An Empirical Study on Academic Commentary and Its Implications on Reading and Writing
Paper and Code
Feb 12, 2016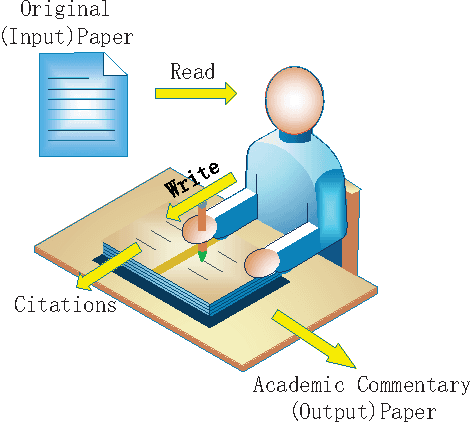
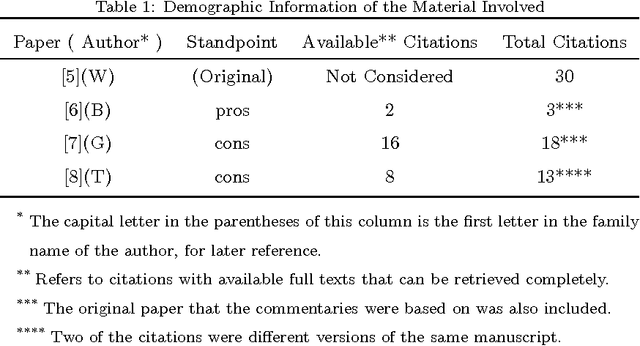
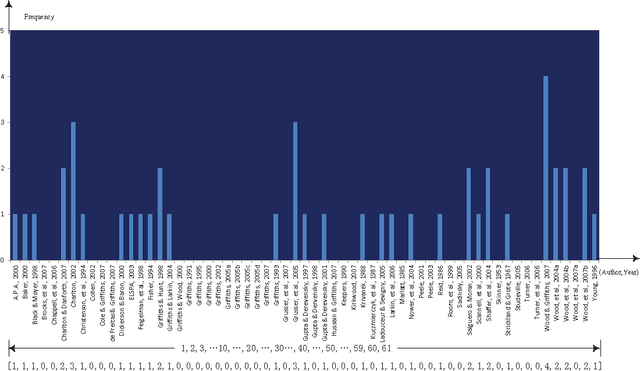

The relationship between reading and writing (RRW) is one of the major themes in learning science. One of its obstacles is that it is difficult to define or measure the latent background knowledge of the individual. However, in an academic research setting, scholars are required to explicitly list their background knowledge in the citation sections of their manuscripts. This unique opportunity was taken advantage of to observe RRW, especially in the published academic commentary scenario. RRW was visualized under a proposed topic process model by using a state of the art version of latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA). The empirical study showed that the academic commentary is modulated both by its target paper and the author's background knowledge. Although this conclusion was obtained in a unique environment, we suggest its implications can also shed light on other similar interesting areas, such as dialog and conversation, group discussion, and social media.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge