Parker Carlson
Efficiency Optimizations for Superblock-based Sparse Retrieval
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Learned sparse retrieval (LSR) is a popular method for first-stage retrieval because it combines the semantic matching of language models with efficient CPU-friendly algorithms. Previous work aggregates blocks into "superblocks" to quickly skip the visitation of blocks during query processing by using an advanced pruning heuristic. This paper proposes a simple and effective superblock pruning scheme that reduces the overhead of superblock score computation while preserving competitive relevance. It combines this scheme with a compact index structure and a robust zero-shot configuration that is effective across LSR models and multiple datasets. This paper provides an analytical justification and evaluation on the MS MARCO and BEIR datasets, demonstrating that the proposed scheme can be a strong alternative for efficient sparse retrieval.
Dynamic Superblock Pruning for Fast Learned Sparse Retrieval
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes superblock pruning (SP) during top-k online document retrieval for learned sparse representations. SP structures the sparse index as a set of superblocks on a sequence of document blocks and conducts a superblock-level selection to decide if some superblocks can be pruned before visiting their child blocks. SP generalizes the previous flat block or cluster-based pruning, allowing the early detection of groups of documents that cannot or are less likely to appear in the final top-k list. SP can accelerate sparse retrieval in a rank-safe or approximate manner under a high-relevance competitiveness constraint. Our experiments show that the proposed scheme significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on MS MARCO passages on a single-threaded CPU.
Approximate Cluster-Based Sparse Document Retrieval with Segmented Maximum Term Weights
Apr 13, 2024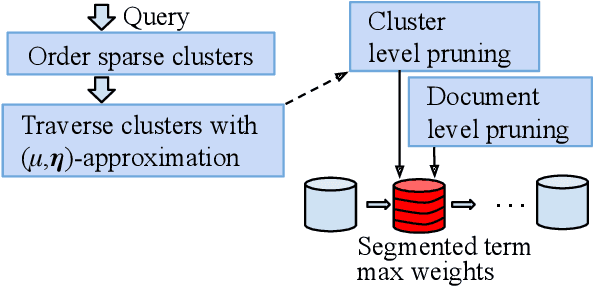
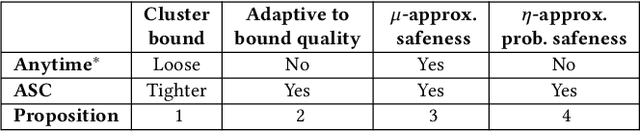
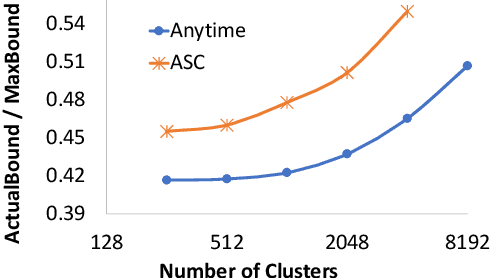
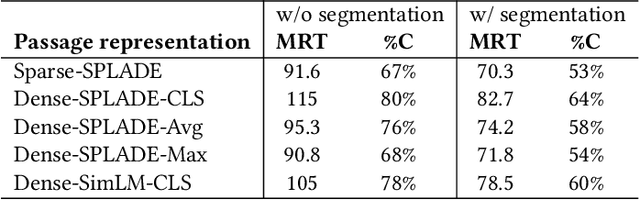
Abstract:This paper revisits cluster-based retrieval that partitions the inverted index into multiple groups and skips the index partially at cluster and document levels during online inference using a learned sparse representation. It proposes an approximate search scheme with two parameters to control the rank-safeness competitiveness of pruning with segmented maximum term weights within each cluster. Cluster-level maximum weight segmentation allows an improvement in the rank score bound estimation and threshold-based pruning to be approximately adaptive to bound estimation tightness, resulting in better relevance and efficiency. The experiments with MS MARCO passage ranking and BEIR datasets demonstrate the usefulness of the proposed scheme with a comparison to the baselines. This paper presents the design of this approximate retrieval scheme with rank-safeness analysis, compares clustering and segmentation options, and reports evaluation results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge