Xiaotong Luo
UniLDiff: Unlocking the Power of Diffusion Priors for All-in-One Image Restoration
Jul 31, 2025



Abstract:All-in-One Image Restoration (AiOIR) has emerged as a promising yet challenging research direction. To address its core challenges, we propose a novel unified image restoration framework based on latent diffusion models (LDMs). Our approach structurally integrates low-quality visual priors into the diffusion process, unlocking the powerful generative capacity of diffusion models for diverse degradations. Specifically, we design a Degradation-Aware Feature Fusion (DAFF) module to enable adaptive handling of diverse degradation types. Furthermore, to mitigate detail loss caused by the high compression and iterative sampling of LDMs, we design a Detail-Aware Expert Module (DAEM) in the decoder to enhance texture and fine-structure recovery. Extensive experiments across multi-task and mixed degradation settings demonstrate that our method consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance, highlighting the practical potential of diffusion priors for unified image restoration. Our code will be released.
Data-free Distillation with Degradation-prompt Diffusion for Multi-weather Image Restoration
Sep 05, 2024



Abstract:Multi-weather image restoration has witnessed incredible progress, while the increasing model capacity and expensive data acquisition impair its applications in memory-limited devices. Data-free distillation provides an alternative for allowing to learn a lightweight student model from a pre-trained teacher model without relying on the original training data. The existing data-free learning methods mainly optimize the models with the pseudo data generated by GANs or the real data collected from the Internet. However, they inevitably suffer from the problems of unstable training or domain shifts with the original data. In this paper, we propose a novel Data-free Distillation with Degradation-prompt Diffusion framework for multi-weather Image Restoration (D4IR). It replaces GANs with pre-trained diffusion models to avoid model collapse and incorporates a degradation-aware prompt adapter to facilitate content-driven conditional diffusion for generating domain-related images. Specifically, a contrast-based degradation prompt adapter is firstly designed to capture degradation-aware prompts from web-collected degraded images. Then, the collected unpaired clean images are perturbed to latent features of stable diffusion, and conditioned with the degradation-aware prompts to synthesize new domain-related degraded images for knowledge distillation. Experiments illustrate that our proposal achieves comparable performance to the model distilled with original training data, and is even superior to other mainstream unsupervised methods.
Anomaly Multi-classification in Industrial Scenarios: Transferring Few-shot Learning to a New Task
Jun 09, 2024



Abstract:In industrial scenarios, it is crucial not only to identify anomalous items but also to classify the type of anomaly. However, research on anomaly multi-classification remains largely unexplored. This paper proposes a novel and valuable research task called anomaly multi-classification. Given the challenges in applying few-shot learning to this task, due to limited training data and unique characteristics of anomaly images, we introduce a baseline model that combines RelationNet and PatchCore. We propose a data generation method that creates pseudo classes and a corresponding proxy task, aiming to bridge the gap in transferring few-shot learning to industrial scenarios. Furthermore, we utilize contrastive learning to improve the vanilla baseline, achieving much better performance than directly fine-tune a ResNet. Experiments conducted on MvTec AD and MvTec3D AD demonstrate that our approach shows superior performance in this novel task.
AIM 2020 Challenge on Efficient Super-Resolution: Methods and Results
Sep 15, 2020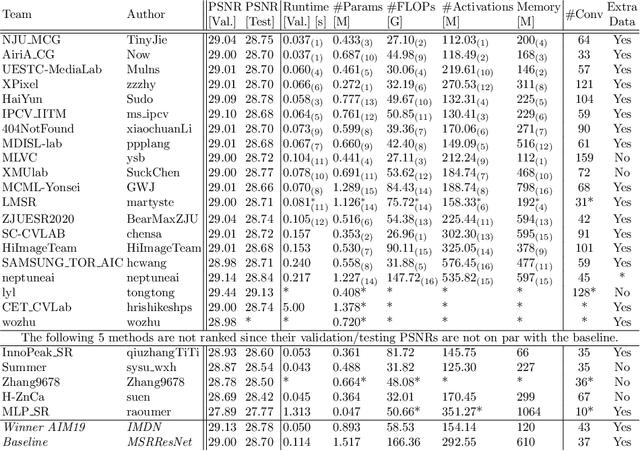
Abstract:This paper reviews the AIM 2020 challenge on efficient single image super-resolution with focus on the proposed solutions and results. The challenge task was to super-resolve an input image with a magnification factor x4 based on a set of prior examples of low and corresponding high resolution images. The goal is to devise a network that reduces one or several aspects such as runtime, parameter count, FLOPs, activations, and memory consumption while at least maintaining PSNR of MSRResNet. The track had 150 registered participants, and 25 teams submitted the final results. They gauge the state-of-the-art in efficient single image super-resolution.
NTIRE 2020 Challenge on Image Demoireing: Methods and Results
May 06, 2020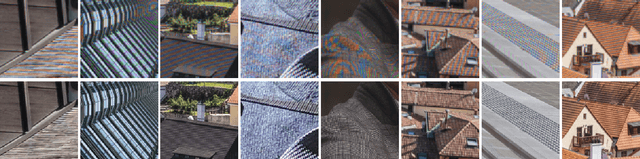
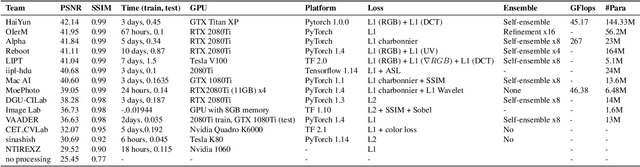
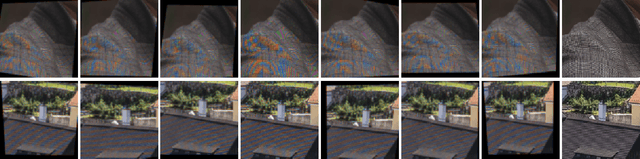
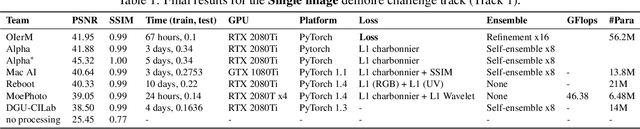
Abstract:This paper reviews the Challenge on Image Demoireing that was part of the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement (NTIRE) workshop, held in conjunction with CVPR 2020. Demoireing is a difficult task of removing moire patterns from an image to reveal an underlying clean image. The challenge was divided into two tracks. Track 1 targeted the single image demoireing problem, which seeks to remove moire patterns from a single image. Track 2 focused on the burst demoireing problem, where a set of degraded moire images of the same scene were provided as input, with the goal of producing a single demoired image as output. The methods were ranked in terms of their fidelity, measured using the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) between the ground truth clean images and the restored images produced by the participants' methods. The tracks had 142 and 99 registered participants, respectively, with a total of 14 and 6 submissions in the final testing stage. The entries span the current state-of-the-art in image and burst image demoireing problems.
Bi-GANs-ST for Perceptual Image Super-resolution
Nov 01, 2018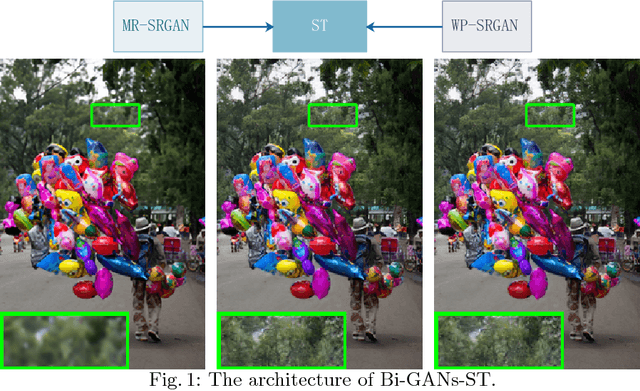
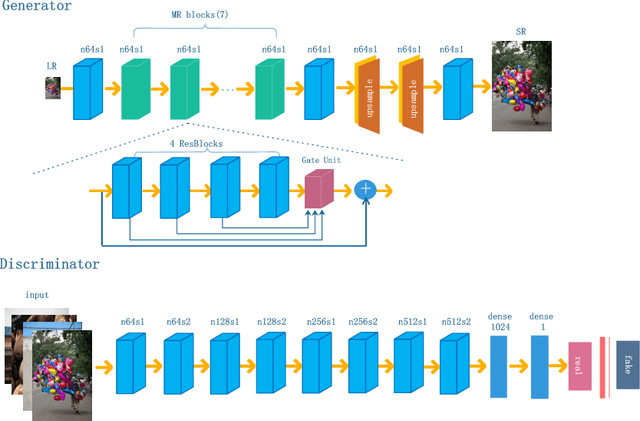


Abstract:Image quality measurement is a critical problem for image super-resolution (SR) algorithms. Usually, they are evaluated by some well-known objective metrics, e.g., PSNR and SSIM, but these indices cannot provide suitable results in accordance with the perception of human being. Recently, a more reasonable perception measurement has been proposed in [1], which is also adopted by the PIRM-SR 2018 challenge. In this paper, motivated by [1], we aim to generate a high-quality SR result which balances between the two indices, i.e., the perception index and root-mean-square error (RMSE). To do so, we design a new deep SR framework, dubbed Bi-GANs-ST, by integrating two complementary generative adversarial networks (GAN) branches. One is memory residual SRGAN (MR-SRGAN), which emphasizes on improving the objective performance, such as reducing the RMSE. The other is weight perception SRGAN (WP-SRGAN), which obtains the result that favors better subjective perception via a two-stage adversarial training mechanism. Then, to produce final result with excellent perception scores and RMSE, we use soft-thresholding method to merge the results generated by the two GANs. Our method performs well on the perceptual image super-resolution task of the PIRM 2018 challenge. Experimental results on five benchmarks show that our proposal achieves highly competent performance compared with other state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge