Xiangen Hu
AI-Augmented LLMs Achieve Therapist-Level Responses in Motivational Interviewing
May 23, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 show potential for scaling motivational interviewing (MI) in addiction care, but require systematic evaluation of therapeutic capabilities. We present a computational framework assessing user-perceived quality (UPQ) through expected and unexpected MI behaviors. Analyzing human therapist and GPT-4 MI sessions via human-AI collaboration, we developed predictive models integrating deep learning and explainable AI to identify 17 MI-consistent (MICO) and MI-inconsistent (MIIN) behavioral metrics. A customized chain-of-thought prompt improved GPT-4's MI performance, reducing inappropriate advice while enhancing reflections and empathy. Although GPT-4 remained marginally inferior to therapists overall, it demonstrated superior advice management capabilities. The model achieved measurable quality improvements through prompt engineering, yet showed limitations in addressing complex emotional nuances. This framework establishes a pathway for optimizing LLM-based therapeutic tools through targeted behavioral metric analysis and human-AI co-evaluation. Findings highlight both the scalability potential and current constraints of LLMs in clinical communication applications.
Generative AI in Education: From Foundational Insights to the Socratic Playground for Learning
Jan 12, 2025



Abstract:This paper explores the synergy between human cognition and Large Language Models (LLMs), highlighting how generative AI can drive personalized learning at scale. We discuss parallels between LLMs and human cognition, emphasizing both the promise and new perspectives on integrating AI systems into education. After examining challenges in aligning technology with pedagogy, we review AutoTutor-one of the earliest Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS)-and detail its successes, limitations, and unfulfilled aspirations. We then introduce the Socratic Playground, a next-generation ITS that uses advanced transformer-based models to overcome AutoTutor's constraints and provide personalized, adaptive tutoring. To illustrate its evolving capabilities, we present a JSON-based tutoring prompt that systematically guides learner reflection while tracking misconceptions. Throughout, we underscore the importance of placing pedagogy at the forefront, ensuring that technology's power is harnessed to enhance teaching and learning rather than overshadow it.
Generative Adversarial Networks for Imputing Sparse Learning Performance
Jul 26, 2024



Abstract:Learning performance data, such as correct or incorrect responses to questions in Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITSs) is crucial for tracking and assessing the learners' progress and mastery of knowledge. However, the issue of data sparsity, characterized by unexplored questions and missing attempts, hampers accurate assessment and the provision of tailored, personalized instruction within ITSs. This paper proposes using the Generative Adversarial Imputation Networks (GAIN) framework to impute sparse learning performance data, reconstructed into a three-dimensional (3D) tensor representation across the dimensions of learners, questions and attempts. Our customized GAIN-based method computational process imputes sparse data in a 3D tensor space, significantly enhanced by convolutional neural networks for its input and output layers. This adaptation also includes the use of a least squares loss function for optimization and aligns the shapes of the input and output with the dimensions of the questions-attempts matrices along the learners' dimension. Through extensive experiments on six datasets from various ITSs, including AutoTutor, ASSISTments and MATHia, we demonstrate that the GAIN approach generally outperforms existing methods such as tensor factorization and other generative adversarial network (GAN) based approaches in terms of imputation accuracy. This finding enhances comprehensive learning data modeling and analytics in AI-based education.
SPL: A Socratic Playground for Learning Powered by Large Language Mode
Jun 20, 2024



Abstract:Dialogue-based Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITSs) have significantly advanced adaptive and personalized learning by automating sophisticated human tutoring strategies within interactive dialogues. However, replicating the nuanced patterns of expert human communication remains a challenge in Natural Language Processing (NLP). Recent advancements in NLP, particularly Large Language Models (LLMs) such as OpenAI's GPT-4, offer promising solutions by providing human-like and context-aware responses based on extensive pre-trained knowledge. Motivated by the effectiveness of LLMs in various educational tasks (e.g., content creation and summarization, problem-solving, and automated feedback provision), our study introduces the Socratic Playground for Learning (SPL), a dialogue-based ITS powered by the GPT-4 model, which employs the Socratic teaching method to foster critical thinking among learners. Through extensive prompt engineering, SPL can generate specific learning scenarios and facilitates efficient multi-turn tutoring dialogues. The SPL system aims to enhance personalized and adaptive learning experiences tailored to individual needs, specifically focusing on improving critical thinking skills. Our pilot experimental results from essay writing tasks demonstrate SPL has the potential to improve tutoring interactions and further enhance dialogue-based ITS functionalities. Our study, exemplified by SPL, demonstrates how LLMs enhance dialogue-based ITSs and expand the accessibility and efficacy of educational technologies.
3DG: A Framework for Using Generative AI for Handling Sparse Learner Performance Data From Intelligent Tutoring Systems
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:Learning performance data (e.g., quiz scores and attempts) is significant for understanding learner engagement and knowledge mastery level. However, the learning performance data collected from Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITSs) often suffers from sparsity, impacting the accuracy of learner modeling and knowledge assessments. To address this, we introduce the 3DG framework (3-Dimensional tensor for Densification and Generation), a novel approach combining tensor factorization with advanced generative models, including Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) and Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), for enhanced data imputation and augmentation. The framework operates by first representing the data as a three-dimensional tensor, capturing dimensions of learners, questions, and attempts. It then densifies the data through tensor factorization and augments it using Generative AI models, tailored to individual learning patterns identified via clustering. Applied to data from an AutoTutor lesson by the Center for the Study of Adult Literacy (CSAL), the 3DG framework effectively generated scalable, personalized simulations of learning performance. Comparative analysis revealed GAN's superior reliability over GPT-4 in this context, underscoring its potential in addressing data sparsity challenges in ITSs and contributing to the advancement of personalized educational technology.
NEOLAF, an LLM-powered neural-symbolic cognitive architecture
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:This paper presents the Never Ending Open Learning Adaptive Framework (NEOLAF), an integrated neural-symbolic cognitive architecture that models and constructs intelligent agents. The NEOLAF framework is a superior approach to constructing intelligent agents than both the pure connectionist and pure symbolic approaches due to its explainability, incremental learning, efficiency, collaborative and distributed learning, human-in-the-loop enablement, and self-improvement. The paper further presents a compelling experiment where a NEOLAF agent, built as a problem-solving agent, is fed with complex math problems from the open-source MATH dataset. The results demonstrate NEOLAF's superior learning capability and its potential to revolutionize the field of cognitive architectures and self-improving adaptive instructional systems.
A Design of A Simple Yet Effective Exercise Recommendation System in K-12 Online Learning
Jun 23, 2022
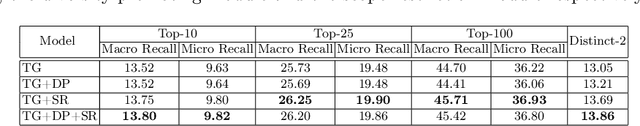
Abstract:We propose a simple but effective method to recommend exercises with high quality and diversity for students. Our method is made up of three key components: (1) candidate generation module; (2) diversity-promoting module; and (3) scope restriction module. The proposed method improves the overall recommendation performance in terms of recall, and increases the diversity of the recommended candidates by 0.81\% compared to the baselines.
An Empirical Study on Academic Commentary and Its Implications on Reading and Writing
Feb 12, 2016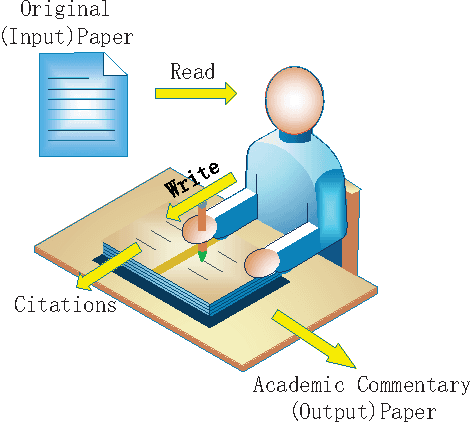
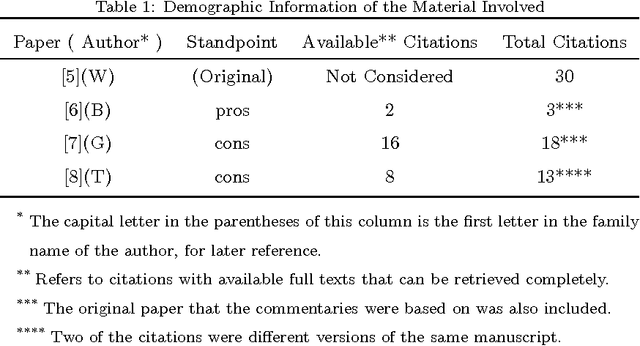
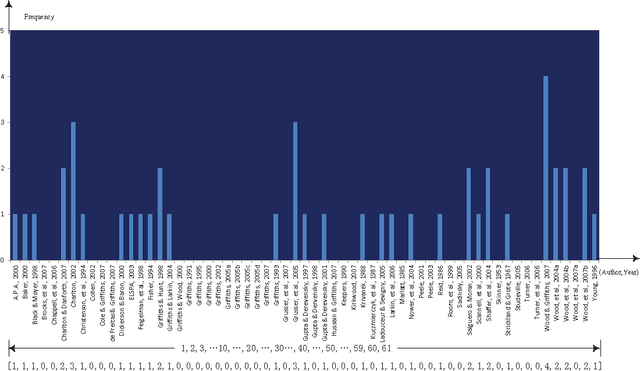

Abstract:The relationship between reading and writing (RRW) is one of the major themes in learning science. One of its obstacles is that it is difficult to define or measure the latent background knowledge of the individual. However, in an academic research setting, scholars are required to explicitly list their background knowledge in the citation sections of their manuscripts. This unique opportunity was taken advantage of to observe RRW, especially in the published academic commentary scenario. RRW was visualized under a proposed topic process model by using a state of the art version of latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA). The empirical study showed that the academic commentary is modulated both by its target paper and the author's background knowledge. Although this conclusion was obtained in a unique environment, we suggest its implications can also shed light on other similar interesting areas, such as dialog and conversation, group discussion, and social media.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge