Yaoyuan Liang
A Theoretical Framework for Data Efficient Multi-Source Transfer Learning Based on Cramér-Rao Bound
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Multi-source transfer learning provides an effective solution to data scarcity in real-world supervised learning scenarios by leveraging multiple source tasks. In this field, existing works typically use all available samples from sources in training, which constrains their training efficiency and may lead to suboptimal results. To address this, we propose a theoretical framework that answers the question: what is the optimal quantity of source samples needed from each source task to jointly train the target model? Specifically, we introduce a generalization error measure that aligns with cross-entropy loss, and minimize it based on the Cram\'er-Rao Bound to determine the optimal transfer quantity for each source task. Additionally, we develop an architecture-agnostic and data-efficient algorithm OTQMS to implement our theoretical results for training deep multi-source transfer learning models. Experimental studies on diverse architectures and two real-world benchmark datasets show that our proposed algorithm significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in both accuracy and data efficiency. The code and supplementary materials are available in https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Materials.
RCA-NOC: Relative Contrastive Alignment for Novel Object Captioning
Dec 11, 2023
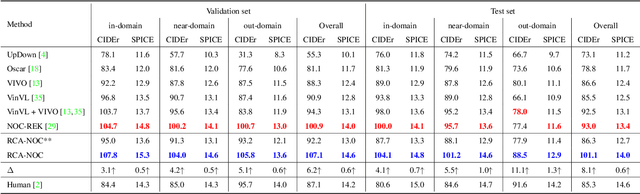
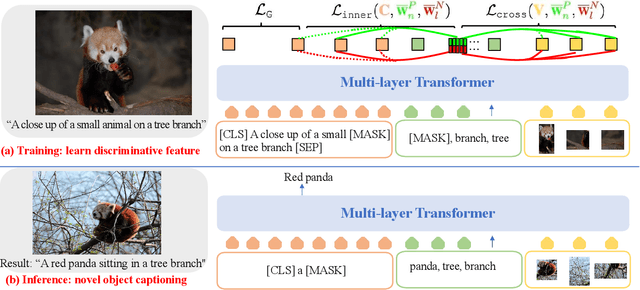

Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to novel object captioning which employs relative contrastive learning to learn visual and semantic alignment. Our approach maximizes compatibility between regions and object tags in a contrastive manner. To set up a proper contrastive learning objective, for each image, we augment tags by leveraging the relative nature of positive and negative pairs obtained from foundation models such as CLIP. We then use the rank of each augmented tag in a list as a relative relevance label to contrast each top-ranked tag with a set of lower-ranked tags. This learning objective encourages the top-ranked tags to be more compatible with their image and text context than lower-ranked tags, thus improving the discriminative ability of the learned multi-modality representation. We evaluate our approach on two datasets and show that our proposed RCA-NOC approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods by a large margin, demonstrating its effectiveness in improving vision-language representation for novel object captioning.
Exploring Iterative Refinement with Diffusion Models for Video Grounding
Oct 26, 2023



Abstract:Video grounding aims to localize the target moment in an untrimmed video corresponding to a given sentence query. Existing methods typically select the best prediction from a set of predefined proposals or directly regress the target span in a single-shot manner, resulting in the absence of a systematical prediction refinement process. In this paper, we propose DiffusionVG, a novel framework with diffusion models that formulates video grounding as a conditional generation task, where the target span is generated from Gaussian noise inputs and interatively refined in the reverse diffusion process. During training, DiffusionVG progressively adds noise to the target span with a fixed forward diffusion process and learns to recover the target span in the reverse diffusion process. In inference, DiffusionVG can generate the target span from Gaussian noise inputs by the learned reverse diffusion process conditioned on the video-sentence representations. Our DiffusionVG follows the encoder-decoder architecture, which firstly encodes the video-sentence features and iteratively denoises the predicted spans in its specialized span refining decoder. Without bells and whistles, our DiffusionVG demonstrates competitive or even superior performance compared to existing well-crafted models on mainstream Charades-STA and ActivityNet Captions benchmarks.
SSLCL: An Efficient Model-Agnostic Supervised Contrastive Learning Framework for Emotion Recognition in Conversations
Oct 25, 2023



Abstract:Emotion recognition in conversations (ERC) is a rapidly evolving task within the natural language processing community, which aims to detect the emotions expressed by speakers during a conversation. Recently, a growing number of ERC methods have focused on leveraging supervised contrastive learning (SCL) to enhance the robustness and generalizability of learned features. However, current SCL-based approaches in ERC are impeded by the constraint of large batch sizes and the lack of compatibility with most existing ERC models. To address these challenges, we propose an efficient and model-agnostic SCL framework named Supervised Sample-Label Contrastive Learning with Soft-HGR Maximal Correlation (SSLCL), which eliminates the need for a large batch size and can be seamlessly integrated with existing ERC models without introducing any model-specific assumptions. Specifically, we introduce a novel perspective on utilizing label representations by projecting discrete labels into dense embeddings through a shallow multilayer perceptron, and formulate the training objective to maximize the similarity between sample features and their corresponding ground-truth label embeddings, while minimizing the similarity between sample features and label embeddings of disparate classes. Moreover, we innovatively adopt the Soft-HGR maximal correlation as a measure of similarity between sample features and label embeddings, leading to significant performance improvements over conventional similarity measures. Additionally, multimodal cues of utterances are effectively leveraged by SSLCL as data augmentations to boost model performances. Extensive experiments on two ERC benchmark datasets, IEMOCAP and MELD, demonstrate the compatibility and superiority of our proposed SSLCL framework compared to existing state-of-the-art SCL methods. Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/TaoShi1998/SSLCL}.
DQ-DETR: Dual Query Detection Transformer for Phrase Extraction and Grounding
Nov 30, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we study the problem of visual grounding by considering both phrase extraction and grounding (PEG). In contrast to the previous phrase-known-at-test setting, PEG requires a model to extract phrases from text and locate objects from images simultaneously, which is a more practical setting in real applications. As phrase extraction can be regarded as a $1$D text segmentation problem, we formulate PEG as a dual detection problem and propose a novel DQ-DETR model, which introduces dual queries to probe different features from image and text for object prediction and phrase mask prediction. Each pair of dual queries is designed to have shared positional parts but different content parts. Such a design effectively alleviates the difficulty of modality alignment between image and text (in contrast to a single query design) and empowers Transformer decoder to leverage phrase mask-guided attention to improve performance. To evaluate the performance of PEG, we also propose a new metric CMAP (cross-modal average precision), analogous to the AP metric in object detection. The new metric overcomes the ambiguity of Recall@1 in many-box-to-one-phrase cases in phrase grounding. As a result, our PEG pre-trained DQ-DETR establishes new state-of-the-art results on all visual grounding benchmarks with a ResNet-101 backbone. For example, it achieves $91.04\%$ and $83.51\%$ in terms of recall rate on RefCOCO testA and testB with a ResNet-101 backbone. Code will be availabl at \url{https://github.com/IDEA-Research/DQ-DETR}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge