Xiaoxin Cui
Towards Effective and Sparse Adversarial Attack on Spiking Neural Networks via Breaking Invisible Surrogate Gradients
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Spiking neural networks (SNNs) have shown their competence in handling spatial-temporal event-based data with low energy consumption. Similar to conventional artificial neural networks (ANNs), SNNs are also vulnerable to gradient-based adversarial attacks, wherein gradients are calculated by spatial-temporal back-propagation (STBP) and surrogate gradients (SGs). However, the SGs may be invisible for an inference-only model as they do not influence the inference results, and current gradient-based attacks are ineffective for binary dynamic images captured by the dynamic vision sensor (DVS). While some approaches addressed the issue of invisible SGs through universal SGs, their SGs lack a correlation with the victim model, resulting in sub-optimal performance. Moreover, the imperceptibility of existing SNN-based binary attacks is still insufficient. In this paper, we introduce an innovative potential-dependent surrogate gradient (PDSG) method to establish a robust connection between the SG and the model, thereby enhancing the adaptability of adversarial attacks across various models with invisible SGs. Additionally, we propose the sparse dynamic attack (SDA) to effectively attack binary dynamic images. Utilizing a generation-reduction paradigm, SDA can fully optimize the sparsity of adversarial perturbations. Experimental results demonstrate that our PDSG and SDA outperform state-of-the-art SNN-based attacks across various models and datasets. Specifically, our PDSG achieves 100% attack success rate on ImageNet, and our SDA obtains 82% attack success rate by modifying only 0.24% of the pixels on CIFAR10DVS. The code is available at https://github.com/ryime/PDSG-SDA .
A High Energy-Efficiency Multi-core Neuromorphic Architecture for Deep SNN Training
Dec 10, 2024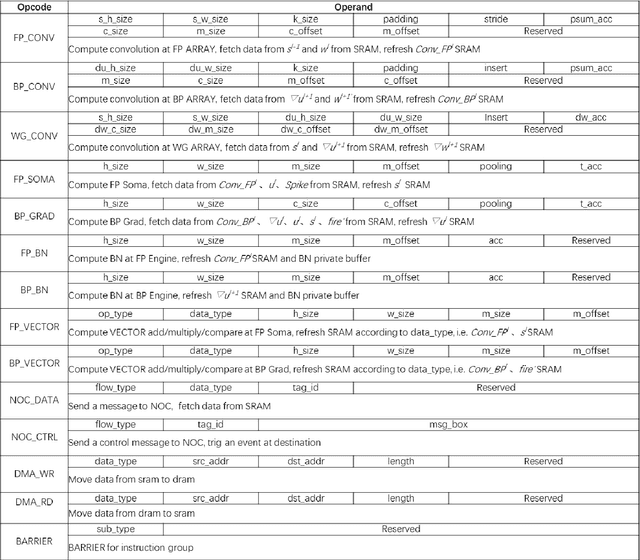
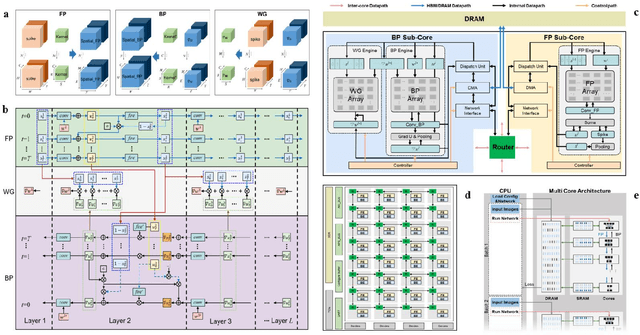
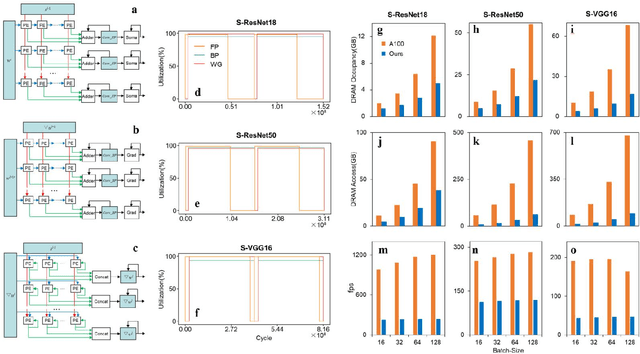
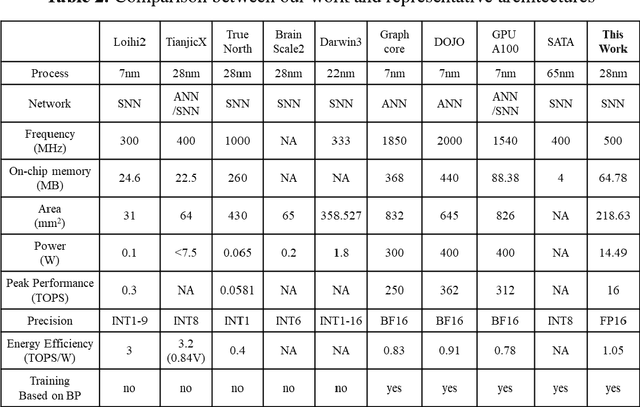
Abstract:There is a growing necessity for edge training to adapt to dynamically changing environment. Neuromorphic computing represents a significant pathway for high-efficiency intelligent computation in energy-constrained edges, but existing neuromorphic architectures lack the ability of directly training spiking neural networks (SNNs) based on backpropagation. We develop a multi-core neuromorphic architecture with Feedforward-Propagation, Back-Propagation, and Weight-Gradient engines in each core, supporting high efficient parallel computing at both the engine and core levels. It combines various data flows and sparse computation optimization by fully leveraging the sparsity in SNN training, obtaining a high energy efficiency of 1.05TFLOPS/W@ FP16 @ 28nm, 55 ~ 85% reduction of DRAM access compared to A100 GPU in SNN trainings, and a 20-core deep SNN training and a 5-worker federated learning on FPGAs. Our study develops the first multi-core neuromorphic architecture supporting the direct SNN training, facilitating the neuromorphic computing in edge-learnable applications.
Towards Lossless ANN-SNN Conversion under Ultra-Low Latency with Dual-Phase Optimization
May 16, 2022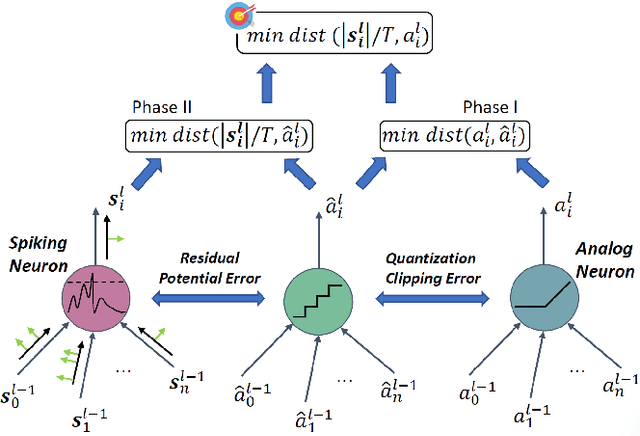
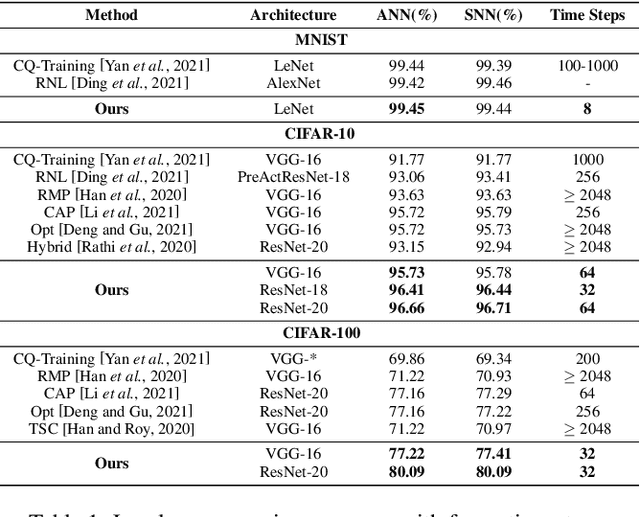
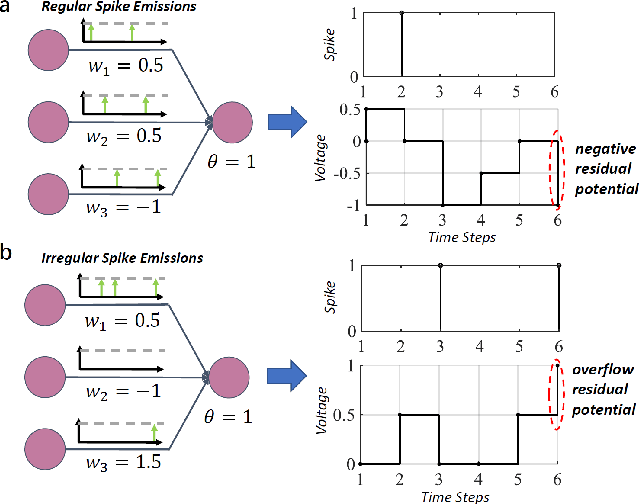
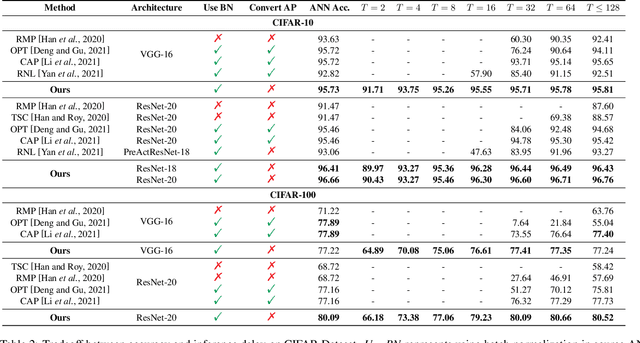
Abstract:Spiking neural network (SNN) operating with asynchronous discrete events shows higher energy efficiency. A popular approach to implement deep SNNs is ANN-SNN conversion combining both efficient training in ANNs and efficient inference in SNNs. However, the previous works mostly required thousands of time steps to achieve lossless conversion. In this paper, we first identify the underlying cause, i.e., misrepresentation of the negative or overflow residual membrane potential in SNNs. Furthermore, we systematically analyze the conversion error between SNNs and ANNs, and then decompose it into three folds: quantization error, clipping error, and residual membrane potential representation error. With such insights, we propose a dual-phase conversion algorithm to minimize those errors. As a result, our model achieves SOTA in both accuracy and accuracy-delay tradeoff with deep architectures (ResNet and VGG net). Specifically, we report SOTA accuracy within 16$\times$ speedup compared with the latest results. Meanwhile, lossless conversion is performed with at least 2$\times$ faster reasoning performance.
Integer-Only Neural Network Quantization Scheme Based on Shift-Batch-Normalization
May 28, 2021
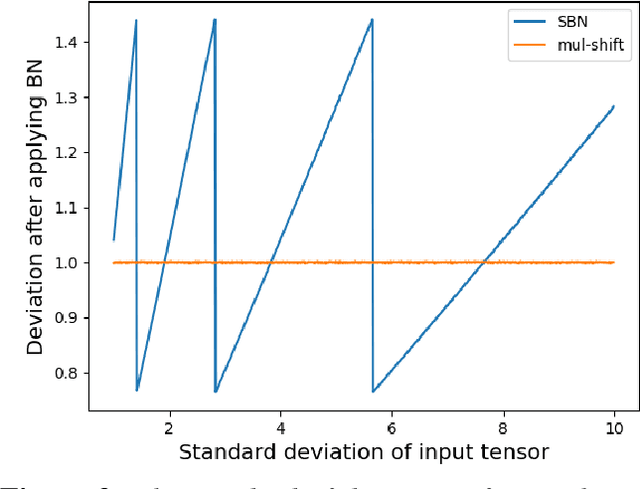
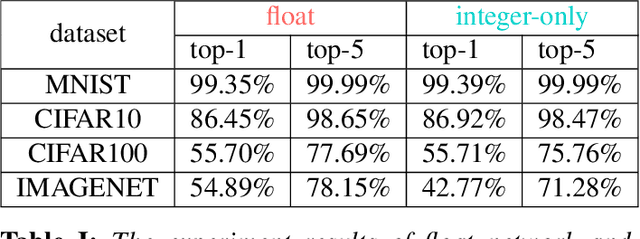
Abstract:Neural networks are very popular in many areas, but great computing complexity makes it hard to run neural networks on devices with limited resources. To address this problem, quantization methods are used to reduce model size and computation cost, making it possible to use neural networks on embedded platforms or mobile devices. In this paper, an integer-only-quantization scheme is introduced. This scheme uses one layer that combines shift-based batch normalization and uniform quantization to implement 4-bit integer-only inference. Without big integer multiplication(which is used in previous integer-only-quantization methods), this scheme can achieve good power and latency efficiency, and is especially suitable to be deployed on co-designed hardware platforms. Tests have proved that this scheme works very well for easy tasks. And for tough tasks, performance loss can be tolerated for its inference efficiency. Our work is available on github: https://github.com/hguq/IntegerNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge