Tri Kurniawan Wijaya
Efficient Large-Scale Cross-Domain Sequential Recommendation with Dynamic State Representations
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Recently, autoregressive recommendation models (ARMs), such as Meta's HSTU model, have emerged as a major breakthrough over traditional Deep Learning Recommendation Models (DLRMs), exhibiting the highly sought-after scaling law behaviour. However, when applied to multi-domain scenarios, the transformer architecture's attention maps become a computational bottleneck, as they attend to all items across every domain. To tackle this challenge, systems must efficiently balance inter and intra-domain knowledge transfer. In this work, we introduce a novel approach for scalable multi-domain recommendation systems by replacing full inter-domain attention with two innovative mechanisms: 1) Transition-Aware Positional Embeddings (TAPE): We propose novel positional embeddings that account for domain-transition specific information. This allows attention to be focused solely on intra-domain items, effectively reducing the unnecessary computational cost associated with attending to irrelevant domains. 2) Dynamic Domain State Representation (DDSR): We introduce a dynamic state representation for each domain, which is stored and accessed during subsequent token predictions. This enables the efficient transfer of relevant domain information without relying on full attention maps. Our method offers a scalable solution to the challenges posed by large-scale, multi-domain recommendation systems and demonstrates significant improvements in retrieval tasks by separately modelling and combining inter- and intra-domain representations.
DS4RS: Community-Driven and Explainable Dataset Search Engine for Recommender System Research
Aug 13, 2025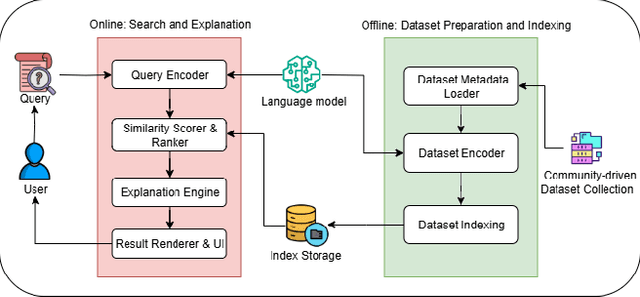
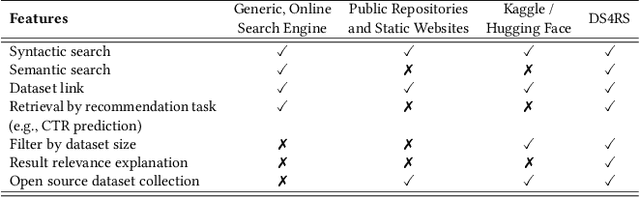
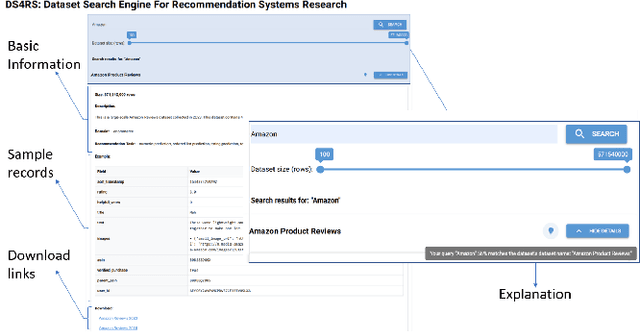
Abstract:Accessing suitable datasets is critical for research and development in recommender systems. However, finding datasets that match specific recommendation task or domains remains a challenge due to scattered sources and inconsistent metadata. To address this gap, we propose a community-driven and explainable dataset search engine tailored for recommender system research. Our system supports semantic search across multiple dataset attributes, such as dataset names, descriptions, and recommendation domain, and provides explanations of search relevance to enhance transparency. The system encourages community participation by allowing users to contribute standardized dataset metadata in public repository. By improving dataset discoverability and search interpretability, the system facilitates more efficient research reproduction. The platform is publicly available at: https://ds4rs.com.
Dataset-Agnostic Recommender Systems
Jan 13, 2025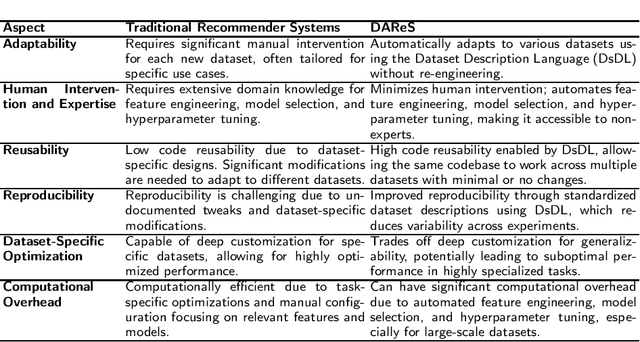
Abstract:[This is a position paper and does not contain any empirical or theoretical results] Recommender systems have become a cornerstone of personalized user experiences, yet their development typically involves significant manual intervention, including dataset-specific feature engineering, hyperparameter tuning, and configuration. To this end, we introduce a novel paradigm: Dataset-Agnostic Recommender Systems (DAReS) that aims to enable a single codebase to autonomously adapt to various datasets without the need for fine-tuning, for a given recommender system task. Central to this approach is the Dataset Description Language (DsDL), a structured format that provides metadata about the dataset's features and labels, and allow the system to understand dataset's characteristics, allowing it to autonomously manage processes like feature selection, missing values imputation, noise removal, and hyperparameter optimization. By reducing the need for domain-specific expertise and manual adjustments, DAReS offers a more efficient and scalable solution for building recommender systems across diverse application domains. It addresses critical challenges in the field, such as reusability, reproducibility, and accessibility for non-expert users or entry-level researchers.
Rs4rs: Semantically Find Recent Publications from Top Recommendation System-Related Venues
Sep 11, 2024
Abstract:Rs4rs is a web application designed to perform semantic search on recent papers from top conferences and journals related to Recommender Systems. Current scholarly search engine tools like Google Scholar, Semantic Scholar, and ResearchGate often yield broad results that fail to target the most relevant high-quality publications. Moreover, manually visiting individual conference and journal websites is a time-consuming process that primarily supports only syntactic searches. Rs4rs addresses these issues by providing a user-friendly platform where researchers can input their topic of interest and receive a list of recent, relevant papers from top Recommender Systems venues. Utilizing semantic search techniques, Rs4rs ensures that the search results are not only precise and relevant but also comprehensive, capturing papers regardless of variations in wording. This tool significantly enhances research efficiency and accuracy, thereby benefitting the research community and public by facilitating access to high-quality, pertinent academic resources in the field of Recommender Systems. Rs4rs is available at https://rs4rs.com.
RBoard: A Unified Platform for Reproducible and Reusable Recommender System Benchmarks
Sep 10, 2024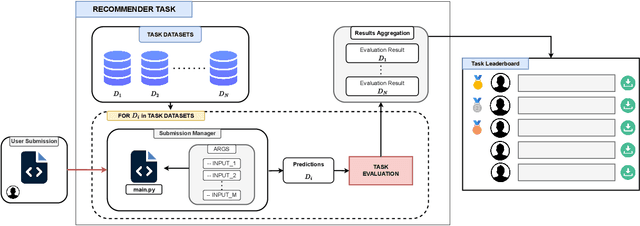
Abstract:Recommender systems research lacks standardized benchmarks for reproducibility and algorithm comparisons. We introduce RBoard, a novel framework addressing these challenges by providing a comprehensive platform for benchmarking diverse recommendation tasks, including CTR prediction, Top-N recommendation, and others. RBoard's primary objective is to enable fully reproducible and reusable experiments across these scenarios. The framework evaluates algorithms across multiple datasets within each task, aggregating results for a holistic performance assessment. It implements standardized evaluation protocols, ensuring consistency and comparability. To facilitate reproducibility, all user-provided code can be easily downloaded and executed, allowing researchers to reliably replicate studies and build upon previous work. By offering a unified platform for rigorous, reproducible evaluation across various recommendation scenarios, RBoard aims to accelerate progress in the field and establish a new standard for recommender systems benchmarking in both academia and industry. The platform is available at https://rboard.org and the demo video can be found at https://bit.ly/rboard-demo.
SPICED: News Similarity Detection Dataset with Multiple Topics and Complexity Levels
Sep 21, 2023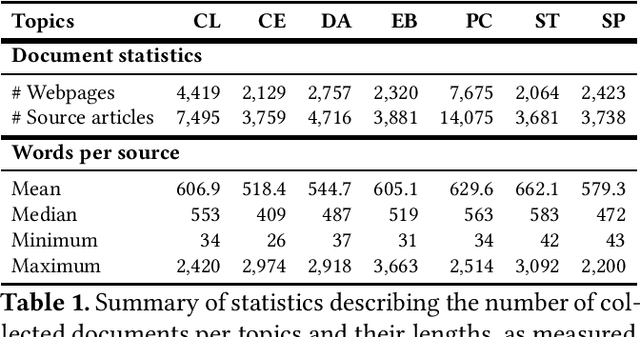
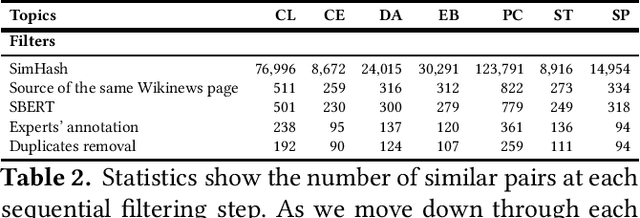
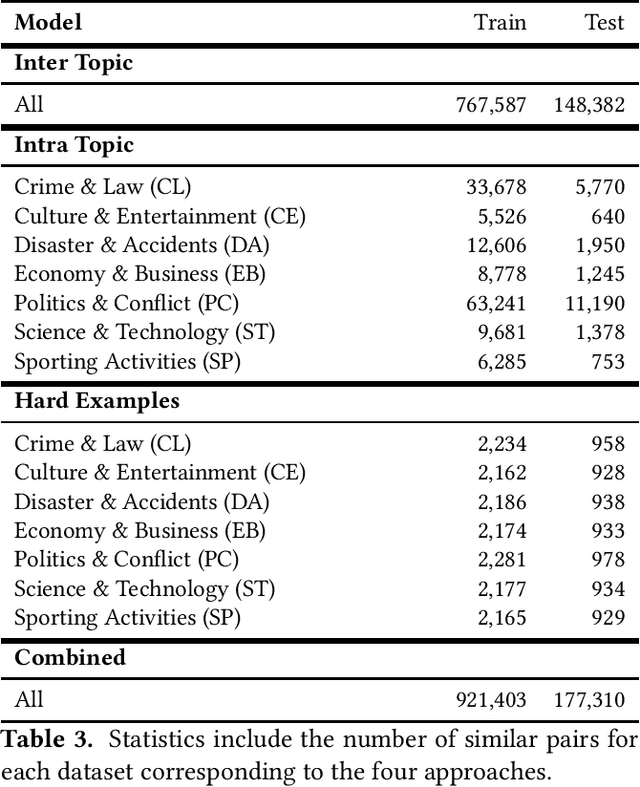
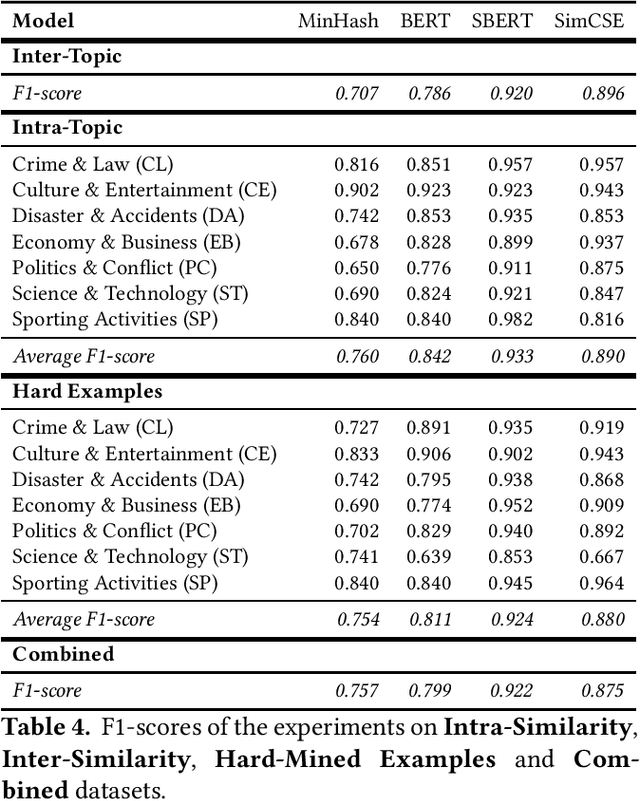
Abstract:Nowadays, the use of intelligent systems to detect redundant information in news articles has become especially prevalent with the proliferation of news media outlets in order to enhance user experience. However, the heterogeneous nature of news can lead to spurious findings in these systems: Simple heuristics such as whether a pair of news are both about politics can provide strong but deceptive downstream performance. Segmenting news similarity datasets into topics improves the training of these models by forcing them to learn how to distinguish salient characteristics under more narrow domains. However, this requires the existence of topic-specific datasets, which are currently lacking. In this article, we propose a new dataset of similar news, SPICED, which includes seven topics: Crime & Law, Culture & Entertainment, Disasters & Accidents, Economy & Business, Politics & Conflicts, Science & Technology, and Sports. Futhermore, we present four distinct approaches for generating news pairs, which are used in the creation of datasets specifically designed for news similarity detection task. We benchmarked the created datasets using MinHash, BERT, SBERT, and SimCSE models.
FedFNN: Faster Training Convergence Through Update Predictions in Federated Recommender Systems
Sep 14, 2023



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a key approach for distributed machine learning, enhancing online personalization while ensuring user data privacy. Instead of sending private data to a central server as in traditional approaches, FL decentralizes computations: devices train locally and share updates with a global server. A primary challenge in this setting is achieving fast and accurate model training - vital for recommendation systems where delays can compromise user engagement. This paper introduces FedFNN, an algorithm that accelerates decentralized model training. In FL, only a subset of users are involved in each training epoch. FedFNN employs supervised learning to predict weight updates from unsampled users, using updates from the sampled set. Our evaluations, using real and synthetic data, show: 1. FedFNN achieves training speeds 5x faster than leading methods, maintaining or improving accuracy; 2. the algorithm's performance is consistent regardless of client cluster variations; 3. FedFNN outperforms other methods in scenarios with limited client availability, converging more quickly.
MM-GEF: Multi-modal representation meet collaborative filtering
Aug 14, 2023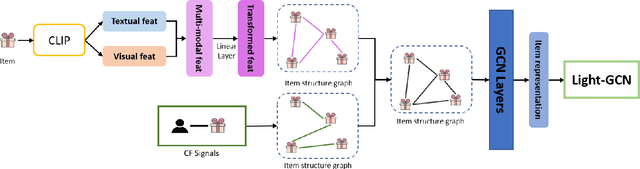
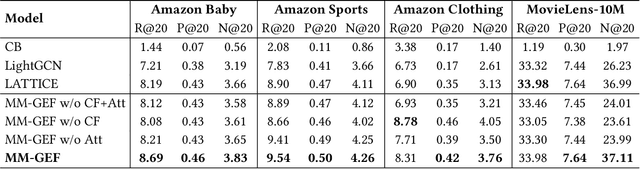
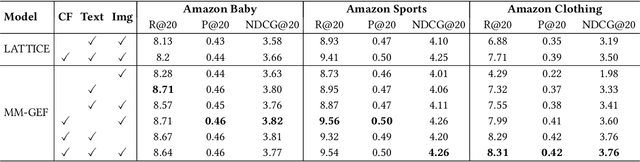
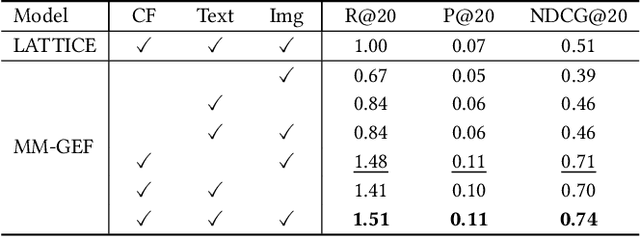
Abstract:In modern e-commerce, item content features in various modalities offer accurate yet comprehensive information to recommender systems. The majority of previous work either focuses on learning effective item representation during modelling user-item interactions, or exploring item-item relationships by analysing multi-modal features. Those methods, however, fail to incorporate the collaborative item-user-item relationships into the multi-modal feature-based item structure. In this work, we propose a graph-based item structure enhancement method MM-GEF: Multi-Modal recommendation with Graph Early-Fusion, which effectively combines the latent item structure underlying multi-modal contents with the collaborative signals. Instead of processing the content feature in different modalities separately, we show that the early-fusion of multi-modal features provides significant improvement. MM-GEF learns refined item representations by injecting structural information obtained from both multi-modal and collaborative signals. Through extensive experiments on four publicly available datasets, we demonstrate systematical improvements of our method over state-of-the-art multi-modal recommendation methods.
STA: Self-controlled Text Augmentation for Improving Text Classifications
Feb 24, 2023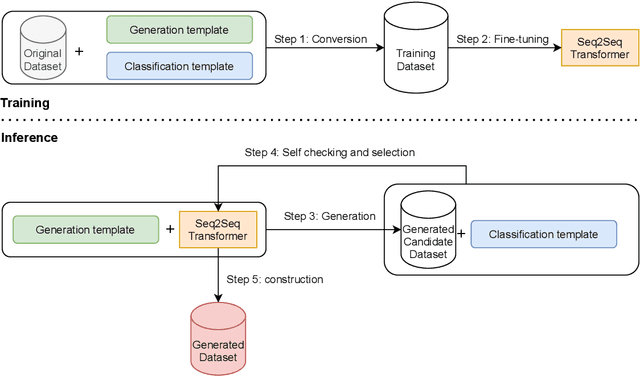

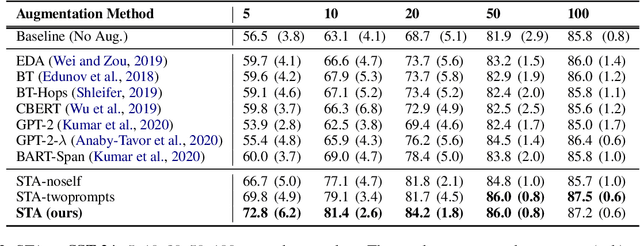
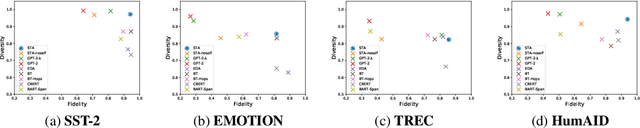
Abstract:Despite recent advancements in Machine Learning, many tasks still involve working in low-data regimes which can make solving natural language problems difficult. Recently, a number of text augmentation techniques have emerged in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) which can enrich the training data with new examples, though they are not without their caveats. For instance, simple rule-based heuristic methods are effective, but lack variation in semantic content and syntactic structure with respect to the original text. On the other hand, more complex deep learning approaches can cause extreme shifts in the intrinsic meaning of the text and introduce unwanted noise into the training data. To more reliably control the quality of the augmented examples, we introduce a state-of-the-art approach for Self-Controlled Text Augmentation (STA). Our approach tightly controls the generation process by introducing a self-checking procedure to ensure that generated examples retain the semantic content of the original text. Experimental results on multiple benchmarking datasets demonstrate that STA substantially outperforms existing state-of-the-art techniques, whilst qualitative analysis reveals that the generated examples are both lexically diverse and semantically reliable.
Exploiting Graph Structured Cross-Domain Representation for Multi-Domain Recommendation
Feb 22, 2023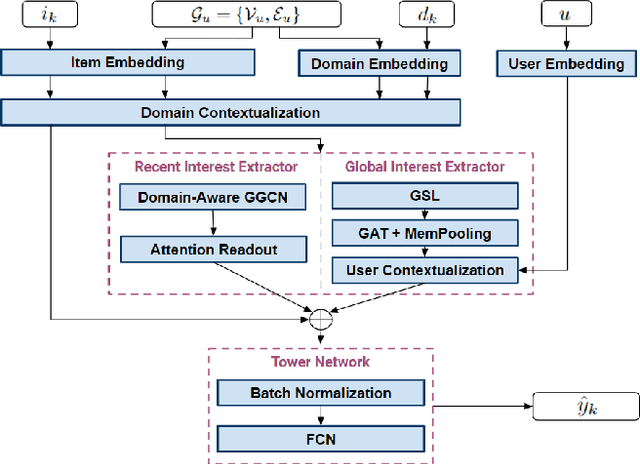
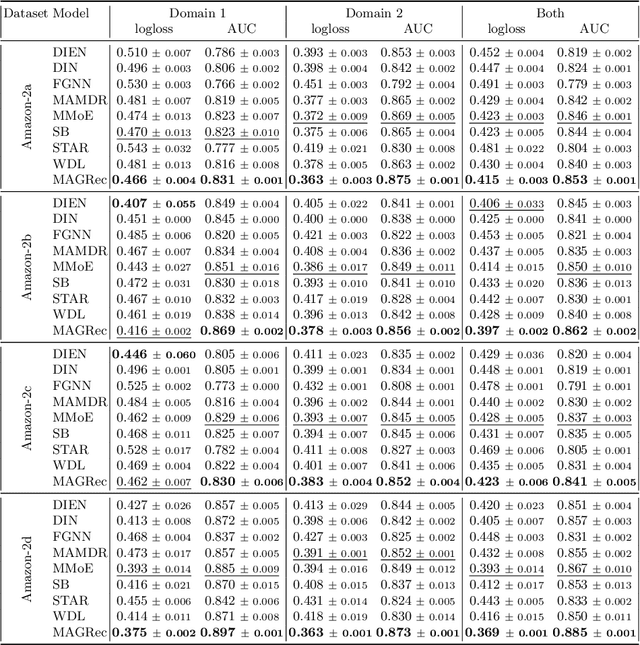
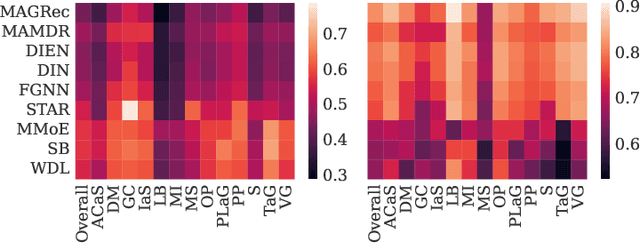
Abstract:Multi-domain recommender systems benefit from cross-domain representation learning and positive knowledge transfer. Both can be achieved by introducing a specific modeling of input data (i.e. disjoint history) or trying dedicated training regimes. At the same time, treating domains as separate input sources becomes a limitation as it does not capture the interplay that naturally exists between domains. In this work, we efficiently learn multi-domain representation of sequential users' interactions using graph neural networks. We use temporal intra- and inter-domain interactions as contextual information for our method called MAGRec (short for Multi-domAin Graph-based Recommender). To better capture all relations in a multi-domain setting, we learn two graph-based sequential representations simultaneously: domain-guided for recent user interest, and general for long-term interest. This approach helps to mitigate the negative knowledge transfer problem from multiple domains and improve overall representation. We perform experiments on publicly available datasets in different scenarios where MAGRec consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, we provide an ablation study and discuss further extensions of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge