Xiuwei Zhang
SOMA: Feature Gradient Enhanced Affine-Flow Matching for SAR-Optical Registration
Nov 17, 2025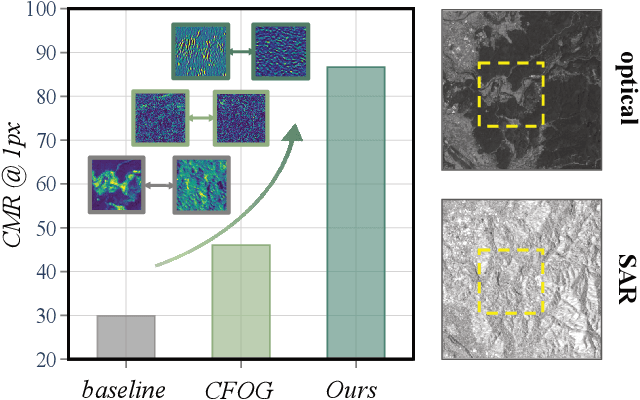
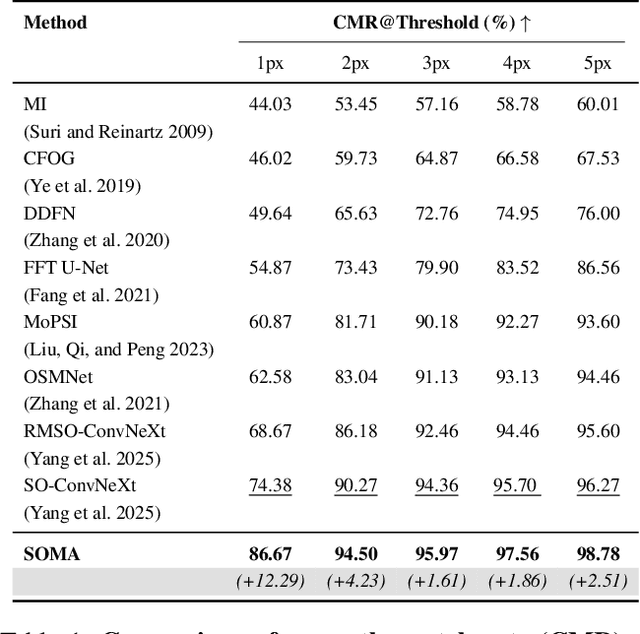
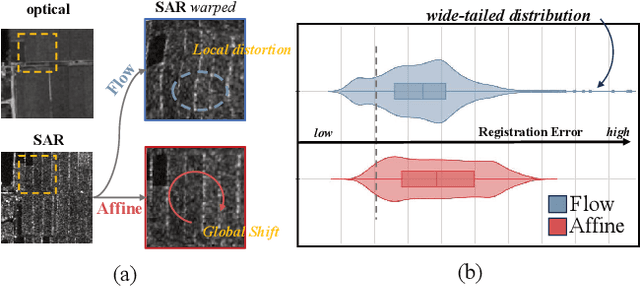
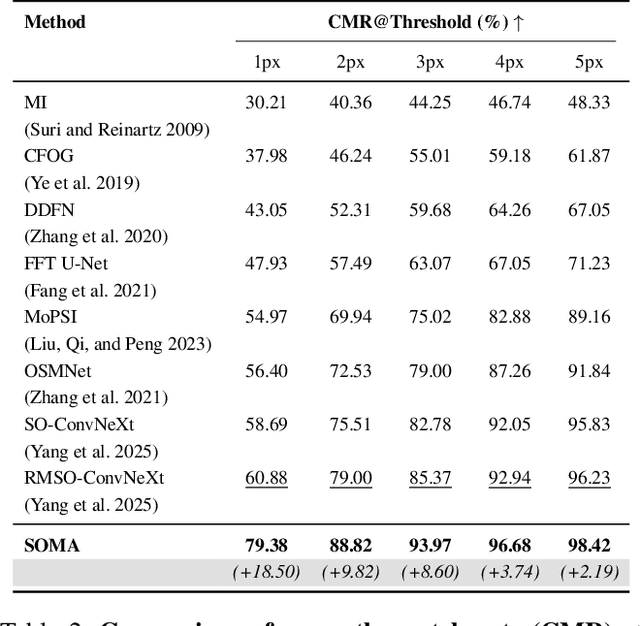
Abstract:Achieving pixel-level registration between SAR and optical images remains a challenging task due to their fundamentally different imaging mechanisms and visual characteristics. Although deep learning has achieved great success in many cross-modal tasks, its performance on SAR-Optical registration tasks is still unsatisfactory. Gradient-based information has traditionally played a crucial role in handcrafted descriptors by highlighting structural differences. However, such gradient cues have not been effectively leveraged in deep learning frameworks for SAR-Optical image matching. To address this gap, we propose SOMA, a dense registration framework that integrates structural gradient priors into deep features and refines alignment through a hybrid matching strategy. Specifically, we introduce the Feature Gradient Enhancer (FGE), which embeds multi-scale, multi-directional gradient filters into the feature space using attention and reconstruction mechanisms to boost feature distinctiveness. Furthermore, we propose the Global-Local Affine-Flow Matcher (GLAM), which combines affine transformation and flow-based refinement within a coarse-to-fine architecture to ensure both structural consistency and local accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that SOMA significantly improves registration precision, increasing the CMR@1px by 12.29% on the SEN1-2 dataset and 18.50% on the GFGE_SO dataset. In addition, SOMA exhibits strong robustness and generalizes well across diverse scenes and resolutions.
FreDFT: Frequency Domain Fusion Transformer for Visible-Infrared Object Detection
Nov 14, 2025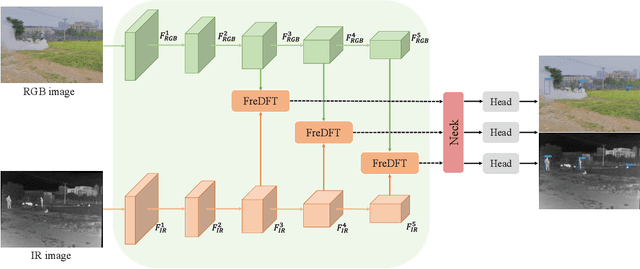

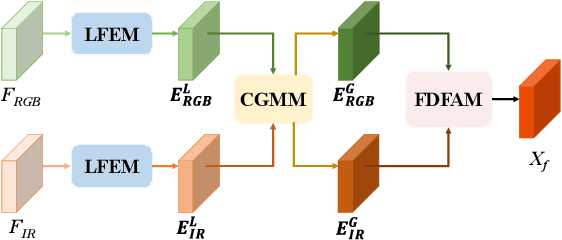
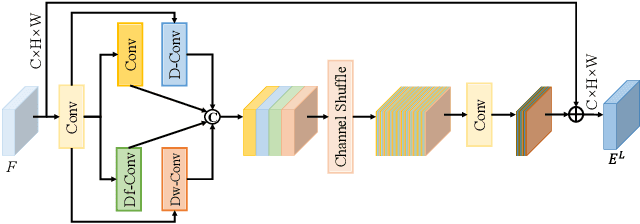
Abstract:Visible-infrared object detection has gained sufficient attention due to its detection performance in low light, fog, and rain conditions. However, visible and infrared modalities captured by different sensors exist the information imbalance problem in complex scenarios, which can cause inadequate cross-modal fusion, resulting in degraded detection performance. \textcolor{red}{Furthermore, most existing methods use transformers in the spatial domain to capture complementary features, ignoring the advantages of developing frequency domain transformers to mine complementary information.} To solve these weaknesses, we propose a frequency domain fusion transformer, called FreDFT, for visible-infrared object detection. The proposed approach employs a novel multimodal frequency domain attention (MFDA) to mine complementary information between modalities and a frequency domain feed-forward layer (FDFFL) via a mixed-scale frequency feature fusion strategy is designed to better enhance multimodal features. To eliminate the imbalance of multimodal information, a cross-modal global modeling module (CGMM) is constructed to perform pixel-wise inter-modal feature interaction in a spatial and channel manner. Moreover, a local feature enhancement module (LFEM) is developed to strengthen multimodal local feature representation and promote multimodal feature fusion by using various convolution layers and applying a channel shuffle. Extensive experimental results have verified that our proposed FreDFT achieves excellent performance on multiple public datasets compared with other state-of-the-art methods. The code of our FreDFT is linked at https://github.com/WenCongWu/FreDFT.
Flow-CDNet: A Novel Network for Detecting Both Slow and Fast Changes in Bitemporal Images
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Change detection typically involves identifying regions with changes between bitemporal images taken at the same location. Besides significant changes, slow changes in bitemporal images are also important in real-life scenarios. For instance, weak changes often serve as precursors to major hazards in scenarios like slopes, dams, and tailings ponds. Therefore, designing a change detection network that simultaneously detects slow and fast changes presents a novel challenge. In this paper, to address this challenge, we propose a change detection network named Flow-CDNet, consisting of two branches: optical flow branch and binary change detection branch. The first branch utilizes a pyramid structure to extract displacement changes at multiple scales. The second one combines a ResNet-based network with the optical flow branch's output to generate fast change outputs. Subsequently, to supervise and evaluate this new change detection framework, a self-built change detection dataset Flow-Change, a loss function combining binary tversky loss and L2 norm loss, along with a new evaluation metric called FEPE are designed. Quantitative experiments conducted on Flow-Change dataset demonstrated that our approach outperforms the existing methods. Furthermore, ablation experiments verified that the two branches can promote each other to enhance the detection performance.
RGB-T Object Detection via Group Shuffled Multi-receptive Attention and Multi-modal Supervision
May 29, 2024



Abstract:Multispectral object detection, utilizing both visible (RGB) and thermal infrared (T) modals, has garnered significant attention for its robust performance across diverse weather and lighting conditions. However, effectively exploiting the complementarity between RGB-T modals while maintaining efficiency remains a critical challenge. In this paper, a very simple Group Shuffled Multi-receptive Attention (GSMA) module is proposed to extract and combine multi-scale RGB and thermal features. Then, the extracted multi-modal features are directly integrated with a multi-level path aggregation neck, which significantly improves the fusion effect and efficiency. Meanwhile, multi-modal object detection often adopts union annotations for both modals. This kind of supervision is not sufficient and unfair, since objects observed in one modal may not be seen in the other modal. To solve this issue, Multi-modal Supervision (MS) is proposed to sufficiently supervise RGB-T object detection. Comprehensive experiments on two challenging benchmarks, KAIST and DroneVehicle, demonstrate the proposed model achieves the state-of-the-art accuracy while maintaining competitive efficiency.
Learning multi-domain feature relation for visible and Long-wave Infrared image patch matching
Aug 09, 2023Abstract:Recently, learning-based algorithms have achieved promising performance on cross-spectral image patch matching, which, however, is still far from satisfactory for practical application. On the one hand, a lack of large-scale dataset with diverse scenes haunts its further improvement for learning-based algorithms, whose performances and generalization rely heavily on the dataset size and diversity. On the other hand, more emphasis has been put on feature relation in the spatial domain whereas the scale dependency between features has often been ignored, leading to performance degeneration especially when encountering significant appearance variations for cross-spectral patches. To address these issues, we publish, to be best of our knowledge, the largest visible and Long-wave Infrared (LWIR) image patch matching dataset, termed VL-CMIM, which contains 1300 pairs of strictly aligned visible and LWIR images and over 2 million patch pairs covering diverse scenes such as asteroid, field, country, build, street and water.In addition, a multi-domain feature relation learning network (MD-FRN) is proposed. Input by the features extracted from a four-branch network, both feature relations in spatial and scale domains are learned via a spatial correlation module (SCM) and multi-scale adaptive aggregation module (MSAG), respectively. To further aggregate the multi-domain relations, a deep domain interactive mechanism (DIM) is applied, where the learnt spatial-relation and scale-relation features are exchanged and further input into MSCRM and SCM. This mechanism allows our model to learn interactive cross-domain feature relations, leading to improved robustness to significant appearance changes due to different modality.
Multispectral Pedestrian Detection via Reference Box Constrained Cross Attention and Modality Balanced Optimization
Feb 01, 2023Abstract:Multispectral pedestrian detection is an important task for many around-the-clock applications, since the visible and thermal modalities can provide complementary information especially under low light conditions. To reduce the influence of hand-designed components in available multispectral pedestrian detectors, we propose a MultiSpectral pedestrian DEtection TRansformer (MS-DETR), which extends deformable DETR to multi-modal paradigm. In order to facilitate the multi-modal learning process, a Reference box Constrained Cross-Attention (RCCA) module is firstly introduced to the multi-modal Transformer decoder, which takes fusion branch together with the reference boxes as intermediaries to enable the interaction of visible and thermal modalities. To further balance the contribution of different modalities, we design a modality-balanced optimization strategy, which aligns the slots of decoders by adaptively adjusting the instance-level weight of three branches. Our end-to-end MS-DETR shows superior performance on the challenging KAIST and CVC-14 benchmark datasets.
Learning Correspondency in Frequency Domain by a Latent-Space Similarity Loss for Multispectral Pansharpening
Jul 18, 2022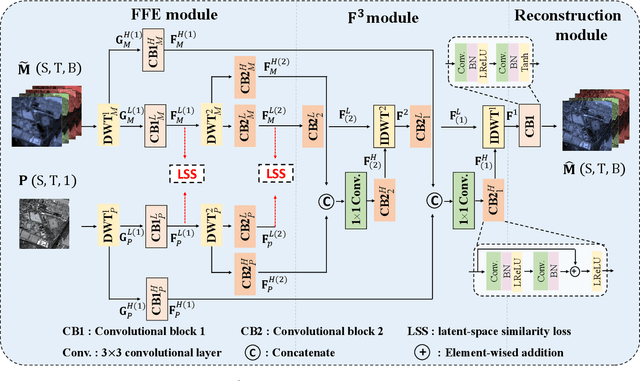

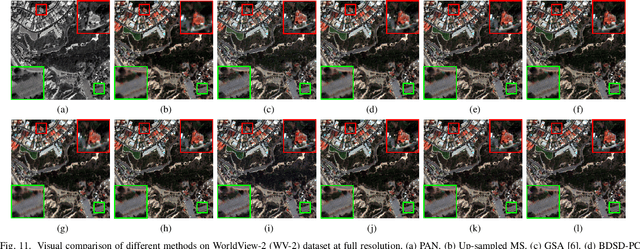
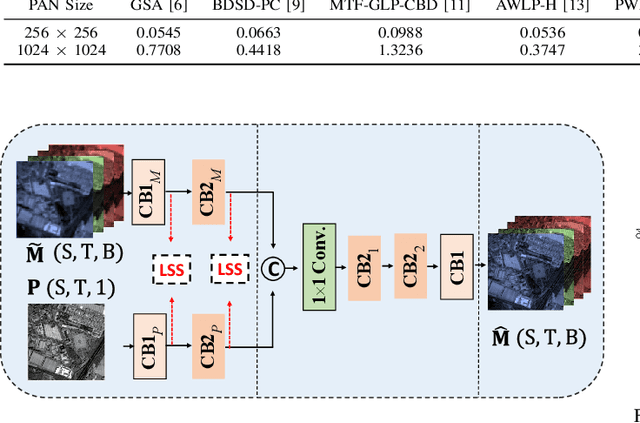
Abstract:The process of fuse a high spatial resolution (HR) panchromatic (PAN) image and a low spatial resolution (LR) multispectral (MS) image to obtain an HRMS image is known as pansharpening. With the development of convolutional neural networks, the performance of pansharpening methods has been improved, however, the blurry effects and the spectral distortion still exist in their fusion results due to the insufficiency in details learning and the mismatch between the high-frequency (HF) and low-frequency (LF) components. Therefore, the improvements of spatial details at the premise of reducing spectral distortion is still a challenge. In this paper, we propose a frequency-aware network (FAN) together with a novel latent-space similarity loss to address above mentioned problems. FAN is composed of three modules, where the frequency feature extraction module aims to extract features in the frequency domain with the help of discrete wavelet transform (DWT) layers, and the inverse DWT (IDWT) layers are then utilized in the frequency feature fusion module to reconstruct the features. Finally, the fusion results are obtained through the reconstruction module. In order to learn the correspondency, we also propose a latent-space similarity loss to constrain the LF features derived from PAN and MS branches, so that HF features of PAN can reasonably be used to supplement that of MS. Experimental results on three datasets at both reduced- and full-resolution demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method compared with several state-of-the-art pansharpening models, especially for the fusion at full resolution.
Approximation of Images via Generalized Higher Order Singular Value Decomposition over Finite-dimensional Commutative Semisimple Algebra
Feb 03, 2022
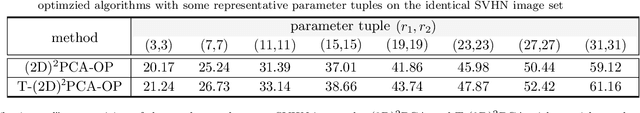
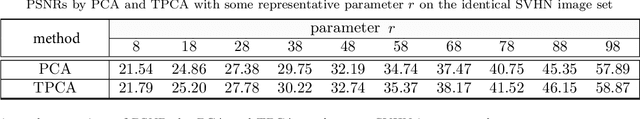
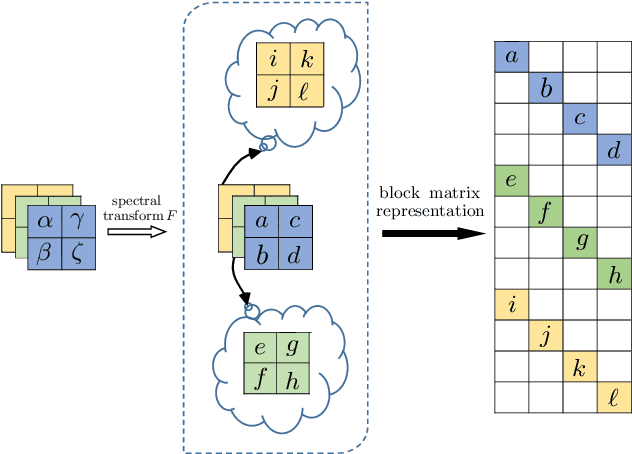
Abstract:Low-rank approximation of images via singular value decomposition is well-received in the era of big data. However, singular value decomposition (SVD) is only for order-two data, i.e., matrices. It is necessary to flatten a higher order input into a matrix or break it into a series of order-two slices to tackle higher order data such as multispectral images and videos with the SVD. Higher order singular value decomposition (HOSVD) extends the SVD and can approximate higher order data using sums of a few rank-one components. We consider the problem of generalizing HOSVD over a finite dimensional commutative algebra. This algebra, referred to as a t-algebra, generalizes the field of complex numbers. The elements of the algebra, called t-scalars, are fix-sized arrays of complex numbers. One can generalize matrices and tensors over t-scalars and then extend many canonical matrix and tensor algorithms, including HOSVD, to obtain higher-performance versions. The generalization of HOSVD is called THOSVD. Its performance of approximating multi-way data can be further improved by an alternating algorithm. THOSVD also unifies a wide range of principal component analysis algorithms. To exploit the potential of generalized algorithms using t-scalars for approximating images, we use a pixel neighborhood strategy to convert each pixel to "deeper-order" t-scalar. Experiments on publicly available images show that the generalized algorithm over t-scalars, namely THOSVD, compares favorably with its canonical counterparts.
Attend to the Difference: Cross-Modality Person Re-identification via Contrastive Correlation
Oct 25, 2019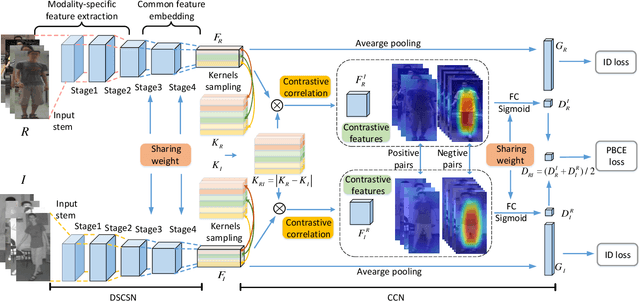
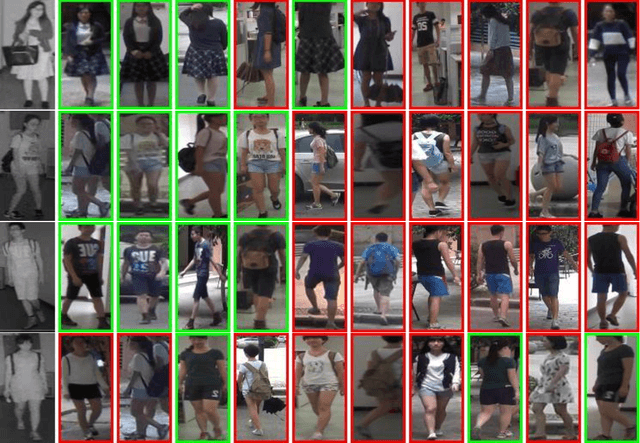

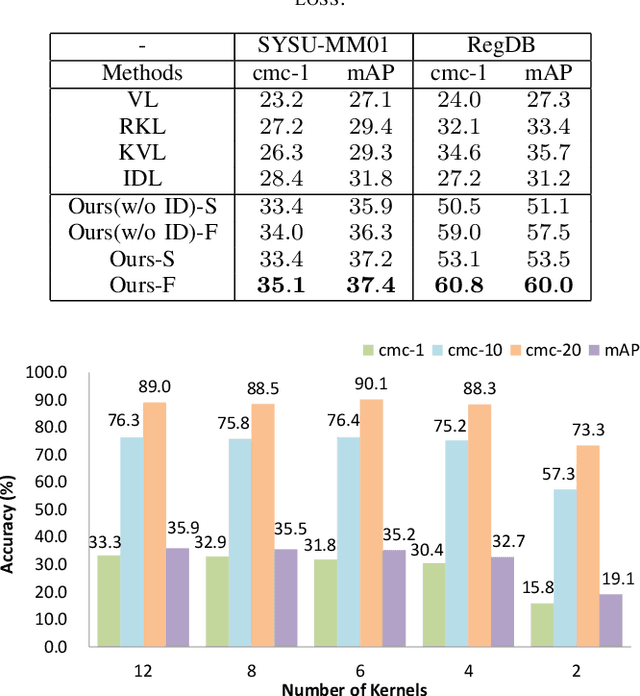
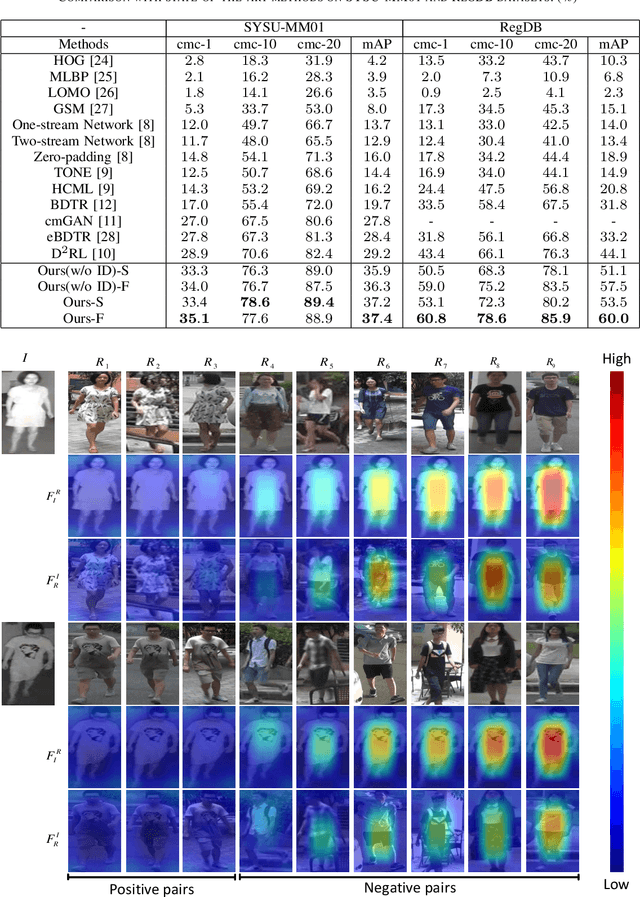
Abstract:The problem of cross-modality person re-identification has been receiving increasing attention recently, due to its practical significance. Motivated by the fact that human usually attend to the difference when they compare two similar objects, we propose a dual-path cross-modality feature learning framework which preserves intrinsic spatial strictures and attends to the difference of input cross-modality image pairs. Our framework is composed by two main components: a Dual-path Spatial-structure-preserving Common Space Network (DSCSN) and a Contrastive Correlation Network (CCN). The former embeds cross-modality images into a common 3D tensor space without losing spatial structures, while the latter extracts contrastive features by dynamically comparing input image pairs. Note that the representations generated for the input RGB and Infrared images are mutually dependant to each other. We conduct extensive experiments on two public available RGB-IR ReID datasets, SYSU-MM01 and RegDB, and our proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms by a large margin with both full and simplified evaluation modes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge