Xinshuang Liu
DynaGSLAM: Real-Time Gaussian-Splatting SLAM for Online Rendering, Tracking, Motion Predictions of Moving Objects in Dynamic Scenes
Mar 15, 2025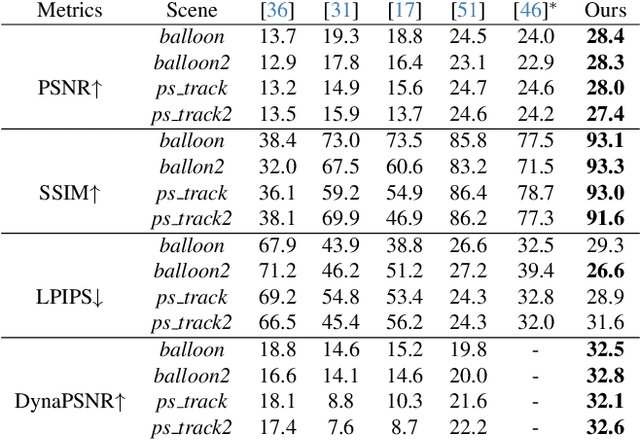

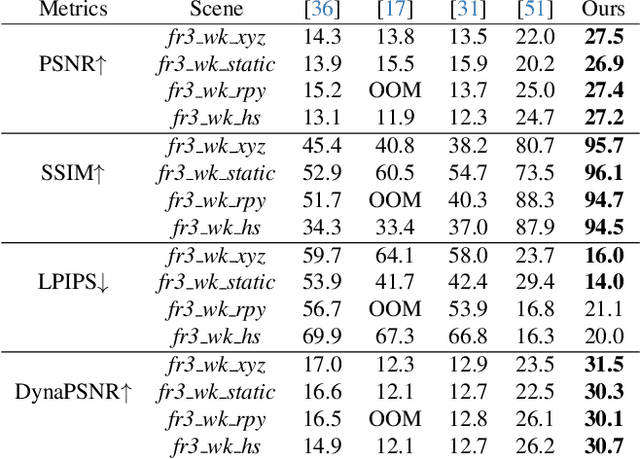
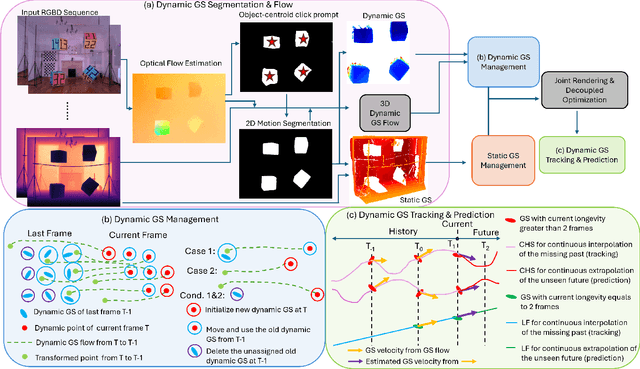
Abstract:Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is one of the most important environment-perception and navigation algorithms for computer vision, robotics, and autonomous cars/drones. Hence, high quality and fast mapping becomes a fundamental problem. With the advent of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) as an explicit representation with excellent rendering quality and speed, state-of-the-art (SOTA) works introduce GS to SLAM. Compared to classical pointcloud-SLAM, GS-SLAM generates photometric information by learning from input camera views and synthesize unseen views with high-quality textures. However, these GS-SLAM fail when moving objects occupy the scene that violate the static assumption of bundle adjustment. The failed updates of moving GS affects the static GS and contaminates the full map over long frames. Although some efforts have been made by concurrent works to consider moving objects for GS-SLAM, they simply detect and remove the moving regions from GS rendering ("anti'' dynamic GS-SLAM), where only the static background could benefit from GS. To this end, we propose the first real-time GS-SLAM, "DynaGSLAM'', that achieves high-quality online GS rendering, tracking, motion predictions of moving objects in dynamic scenes while jointly estimating accurate ego motion. Our DynaGSLAM outperforms SOTA static & "Anti'' dynamic GS-SLAM on three dynamic real datasets, while keeping speed and memory efficiency in practice.
Self-Updatable Large Language Models with Parameter Integration
Oct 01, 2024



Abstract:Despite significant advancements in large language models (LLMs), the rapid and frequent integration of small-scale experiences, such as interactions with surrounding objects, remains a substantial challenge. Two critical factors in assimilating these experiences are (1) Efficacy: the ability to accurately remember recent events; (2) Retention: the capacity to recall long-past experiences. Current methods either embed experiences within model parameters using continual learning, model editing, or knowledge distillation techniques, which often struggle with rapid updates and complex interactions, or rely on external storage to achieve long-term retention, thereby increasing storage requirements. In this paper, we propose SELF-PARAM (Self-Updatable Large Language Models with Parameter Integration). SELF-PARAM requires no extra parameters while ensuring near-optimal efficacy and long-term retention. Our method employs a training objective that minimizes the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence between the predictions of an original model (with access to contextual information) and a target model (without such access). By generating diverse question-answer pairs related to the knowledge and minimizing the KL divergence across this dataset, we update the target model to internalize the knowledge seamlessly within its parameters. Evaluations on question-answering and conversational recommendation tasks demonstrate that SELF-PARAM significantly outperforms existing methods, even when accounting for non-zero storage requirements. This advancement paves the way for more efficient and scalable integration of experiences in large language models by embedding knowledge directly into model parameters.
RecWizard: A Toolkit for Conversational Recommendation with Modular, Portable Models and Interactive User Interface
Feb 23, 2024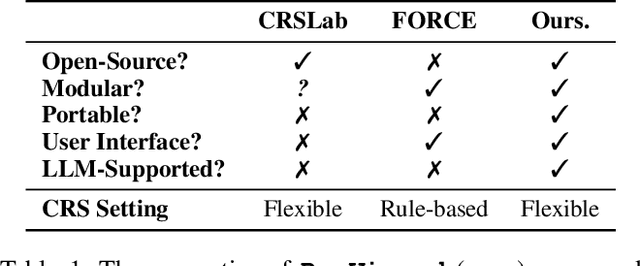
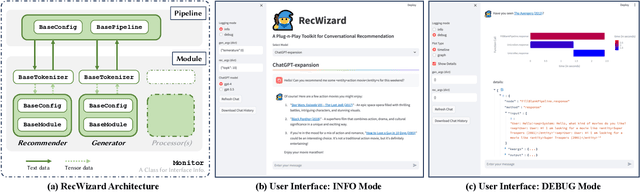
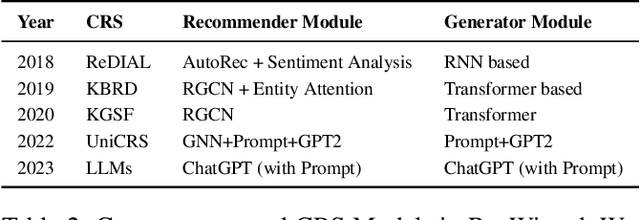

Abstract:We present a new Python toolkit called RecWizard for Conversational Recommender Systems (CRS). RecWizard offers support for development of models and interactive user interface, drawing from the best practices of the Huggingface ecosystems. CRS with RecWizard are modular, portable, interactive and Large Language Models (LLMs)-friendly, to streamline the learning process and reduce the additional effort for CRS research. For more comprehensive information about RecWizard, please check our GitHub https://github.com/McAuley-Lab/RecWizard.
Action2video: Generating Videos of Human 3D Actions
Nov 12, 2021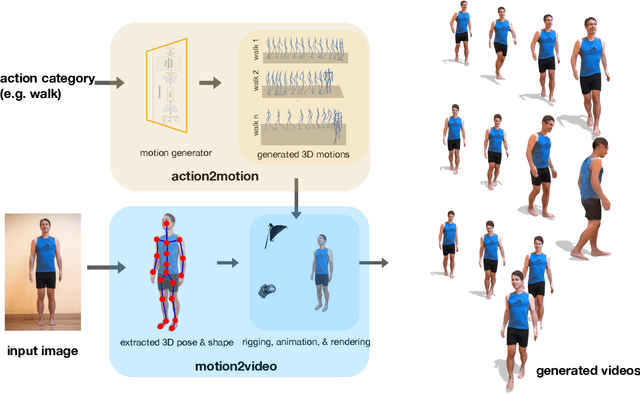
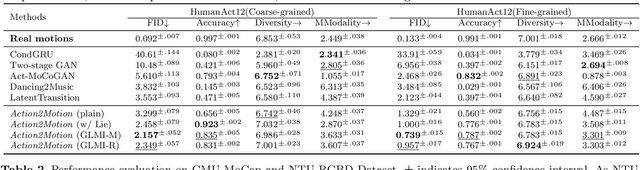
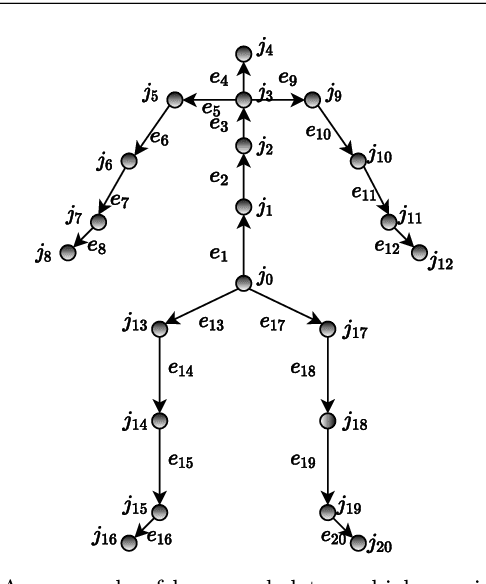
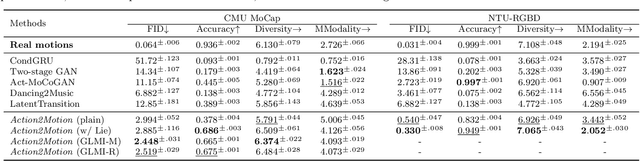
Abstract:We aim to tackle the interesting yet challenging problem of generating videos of diverse and natural human motions from prescribed action categories. The key issue lies in the ability to synthesize multiple distinct motion sequences that are realistic in their visual appearances. It is achieved in this paper by a two-step process that maintains internal 3D pose and shape representations, action2motion and motion2video. Action2motion stochastically generates plausible 3D pose sequences of a prescribed action category, which are processed and rendered by motion2video to form 2D videos. Specifically, the Lie algebraic theory is engaged in representing natural human motions following the physical law of human kinematics; a temporal variational auto-encoder (VAE) is developed that encourages diversity of output motions. Moreover, given an additional input image of a clothed human character, an entire pipeline is proposed to extract his/her 3D detailed shape, and to render in videos the plausible motions from different views. This is realized by improving existing methods to extract 3D human shapes and textures from single 2D images, rigging, animating, and rendering to form 2D videos of human motions. It also necessitates the curation and reannotation of 3D human motion datasets for training purpose. Thorough empirical experiments including ablation study, qualitative and quantitative evaluations manifest the applicability of our approach, and demonstrate its competitiveness in addressing related tasks, where components of our approach are compared favorably to the state-of-the-arts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge