RCA-NOC: Relative Contrastive Alignment for Novel Object Captioning
Paper and Code
Dec 11, 2023
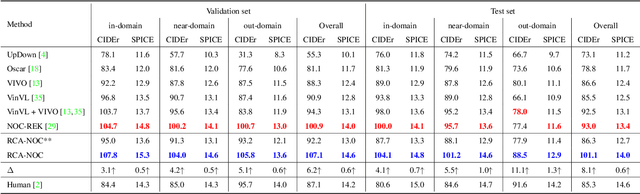
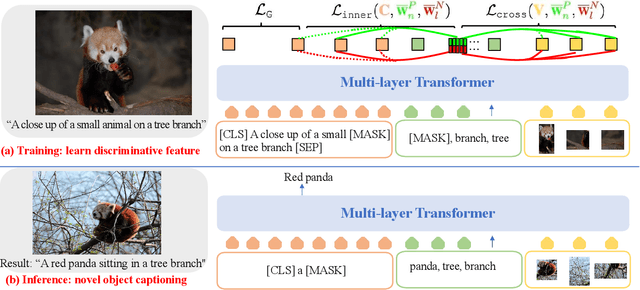

In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to novel object captioning which employs relative contrastive learning to learn visual and semantic alignment. Our approach maximizes compatibility between regions and object tags in a contrastive manner. To set up a proper contrastive learning objective, for each image, we augment tags by leveraging the relative nature of positive and negative pairs obtained from foundation models such as CLIP. We then use the rank of each augmented tag in a list as a relative relevance label to contrast each top-ranked tag with a set of lower-ranked tags. This learning objective encourages the top-ranked tags to be more compatible with their image and text context than lower-ranked tags, thus improving the discriminative ability of the learned multi-modality representation. We evaluate our approach on two datasets and show that our proposed RCA-NOC approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods by a large margin, demonstrating its effectiveness in improving vision-language representation for novel object captioning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge