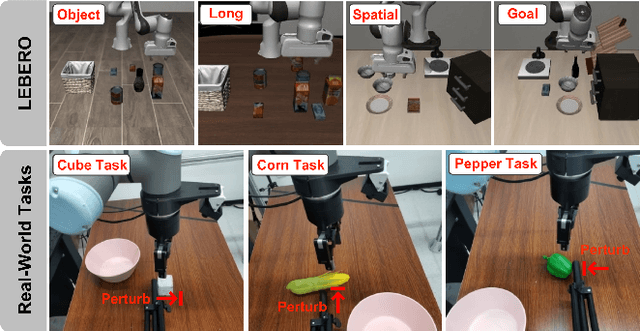
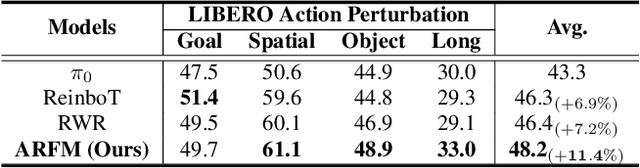
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models based on flow matching have shown excellent performance in general-purpose robotic manipulation tasks. However, the action accuracy of these models on complex downstream tasks is unsatisfactory. One important reason is that these models rely solely on the post-training paradigm of imitation learning, which makes it difficult to have a deeper understanding of the distribution properties of data quality, which is exactly what Reinforcement Learning (RL) excels at. In this paper, we theoretically propose an offline RL post-training objective for VLA flow models and induce an efficient and feasible offline RL fine-tuning algorithm -- Adaptive Reinforced Flow Matching (ARFM). By introducing an adaptively adjusted scaling factor in the VLA flow model loss, we construct a principled bias-variance trade-off objective function to optimally control the impact of RL signal on flow loss. ARFM adaptively balances RL advantage preservation and flow loss gradient variance control, resulting in a more stable and efficient fine-tuning process. Extensive simulation and real-world experimental results show that ARFM exhibits excellent generalization, robustness, few-shot learning, and continuous learning performance.
Prism: Unleashing GPU Sharing for Cost-Efficient Multi-LLM Serving
May 06, 2025



Abstract:Serving large language models (LLMs) is expensive, especially for providers hosting many models, making cost reduction essential. The unique workload patterns of serving multiple LLMs (i.e., multi-LLM serving) create new opportunities and challenges for this task. The long-tail popularity of models and their long idle periods present opportunities to improve utilization through GPU sharing. However, existing GPU sharing systems lack the ability to adjust their resource allocation and sharing policies at runtime, making them ineffective at meeting latency service-level objectives (SLOs) under rapidly fluctuating workloads. This paper presents Prism, a multi-LLM serving system that unleashes the full potential of GPU sharing to achieve both cost efficiency and SLO attainment. At its core, Prism tackles a key limitation of existing systems$\unicode{x2014}$the lack of $\textit{cross-model memory coordination}$, which is essential for flexibly sharing GPU memory across models under dynamic workloads. Prism achieves this with two key designs. First, it supports on-demand memory allocation by dynamically mapping physical to virtual memory pages, allowing flexible memory redistribution among models that space- and time-share a GPU. Second, it improves memory efficiency through a two-level scheduling policy that dynamically adjusts sharing strategies based on models' runtime demands. Evaluations on real-world traces show that Prism achieves more than $2\times$ cost savings and $3.3\times$ SLO attainment compared to state-of-the-art systems.
ConServe: Harvesting GPUs for Low-Latency and High-Throughput Large Language Model Serving
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:Many applications are leveraging large language models (LLMs) for complex tasks, and they generally demand low inference latency and high serving throughput for interactive online jobs such as chatbots. However, the tight latency requirement and high load variance of applications pose challenges to serving systems in achieving high GPU utilization. Due to the high costs of scheduling and preemption, today's systems generally use separate clusters to serve online and offline inference tasks, and dedicate GPUs for online inferences to avoid interference. This approach leads to underutilized GPUs because one must reserve enough GPU resources for the peak expected load, even if the average load is low. This paper proposes to harvest stranded GPU resources for offline LLM inference tasks such as document summarization and LLM benchmarking. Unlike online inferences, these tasks usually run in a batch-processing manner with loose latency requirements, making them a good fit for stranded resources that are only available shortly. To enable safe and efficient GPU harvesting without interfering with online tasks, we built ConServe, an LLM serving system that contains (1) an execution engine that preempts running offline tasks upon the arrival of online tasks, (2) an incremental checkpointing mechanism that minimizes the amount of recomputation required by preemptions, and (3) a scheduler that adaptively batches offline tasks for higher GPU utilization. Our evaluation demonstrates that ConServe achieves strong performance isolation when co-serving online and offline tasks but at a much higher GPU utilization. When colocating practical online and offline workloads on popular models such as Llama-2-7B, ConServe achieves 2.35$\times$ higher throughput than state-of-the-art online serving systems and reduces serving latency by 84$\times$ compared to existing co-serving systems.
Weighted KL-Divergence for Document Ranking Model Refinement
Jun 10, 2024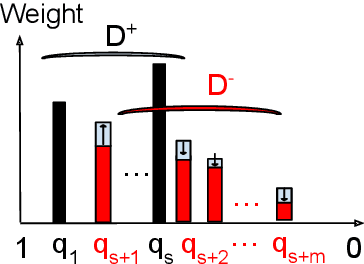
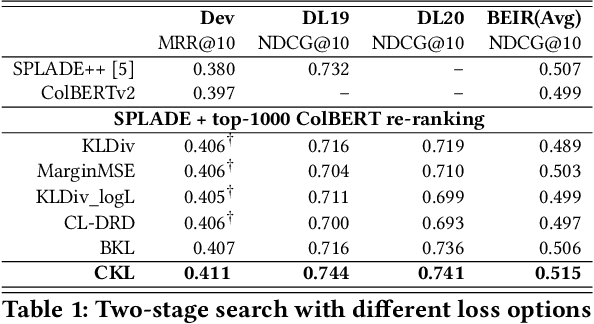
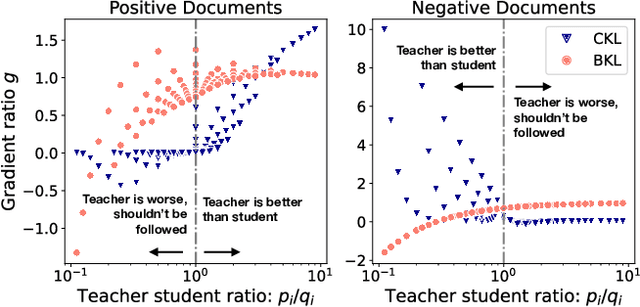
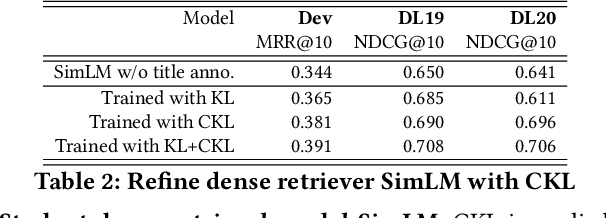
Abstract:Transformer-based retrieval and reranking models for text document search are often refined through knowledge distillation together with contrastive learning. A tight distribution matching between the teacher and student models can be hard as over-calibration may degrade training effectiveness when a teacher does not perform well. This paper contrastively reweights KL divergence terms to prioritize the alignment between a student and a teacher model for proper separation of positive and negative documents. This paper analyzes and evaluates the proposed loss function on the MS MARCO and BEIR datasets to demonstrate its effectiveness in improving the relevance of tested student models.
Approximate Cluster-Based Sparse Document Retrieval with Segmented Maximum Term Weights
Apr 13, 2024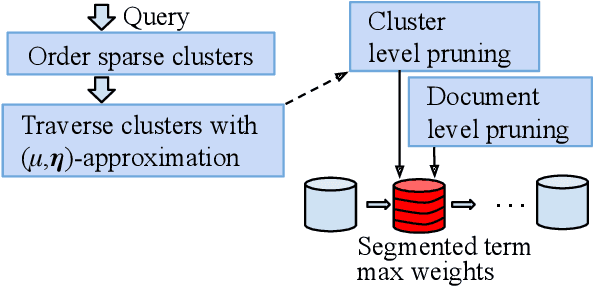
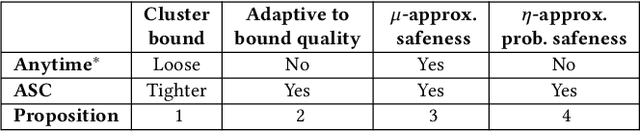
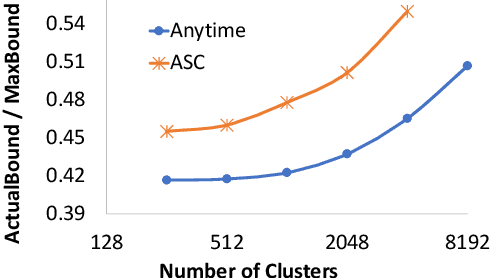
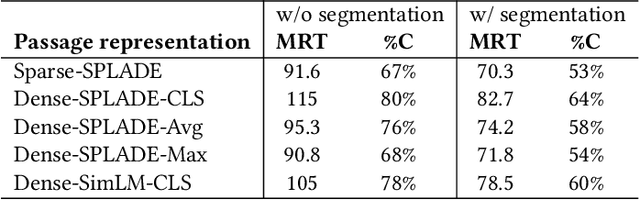
Abstract:This paper revisits cluster-based retrieval that partitions the inverted index into multiple groups and skips the index partially at cluster and document levels during online inference using a learned sparse representation. It proposes an approximate search scheme with two parameters to control the rank-safeness competitiveness of pruning with segmented maximum term weights within each cluster. Cluster-level maximum weight segmentation allows an improvement in the rank score bound estimation and threshold-based pruning to be approximately adaptive to bound estimation tightness, resulting in better relevance and efficiency. The experiments with MS MARCO passage ranking and BEIR datasets demonstrate the usefulness of the proposed scheme with a comparison to the baselines. This paper presents the design of this approximate retrieval scheme with rank-safeness analysis, compares clustering and segmentation options, and reports evaluation results.
Representation Sparsification with Hybrid Thresholding for Fast SPLADE-based Document Retrieval
Jun 20, 2023


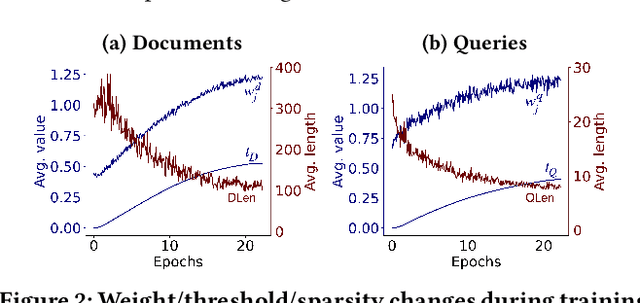
Abstract:Learned sparse document representations using a transformer-based neural model has been found to be attractive in both relevance effectiveness and time efficiency. This paper describes a representation sparsification scheme based on hard and soft thresholding with an inverted index approximation for faster SPLADE-based document retrieval. It provides analytical and experimental results on the impact of this learnable hybrid thresholding scheme.
* This paper is published in SIGIR'23
Optimizing Guided Traversal for Fast Learned Sparse Retrieval
May 02, 2023
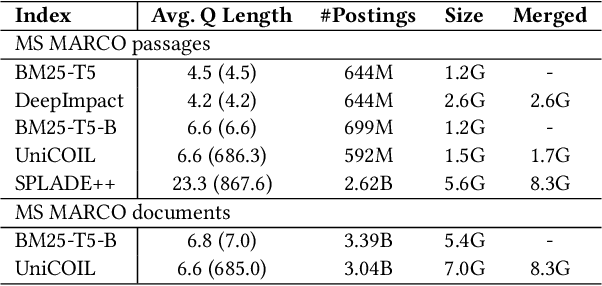
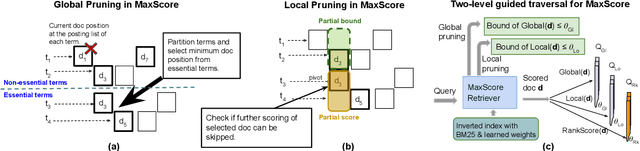
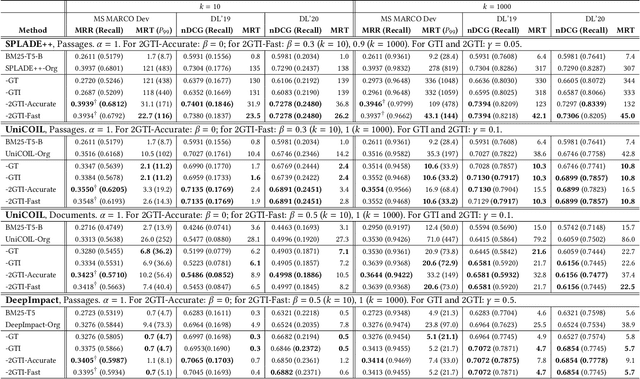
Abstract:Recent studies show that BM25-driven dynamic index skipping can greatly accelerate MaxScore-based document retrieval based on the learned sparse representation derived by DeepImpact. This paper investigates the effectiveness of such a traversal guidance strategy during top k retrieval when using other models such as SPLADE and uniCOIL, and finds that unconstrained BM25-driven skipping could have a visible relevance degradation when the BM25 model is not well aligned with a learned weight model or when retrieval depth k is small. This paper generalizes the previous work and optimizes the BM25 guided index traversal with a two-level pruning control scheme and model alignment for fast retrieval using a sparse representation. Although there can be a cost of increased latency, the proposed scheme is much faster than the original MaxScore method without BM25 guidance while retaining the relevance effectiveness. This paper analyzes the competitiveness of this two-level pruning scheme, and evaluates its tradeoff in ranking relevance and time efficiency when searching several test datasets.
* This paper is published in WWW'23
Bamboo: Making Preemptible Instances Resilient for Affordable Training of Large DNNs
Apr 26, 2022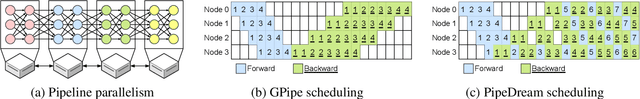


Abstract:DNN models across many domains continue to grow in size, resulting in high resource requirements for effective training, and unpalatable (and often unaffordable) costs for organizations and research labs across scales. This paper aims to significantly reduce training costs with effective use of preemptible instances, i.e., those that can be obtained at a much cheaper price while idle, but may be preempted whenever requested by priority users. Doing so, however, requires new forms of resiliency and efficiency to cope with the possibility of frequent preemptions - a failure model that is drastically different from the occasional failures in normal cluster settings that existing checkpointing techniques target. We present Bamboo, a distributed system that tackles these challenges by introducing redundant computations into the training pipeline, i.e., whereby one node performs computations over not only its own layers but also over some layers in its neighbor. Our key insight is that training large models often requires pipeline parallelism where "pipeline bubbles" naturally exist. Bamboo carefully fills redundant computations into these bubbles, providing resilience at a low cost. Across a variety of widely used DNN models, Bamboo outperforms traditional checkpointing by 3.7x in training throughput, and reduces costs by 2.4x compared to a setting where on-demand instances are used.
Dual Skipping Guidance for Document Retrieval with Learned Sparse Representations
Apr 23, 2022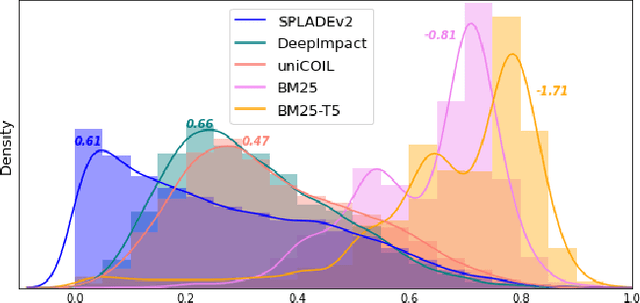
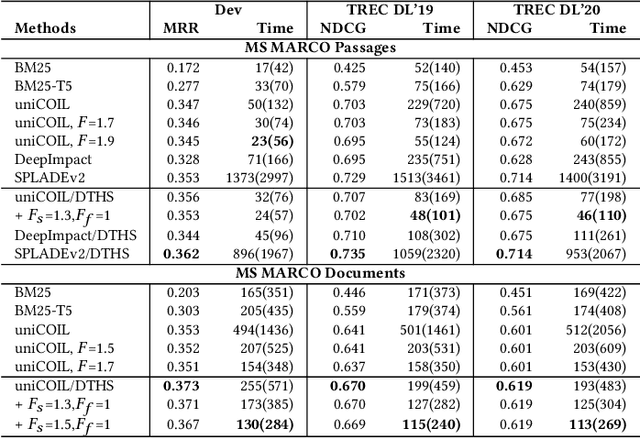
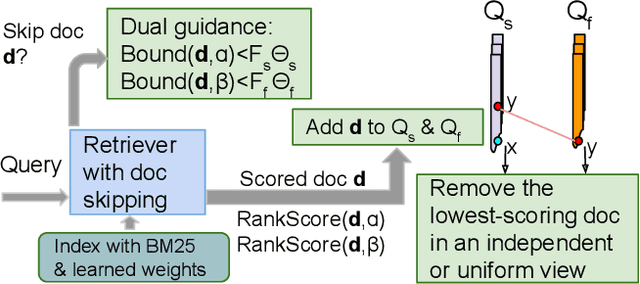
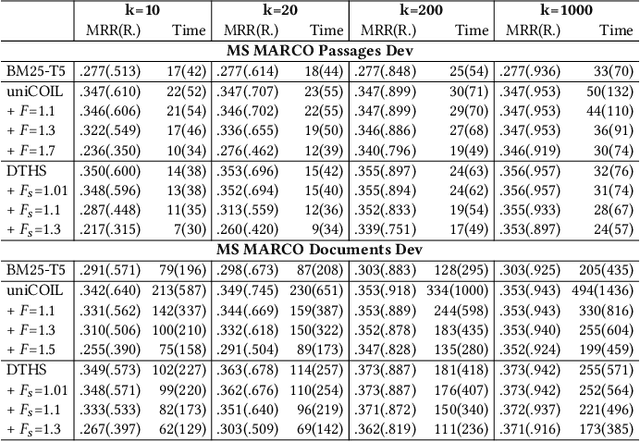
Abstract:This paper proposes a dual skipping guidance scheme with hybrid scoring to accelerate document retrieval that uses learned sparse representations while still delivering a good relevance. This scheme uses both lexical BM25 and learned neural term weights to bound and compose the rank score of a candidate document separately for skipping and final ranking, and maintains two top-k thresholds during inverted index traversal. This paper evaluates time efficiency and ranking relevance of the proposed scheme in searching MS MARCO TREC datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge