Xinqiang Wang
Approximation of Images via Generalized Higher Order Singular Value Decomposition over Finite-dimensional Commutative Semisimple Algebra
Feb 03, 2022
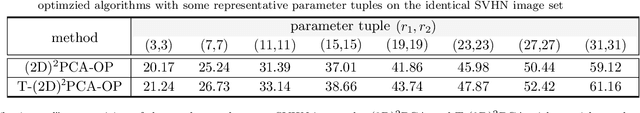
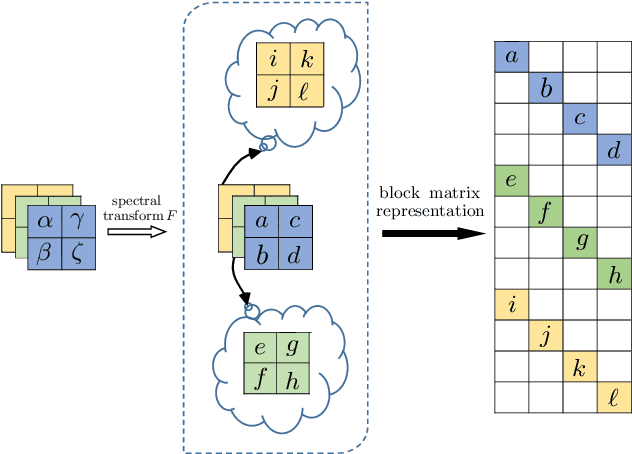
Abstract:Low-rank approximation of images via singular value decomposition is well-received in the era of big data. However, singular value decomposition (SVD) is only for order-two data, i.e., matrices. It is necessary to flatten a higher order input into a matrix or break it into a series of order-two slices to tackle higher order data such as multispectral images and videos with the SVD. Higher order singular value decomposition (HOSVD) extends the SVD and can approximate higher order data using sums of a few rank-one components. We consider the problem of generalizing HOSVD over a finite dimensional commutative algebra. This algebra, referred to as a t-algebra, generalizes the field of complex numbers. The elements of the algebra, called t-scalars, are fix-sized arrays of complex numbers. One can generalize matrices and tensors over t-scalars and then extend many canonical matrix and tensor algorithms, including HOSVD, to obtain higher-performance versions. The generalization of HOSVD is called THOSVD. Its performance of approximating multi-way data can be further improved by an alternating algorithm. THOSVD also unifies a wide range of principal component analysis algorithms. To exploit the potential of generalized algorithms using t-scalars for approximating images, we use a pixel neighborhood strategy to convert each pixel to "deeper-order" t-scalar. Experiments on publicly available images show that the generalized algorithm over t-scalars, namely THOSVD, compares favorably with its canonical counterparts.
Generalized Image Reconstruction over T-Algebra
Jan 20, 2021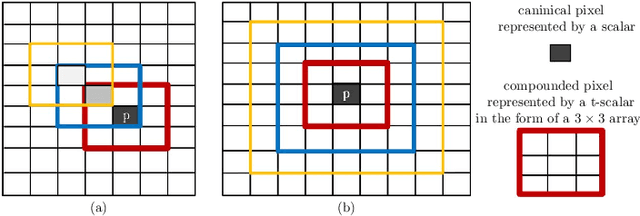



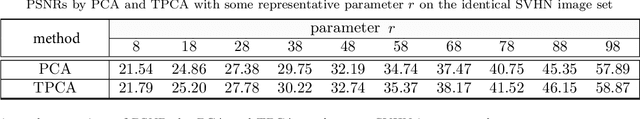
Abstract:Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is well known for its capability of dimension reduction and data compression. However, when using PCA for compressing/reconstructing images, images need to be recast to vectors. The vectorization of images makes some correlation constraints of neighboring pixels and spatial information lost. To deal with the drawbacks of the vectorizations adopted by PCA, we used small neighborhoods of each pixel to form compounded pixels and use a tensorial version of PCA, called TPCA (Tensorial Principal Component Analysis), to compress and reconstruct a compounded image of compounded pixels. Our experiments on public data show that TPCA compares favorably with PCA in compressing and reconstructing images. We also show in our experiments that the performance of TPCA increases when the order of compounded pixels increases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge