Jimuyang Zhang
XVO: Generalized Visual Odometry via Cross-Modal Self-Training
Oct 08, 2023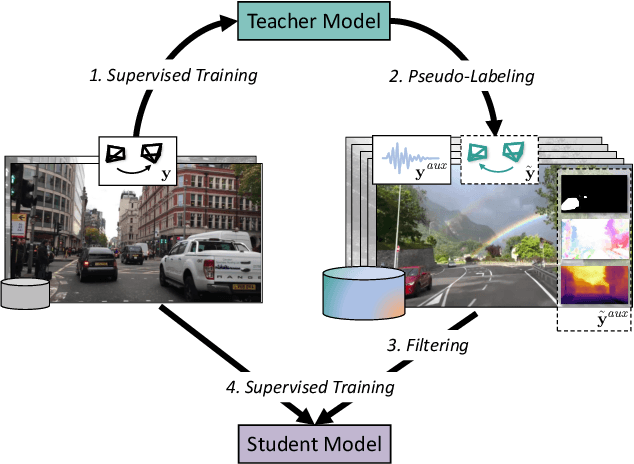
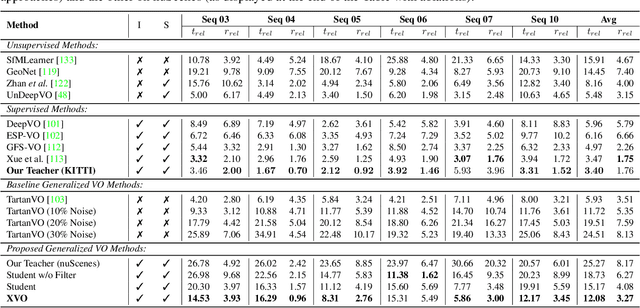
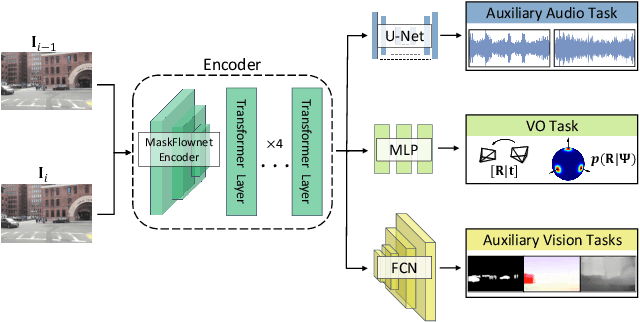
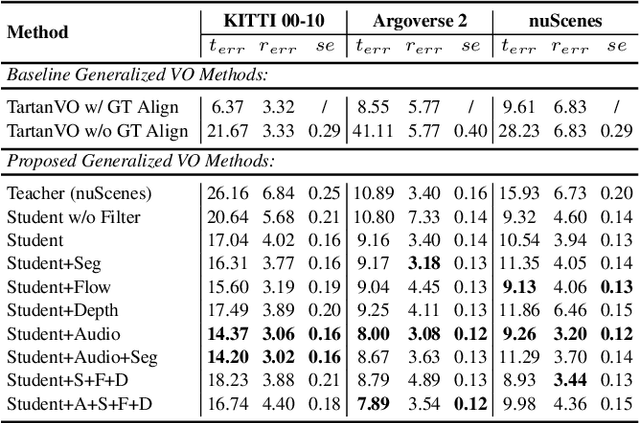
Abstract:We propose XVO, a semi-supervised learning method for training generalized monocular Visual Odometry (VO) models with robust off-the-self operation across diverse datasets and settings. In contrast to standard monocular VO approaches which often study a known calibration within a single dataset, XVO efficiently learns to recover relative pose with real-world scale from visual scene semantics, i.e., without relying on any known camera parameters. We optimize the motion estimation model via self-training from large amounts of unconstrained and heterogeneous dash camera videos available on YouTube. Our key contribution is twofold. First, we empirically demonstrate the benefits of semi-supervised training for learning a general-purpose direct VO regression network. Second, we demonstrate multi-modal supervision, including segmentation, flow, depth, and audio auxiliary prediction tasks, to facilitate generalized representations for the VO task. Specifically, we find audio prediction task to significantly enhance the semi-supervised learning process while alleviating noisy pseudo-labels, particularly in highly dynamic and out-of-domain video data. Our proposed teacher network achieves state-of-the-art performance on the commonly used KITTI benchmark despite no multi-frame optimization or knowledge of camera parameters. Combined with the proposed semi-supervised step, XVO demonstrates off-the-shelf knowledge transfer across diverse conditions on KITTI, nuScenes, and Argoverse without fine-tuning.
Coaching a Teachable Student
Jun 16, 2023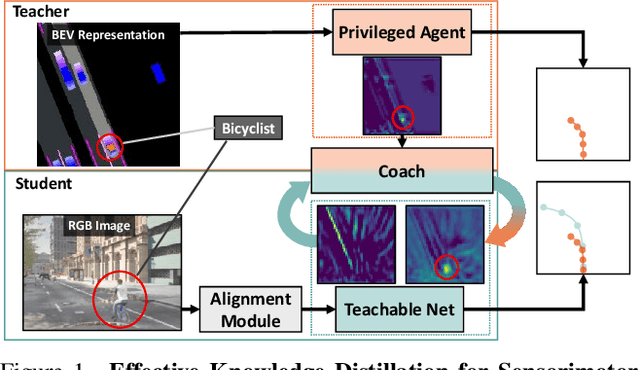
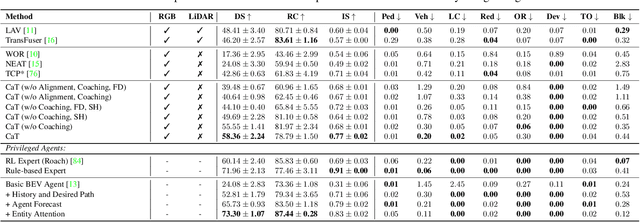
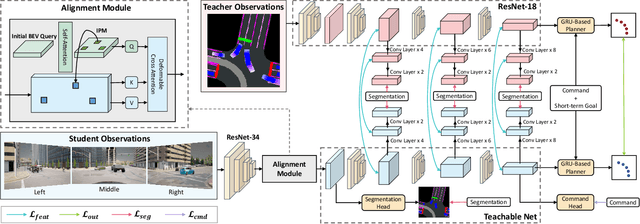
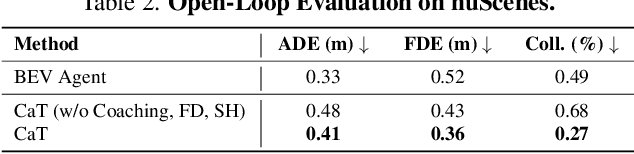
Abstract:We propose a novel knowledge distillation framework for effectively teaching a sensorimotor student agent to drive from the supervision of a privileged teacher agent. Current distillation for sensorimotor agents methods tend to result in suboptimal learned driving behavior by the student, which we hypothesize is due to inherent differences between the input, modeling capacity, and optimization processes of the two agents. We develop a novel distillation scheme that can address these limitations and close the gap between the sensorimotor agent and its privileged teacher. Our key insight is to design a student which learns to align their input features with the teacher's privileged Bird's Eye View (BEV) space. The student then can benefit from direct supervision by the teacher over the internal representation learning. To scaffold the difficult sensorimotor learning task, the student model is optimized via a student-paced coaching mechanism with various auxiliary supervision. We further propose a high-capacity imitation learned privileged agent that surpasses prior privileged agents in CARLA and ensures the student learns safe driving behavior. Our proposed sensorimotor agent results in a robust image-based behavior cloning agent in CARLA, improving over current models by over 20.6% in driving score without requiring LiDAR, historical observations, ensemble of models, on-policy data aggregation or reinforcement learning.
SelfD: Self-Learning Large-Scale Driving Policies From the Web
Apr 21, 2022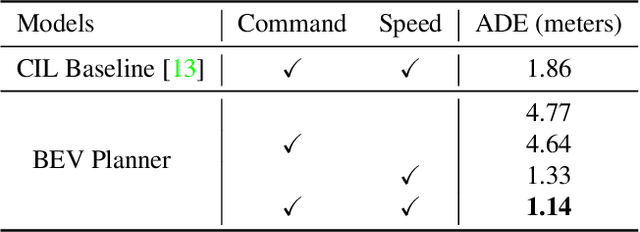
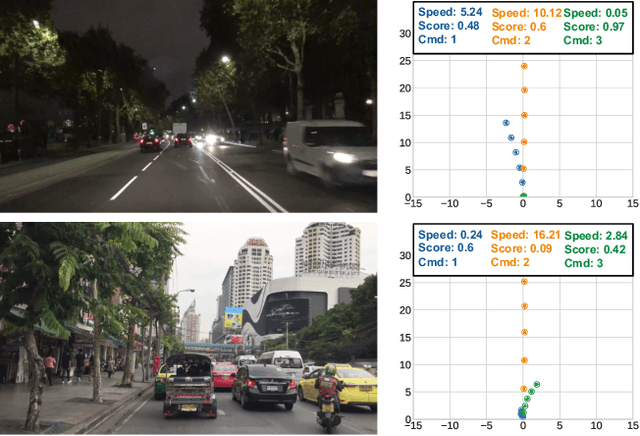
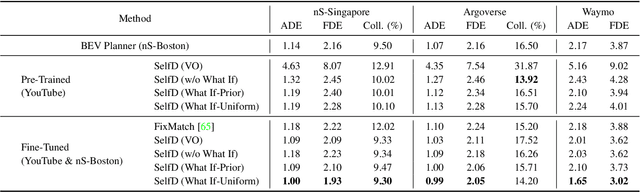
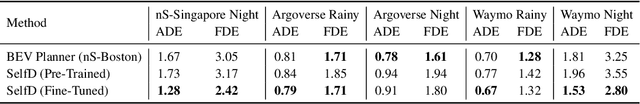
Abstract:Effectively utilizing the vast amounts of ego-centric navigation data that is freely available on the internet can advance generalized intelligent systems, i.e., to robustly scale across perspectives, platforms, environmental conditions, scenarios, and geographical locations. However, it is difficult to directly leverage such large amounts of unlabeled and highly diverse data for complex 3D reasoning and planning tasks. Consequently, researchers have primarily focused on its use for various auxiliary pixel- and image-level computer vision tasks that do not consider an ultimate navigational objective. In this work, we introduce SelfD, a framework for learning scalable driving by utilizing large amounts of online monocular images. Our key idea is to leverage iterative semi-supervised training when learning imitative agents from unlabeled data. To handle unconstrained viewpoints, scenes, and camera parameters, we train an image-based model that directly learns to plan in the Bird's Eye View (BEV) space. Next, we use unlabeled data to augment the decision-making knowledge and robustness of an initially trained model via self-training. In particular, we propose a pseudo-labeling step which enables making full use of highly diverse demonstration data through "hypothetical" planning-based data augmentation. We employ a large dataset of publicly available YouTube videos to train SelfD and comprehensively analyze its generalization benefits across challenging navigation scenarios. Without requiring any additional data collection or annotation efforts, SelfD demonstrates consistent improvements (by up to 24%) in driving performance evaluation on nuScenes, Argoverse, Waymo, and CARLA.
Learning by Watching
Jun 10, 2021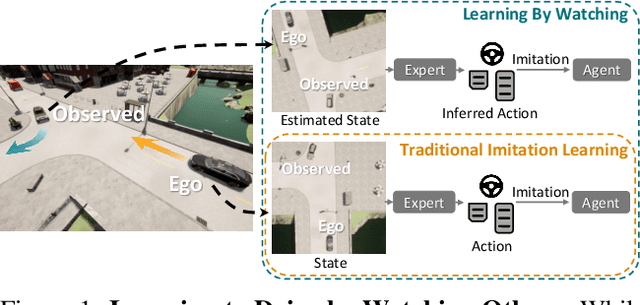

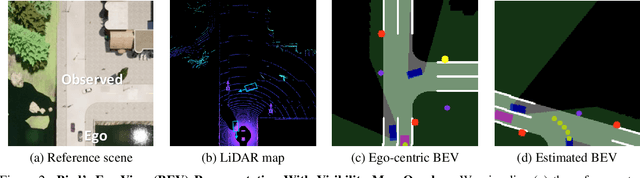
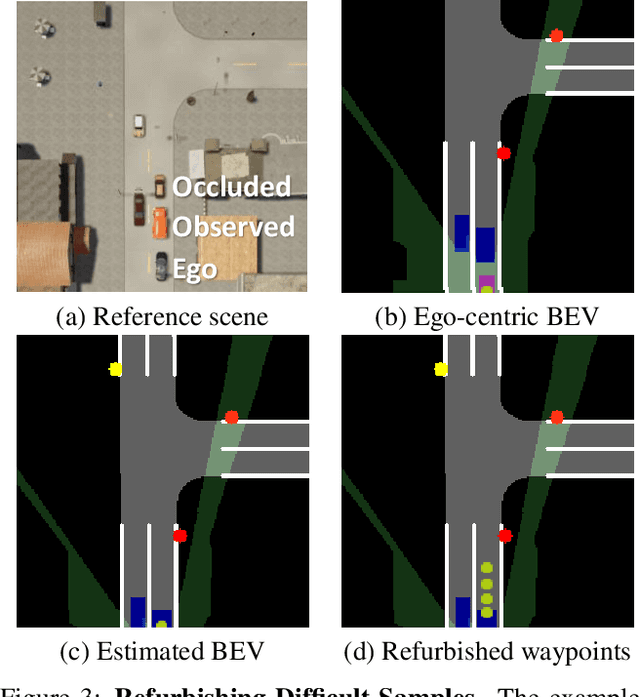
Abstract:When in a new situation or geographical location, human drivers have an extraordinary ability to watch others and learn maneuvers that they themselves may have never performed. In contrast, existing techniques for learning to drive preclude such a possibility as they assume direct access to an instrumented ego-vehicle with fully known observations and expert driver actions. However, such measurements cannot be directly accessed for the non-ego vehicles when learning by watching others. Therefore, in an application where data is regarded as a highly valuable asset, current approaches completely discard the vast portion of the training data that can be potentially obtained through indirect observation of surrounding vehicles. Motivated by this key insight, we propose the Learning by Watching (LbW) framework which enables learning a driving policy without requiring full knowledge of neither the state nor expert actions. To increase its data, i.e., with new perspectives and maneuvers, LbW makes use of the demonstrations of other vehicles in a given scene by (1) transforming the ego-vehicle's observations to their points of view, and (2) inferring their expert actions. Our LbW agent learns more robust driving policies while enabling data-efficient learning, including quick adaptation of the policy to rare and novel scenarios. In particular, LbW drives robustly even with a fraction of available driving data required by existing methods, achieving an average success rate of 92% on the original CARLA benchmark with only 30 minutes of total driving data and 82% with only 10 minutes.
Multiple Object Tracking by Flowing and Fusing
Jan 30, 2020
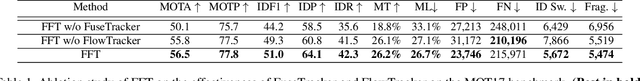
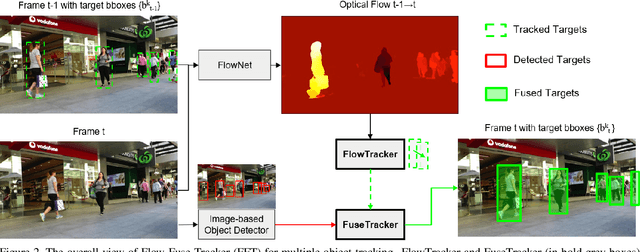
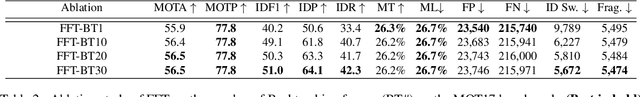
Abstract:Most of Multiple Object Tracking (MOT) approaches compute individual target features for two subtasks: estimating target-wise motions and conducting pair-wise Re-Identification (Re-ID). Because of the indefinite number of targets among video frames, both subtasks are very difficult to scale up efficiently in end-to-end Deep Neural Networks (DNNs). In this paper, we design an end-to-end DNN tracking approach, Flow-Fuse-Tracker (FFT), that addresses the above issues with two efficient techniques: target flowing and target fusing. Specifically, in target flowing, a FlowTracker DNN module learns the indefinite number of target-wise motions jointly from pixel-level optical flows. In target fusing, a FuseTracker DNN module refines and fuses targets proposed by FlowTracker and frame-wise object detection, instead of trusting either of the two inaccurate sources of target proposal. Because FlowTracker can explore complex target-wise motion patterns and FuseTracker can refine and fuse targets from FlowTracker and detectors, our approach can achieve the state-of-the-art results on several MOT benchmarks. As an online MOT approach, FFT produced the top MOTA of 46.3 on the 2DMOT15, 56.5 on the MOT16, and 56.5 on the MOT17 tracking benchmarks, surpassing all the online and offline methods in existing publications.
Frame-wise Motion and Appearance for Real-time Multiple Object Tracking
May 06, 2019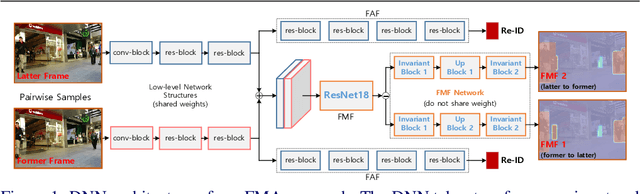
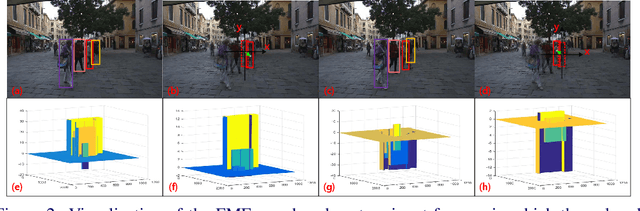

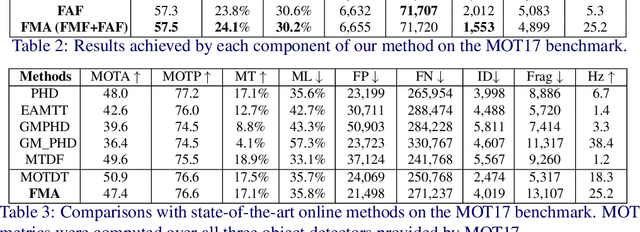
Abstract:The main challenge of Multiple Object Tracking (MOT) is the efficiency in associating indefinite number of objects between video frames. Standard motion estimators used in tracking, e.g., Long Short Term Memory (LSTM), only deal with single object, while Re-IDentification (Re-ID) based approaches exhaustively compare object appearances. Both approaches are computationally costly when they are scaled to a large number of objects, making it very difficult for real-time MOT. To address these problems, we propose a highly efficient Deep Neural Network (DNN) that simultaneously models association among indefinite number of objects. The inference computation of the DNN does not increase with the number of objects. Our approach, Frame-wise Motion and Appearance (FMA), computes the Frame-wise Motion Fields (FMF) between two frames, which leads to very fast and reliable matching among a large number of object bounding boxes. As auxiliary information is used to fix uncertain matches, Frame-wise Appearance Features (FAF) are learned in parallel with FMFs. Extensive experiments on the MOT17 benchmark show that our method achieved real-time MOT with competitive results as the state-of-the-art approaches.
Temporal Unet: Sample Level Human Action Recognition using WiFi
Apr 19, 2019


Abstract:Human doing actions will result in WiFi distortion, which is widely explored for action recognition, such as the elderly fallen detection, hand sign language recognition, and keystroke estimation. As our best survey, past work recognizes human action by categorizing one complete distortion series into one action, which we term as series-level action recognition. In this paper, we introduce a much more fine-grained and challenging action recognition task into WiFi sensing domain, i.e., sample-level action recognition. In this task, every WiFi distortion sample in the whole series should be categorized into one action, which is a critical technique in precise action localization, continuous action segmentation, and real-time action recognition. To achieve WiFi-based sample-level action recognition, we fully analyze approaches in image-based semantic segmentation as well as in video-based frame-level action recognition, then propose a simple yet efficient deep convolutional neural network, i.e., Temporal Unet. Experimental results show that Temporal Unet achieves this novel task well. Codes have been made publicly available at https://github.com/geekfeiw/WiSLAR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge