Xin Chang
Automated Review Generation Method Based on Large Language Models
Jul 30, 2024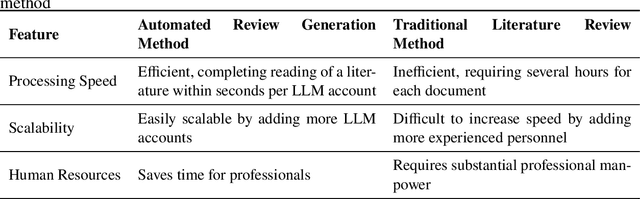
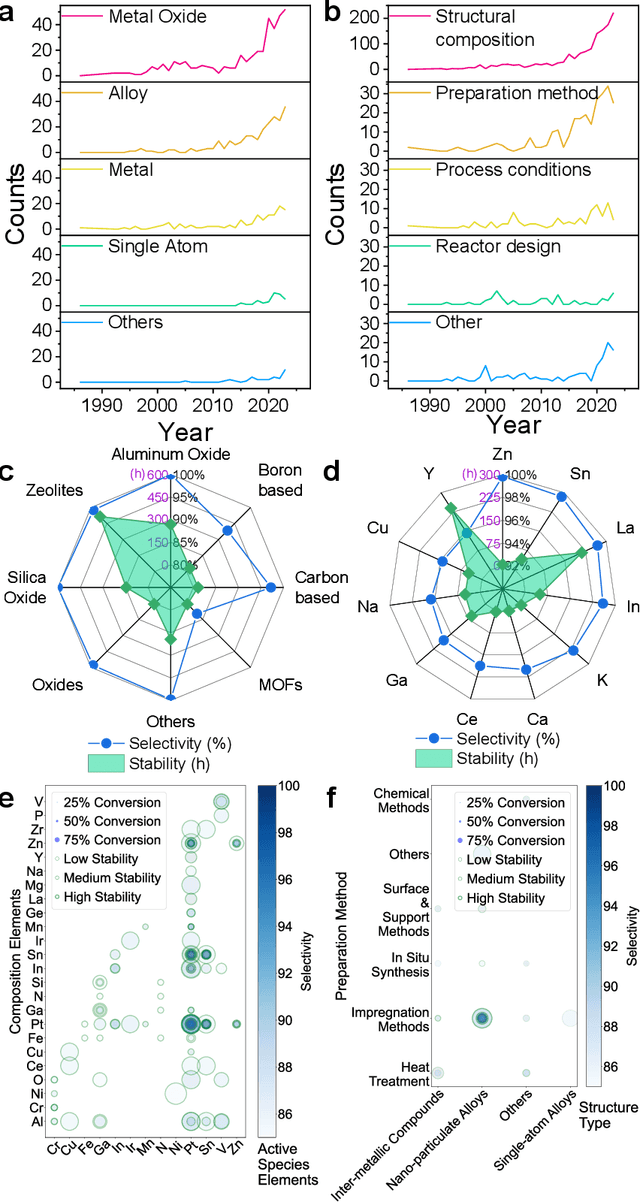
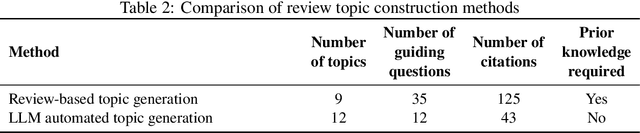
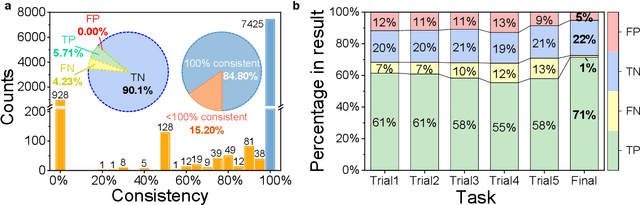
Abstract:Literature research, vital for scientific advancement, is overwhelmed by the vast ocean of available information. Addressing this, we propose an automated review generation method based on Large Language Models (LLMs) to streamline literature processing and reduce cognitive load. In case study on propane dehydrogenation (PDH) catalysts, our method swiftly generated comprehensive reviews from 343 articles, averaging seconds per article per LLM account. Extended analysis of 1041 articles provided deep insights into catalysts' composition, structure, and performance. Recognizing LLMs' hallucinations, we employed a multi-layered quality control strategy, ensuring our method's reliability and effective hallucination mitigation. Expert verification confirms the accuracy and citation integrity of generated reviews, demonstrating LLM hallucination risks reduced to below 0.5% with over 95% confidence. Released Windows application enables one-click review generation, aiding researchers in tracking advancements and recommending literature. This approach showcases LLMs' role in enhancing scientific research productivity and sets the stage for further exploration.
Efficient Single-Image Depth Estimation on Mobile Devices, Mobile AI & AIM 2022 Challenge: Report
Nov 07, 2022
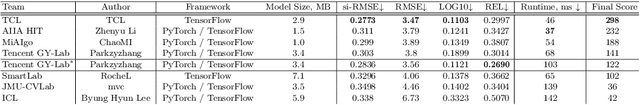
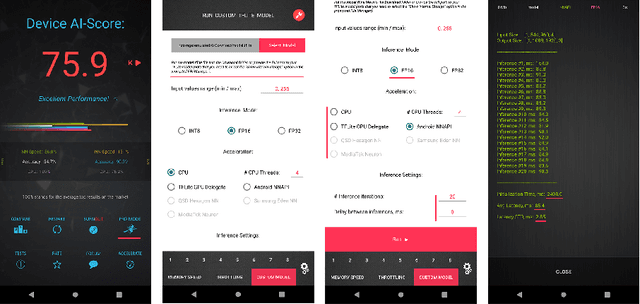
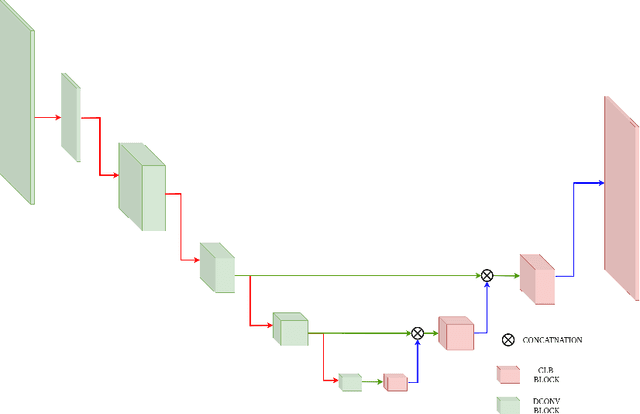
Abstract:Various depth estimation models are now widely used on many mobile and IoT devices for image segmentation, bokeh effect rendering, object tracking and many other mobile tasks. Thus, it is very crucial to have efficient and accurate depth estimation models that can run fast on low-power mobile chipsets. In this Mobile AI challenge, the target was to develop deep learning-based single image depth estimation solutions that can show a real-time performance on IoT platforms and smartphones. For this, the participants used a large-scale RGB-to-depth dataset that was collected with the ZED stereo camera capable to generated depth maps for objects located at up to 50 meters. The runtime of all models was evaluated on the Raspberry Pi 4 platform, where the developed solutions were able to generate VGA resolution depth maps at up to 27 FPS while achieving high fidelity results. All models developed in the challenge are also compatible with any Android or Linux-based mobile devices, their detailed description is provided in this paper.
Multi-modal Residual Perceptron Network for Audio-Video Emotion Recognition
Jul 30, 2021



Abstract:Audio-Video Emotion Recognition is now attacked with Deep Neural Network modeling tools. In published papers, as a rule, the authors show only cases of the superiority in multi-modality over audio-only or video-only modality. However, there are cases superiority in uni-modality can be found. In our research, we hypothesize that for fuzzy categories of emotional events, the within-modal and inter-modal noisy information represented indirectly in the parameters of the modeling neural network impedes better performance in the existing late fusion and end-to-end multi-modal network training strategies. To take advantage and overcome the deficiencies in both solutions, we define a Multi-modal Residual Perceptron Network which performs end-to-end learning from multi-modal network branches, generalizing better multi-modal feature representation. For the proposed Multi-modal Residual Perceptron Network and the novel time augmentation for streaming digital movies, the state-of-art average recognition rate was improved to 91.4% for The Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song dataset and to 83.15% for Crowd-sourced Emotional multi-modal Actors dataset. Moreover, the Multi-modal Residual Perceptron Network concept shows its potential for multi-modal applications dealing with signal sources not only of optical and acoustical types.
ReMOTS: Self-Supervised Refining Multi-Object Tracking and Segmentation
Jul 08, 2020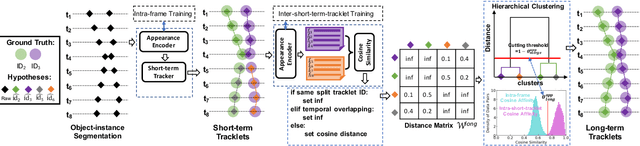
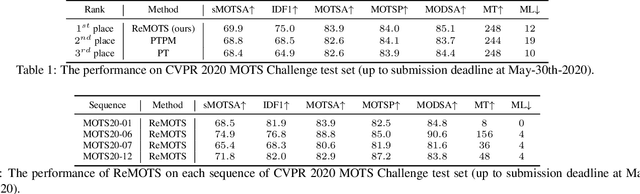
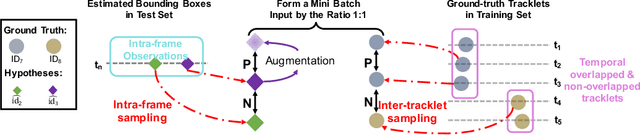
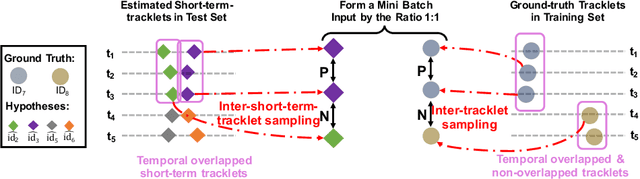
Abstract:We aim to improve the performance of Multiple Object Tracking and Segmentation (MOTS) by refinement. However, it remains challenging for refining MOTS results, which could be attributed to that appearance features are not adapted to target videos and it is also difficult to find proper thresholds to discriminate them. To tackle this issue, we propose a self-supervised refining MOTS (i.e., ReMOTS) framework. ReMOTS mainly takes four steps to refine MOTS results from the data association perspective. (1) Training the appearance encoder using predicted masks. (2) Associating observations across adjacent frames to form short-term tracklets. (3) Training the appearance encoder using short-term tracklets as reliable pseudo labels. (4) Merging short-term tracklets to long-term tracklets utilizing adopted appearance features and thresholds that are automatically obtained from statistical information. Using ReMOTS, we reached the $1^{st}$ place on CVPR 2020 MOTS Challenge 1, with an sMOTSA score of $69.9$.
Multiple Object Tracking by Flowing and Fusing
Jan 30, 2020
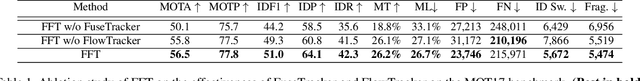
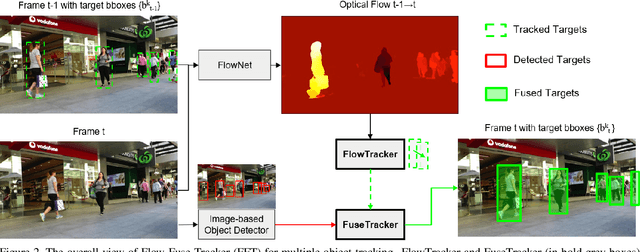
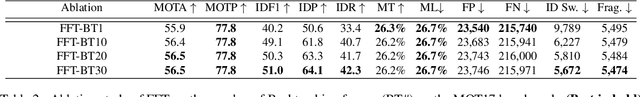
Abstract:Most of Multiple Object Tracking (MOT) approaches compute individual target features for two subtasks: estimating target-wise motions and conducting pair-wise Re-Identification (Re-ID). Because of the indefinite number of targets among video frames, both subtasks are very difficult to scale up efficiently in end-to-end Deep Neural Networks (DNNs). In this paper, we design an end-to-end DNN tracking approach, Flow-Fuse-Tracker (FFT), that addresses the above issues with two efficient techniques: target flowing and target fusing. Specifically, in target flowing, a FlowTracker DNN module learns the indefinite number of target-wise motions jointly from pixel-level optical flows. In target fusing, a FuseTracker DNN module refines and fuses targets proposed by FlowTracker and frame-wise object detection, instead of trusting either of the two inaccurate sources of target proposal. Because FlowTracker can explore complex target-wise motion patterns and FuseTracker can refine and fuse targets from FlowTracker and detectors, our approach can achieve the state-of-the-art results on several MOT benchmarks. As an online MOT approach, FFT produced the top MOTA of 46.3 on the 2DMOT15, 56.5 on the MOT16, and 56.5 on the MOT17 tracking benchmarks, surpassing all the online and offline methods in existing publications.
Human Face Expressions from Images - 2D Face Geometry and 3D Face Local Motion versus Deep Neural Features
Jan 31, 2019



Abstract:Several computer algorithms for recognition of visible human emotions are compared at the web camera scenario using CNN/MMOD face detector. The recognition refers to four face expressions: smile, surprise, anger, and neutral. At the feature extraction stage, the following three concepts of face description are confronted: (a) static 2D face geometry represented by its 68 characteristic landmarks (FP68); (b) dynamic 3D geometry defined by motion parameters for eight distinguished face parts (denoted as AU8) of personalized Candide-3 model; (c) static 2D visual description as 2D array of gray scale pixels (known as facial raw image). At the classification stage, the performance of two major models are analyzed: (a) support vector machine (SVM) with kernel options; (b) convolutional neural network (CNN) with variety of relevant tensor processing layers and blocks of them. The models are trained for frontal views of human faces while they are tested for arbitrary head poses. For geometric features, the success rate (accuracy) indicate nearly triple increase of performance of CNN with respect to SVM classifiers. For raw images, CNN outperforms in accuracy its best geometric counterpart (AU/CNN) by about 30 percent while the best SVM solutions are inferior nearly four times. For F-score the high advantage of raw/CNN over geometric/CNN and geometric/SVM is observed, as well. We conclude that contrary to CNN based emotion classifiers, the generalization capability wrt human head pose is for SVM based emotion classifiers poor.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge