Richard Tong
Generative AI in Education: From Foundational Insights to the Socratic Playground for Learning
Jan 12, 2025



Abstract:This paper explores the synergy between human cognition and Large Language Models (LLMs), highlighting how generative AI can drive personalized learning at scale. We discuss parallels between LLMs and human cognition, emphasizing both the promise and new perspectives on integrating AI systems into education. After examining challenges in aligning technology with pedagogy, we review AutoTutor-one of the earliest Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS)-and detail its successes, limitations, and unfulfilled aspirations. We then introduce the Socratic Playground, a next-generation ITS that uses advanced transformer-based models to overcome AutoTutor's constraints and provide personalized, adaptive tutoring. To illustrate its evolving capabilities, we present a JSON-based tutoring prompt that systematically guides learner reflection while tracking misconceptions. Throughout, we underscore the importance of placing pedagogy at the forefront, ensuring that technology's power is harnessed to enhance teaching and learning rather than overshadow it.
Developing and Deploying Industry Standards for Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED): Challenges, Strategies, and Future Directions
Mar 25, 2024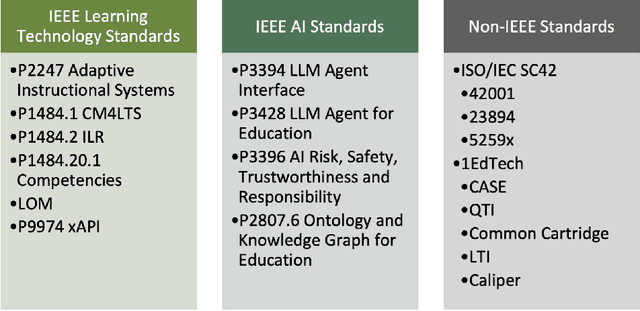
Abstract:The adoption of Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED) holds the promise of revolutionizing educational practices by offering personalized learning experiences, automating administrative and pedagogical tasks, and reducing the cost of content creation. However, the lack of standardized practices in the development and deployment of AIED solutions has led to fragmented ecosystems, which presents challenges in interoperability, scalability, and ethical governance. This article aims to address the critical need to develop and implement industry standards in AIED, offering a comprehensive analysis of the current landscape, challenges, and strategic approaches to overcome these obstacles. We begin by examining the various applications of AIED in various educational settings and identify key areas lacking in standardization, including system interoperability, ontology mapping, data integration, evaluation, and ethical governance. Then, we propose a multi-tiered framework for establishing robust industry standards for AIED. In addition, we discuss methodologies for the iterative development and deployment of standards, incorporating feedback loops from real-world applications to refine and adapt standards over time. The paper also highlights the role of emerging technologies and pedagogical theories in shaping future standards for AIED. Finally, we outline a strategic roadmap for stakeholders to implement these standards, fostering a cohesive and ethical AIED ecosystem. By establishing comprehensive industry standards, such as those by IEEE Artificial Intelligence Standards Committee (AISC) and International Organization for Standardization (ISO), we can accelerate and scale AIED solutions to improve educational outcomes, ensuring that technological advances align with the principles of inclusivity, fairness, and educational excellence.
MUTLA: A Large-Scale Dataset for Multimodal Teaching and Learning Analytics
Oct 05, 2019


Abstract:Automatic analysis of teacher and student interactions could be very important to improve the quality of teaching and student engagement. However, despite some recent progress in utilizing multimodal data for teaching and learning analytics, a thorough analysis of a rich multimodal dataset coming for a complex real learning environment has yet to be done. To bridge this gap, we present a large-scale MUlti-modal Teaching and Learning Analytics (MUTLA) dataset. This dataset includes time-synchronized multimodal data records of students (learning logs, videos, EEG brainwaves) as they work in various subjects from Squirrel AI Learning System (SAIL) to solve problems of varying difficulty levels. The dataset resources include user records from the learner records store of SAIL, brainwave data collected by EEG headset devices, and video data captured by web cameras while students worked in the SAIL products. Our hope is that by analyzing real-world student learning activities, facial expressions, and brainwave patterns, researchers can better predict engagement, which can then be used to improve adaptive learning selection and student learning outcomes. An additional goal is to provide a dataset gathered from real-world educational activities versus those from controlled lab environments to benefit the educational learning community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge