Victor Storchan
On the Societal Impact of Open Foundation Models
Feb 27, 2024

Abstract:Foundation models are powerful technologies: how they are released publicly directly shapes their societal impact. In this position paper, we focus on open foundation models, defined here as those with broadly available model weights (e.g. Llama 2, Stable Diffusion XL). We identify five distinctive properties (e.g. greater customizability, poor monitoring) of open foundation models that lead to both their benefits and risks. Open foundation models present significant benefits, with some caveats, that span innovation, competition, the distribution of decision-making power, and transparency. To understand their risks of misuse, we design a risk assessment framework for analyzing their marginal risk. Across several misuse vectors (e.g. cyberattacks, bioweapons), we find that current research is insufficient to effectively characterize the marginal risk of open foundation models relative to pre-existing technologies. The framework helps explain why the marginal risk is low in some cases, clarifies disagreements about misuse risks by revealing that past work has focused on different subsets of the framework with different assumptions, and articulates a way forward for more constructive debate. Overall, our work helps support a more grounded assessment of the societal impact of open foundation models by outlining what research is needed to empirically validate their theoretical benefits and risks.
Transductive Learning for Textual Few-Shot Classification in API-based Embedding Models
Oct 21, 2023



Abstract:Proprietary and closed APIs are becoming increasingly common to process natural language, and are impacting the practical applications of natural language processing, including few-shot classification. Few-shot classification involves training a model to perform a new classification task with a handful of labeled data. This paper presents three contributions. First, we introduce a scenario where the embedding of a pre-trained model is served through a gated API with compute-cost and data-privacy constraints. Second, we propose a transductive inference, a learning paradigm that has been overlooked by the NLP community. Transductive inference, unlike traditional inductive learning, leverages the statistics of unlabeled data. We also introduce a new parameter-free transductive regularizer based on the Fisher-Rao loss, which can be used on top of the gated API embeddings. This method fully utilizes unlabeled data, does not share any label with the third-party API provider and could serve as a baseline for future research. Third, we propose an improved experimental setting and compile a benchmark of eight datasets involving multiclass classification in four different languages, with up to 151 classes. We evaluate our methods using eight backbone models, along with an episodic evaluation over 1,000 episodes, which demonstrate the superiority of transductive inference over the standard inductive setting.
On the Current and Emerging Challenges of Developing Fair and Ethical AI Solutions in Financial Services
Nov 02, 2021Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) continues to find more numerous and more critical applications in the financial services industry, giving rise to fair and ethical AI as an industry-wide objective. While many ethical principles and guidelines have been published in recent years, they fall short of addressing the serious challenges that model developers face when building ethical AI solutions. We survey the practical and overarching issues surrounding model development, from design and implementation complexities, to the shortage of tools, and the lack of organizational constructs. We show how practical considerations reveal the gaps between high-level principles and concrete, deployed AI applications, with the aim of starting industry-wide conversations toward solution approaches.
* 10 pages; expanded from conference version
Beyond Fairness Metrics: Roadblocks and Challenges for Ethical AI in Practice
Aug 11, 2021Abstract:We review practical challenges in building and deploying ethical AI at the scale of contemporary industrial and societal uses. Apart from the purely technical concerns that are the usual focus of academic research, the operational challenges of inconsistent regulatory pressures, conflicting business goals, data quality issues, development processes, systems integration practices, and the scale of deployment all conspire to create new ethical risks. Such ethical concerns arising from these practical considerations are not adequately addressed by existing research results. We argue that a holistic consideration of ethics in the development and deployment of AI systems is necessary for building ethical AI in practice, and exhort researchers to consider the full operational contexts of AI systems when assessing ethical risks.
Seven challenges for harmonizing explainability requirements
Aug 11, 2021Abstract:Regulators have signalled an interest in adopting explainable AI(XAI) techniques to handle the diverse needs for model governance, operational servicing, and compliance in the financial services industry. In this short overview, we review the recent technical literature in XAI and argue that based on our current understanding of the field, the use of XAI techniques in practice necessitate a highly contextualized approach considering the specific needs of stakeholders for particular business applications.
Learning who is in the market from time series: market participant discovery through adversarial calibration of multi-agent simulators
Aug 02, 2021
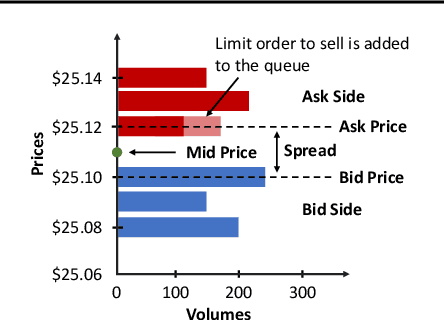
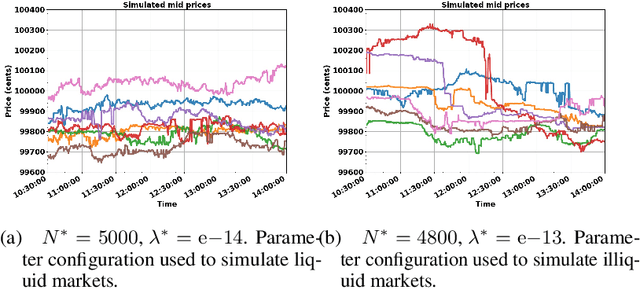
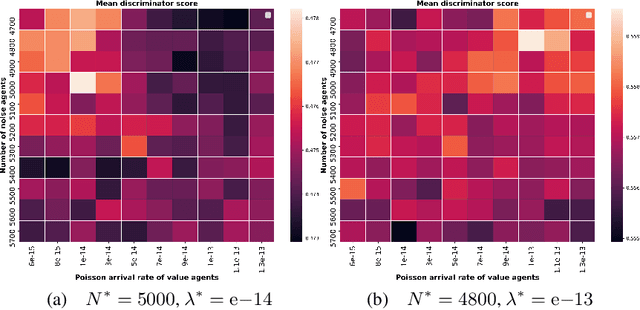
Abstract:In electronic trading markets often only the price or volume time series, that result from interaction of multiple market participants, are directly observable. In order to test trading strategies before deploying them to real-time trading, multi-agent market environments calibrated so that the time series that result from interaction of simulated agents resemble historical are often used. To ensure adequate testing, one must test trading strategies in a variety of market scenarios -- which includes both scenarios that represent ordinary market days as well as stressed markets (most recently observed due to the beginning of COVID pandemic). In this paper, we address the problem of multi-agent simulator parameter calibration to allow simulator capture characteristics of different market regimes. We propose a novel two-step method to train a discriminator that is able to distinguish between "real" and "fake" price and volume time series as a part of GAN with self-attention, and then utilize it within an optimization framework to tune parameters of a simulator model with known agent archetypes to represent a market scenario. We conclude with experimental results that demonstrate effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge