Steven Derby
Efficient Large-Scale Cross-Domain Sequential Recommendation with Dynamic State Representations
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Recently, autoregressive recommendation models (ARMs), such as Meta's HSTU model, have emerged as a major breakthrough over traditional Deep Learning Recommendation Models (DLRMs), exhibiting the highly sought-after scaling law behaviour. However, when applied to multi-domain scenarios, the transformer architecture's attention maps become a computational bottleneck, as they attend to all items across every domain. To tackle this challenge, systems must efficiently balance inter and intra-domain knowledge transfer. In this work, we introduce a novel approach for scalable multi-domain recommendation systems by replacing full inter-domain attention with two innovative mechanisms: 1) Transition-Aware Positional Embeddings (TAPE): We propose novel positional embeddings that account for domain-transition specific information. This allows attention to be focused solely on intra-domain items, effectively reducing the unnecessary computational cost associated with attending to irrelevant domains. 2) Dynamic Domain State Representation (DDSR): We introduce a dynamic state representation for each domain, which is stored and accessed during subsequent token predictions. This enables the efficient transfer of relevant domain information without relying on full attention maps. Our method offers a scalable solution to the challenges posed by large-scale, multi-domain recommendation systems and demonstrates significant improvements in retrieval tasks by separately modelling and combining inter- and intra-domain representations.
SPICED: News Similarity Detection Dataset with Multiple Topics and Complexity Levels
Sep 21, 2023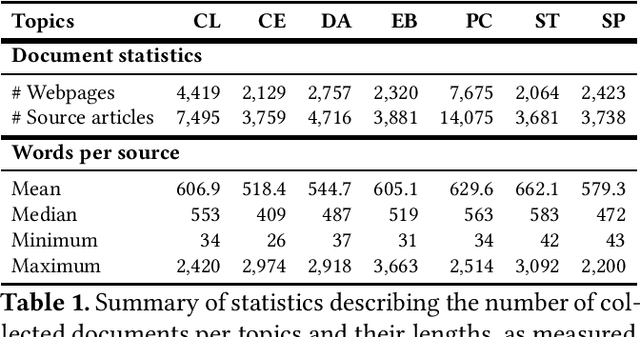
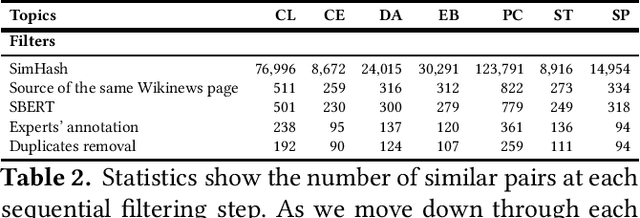
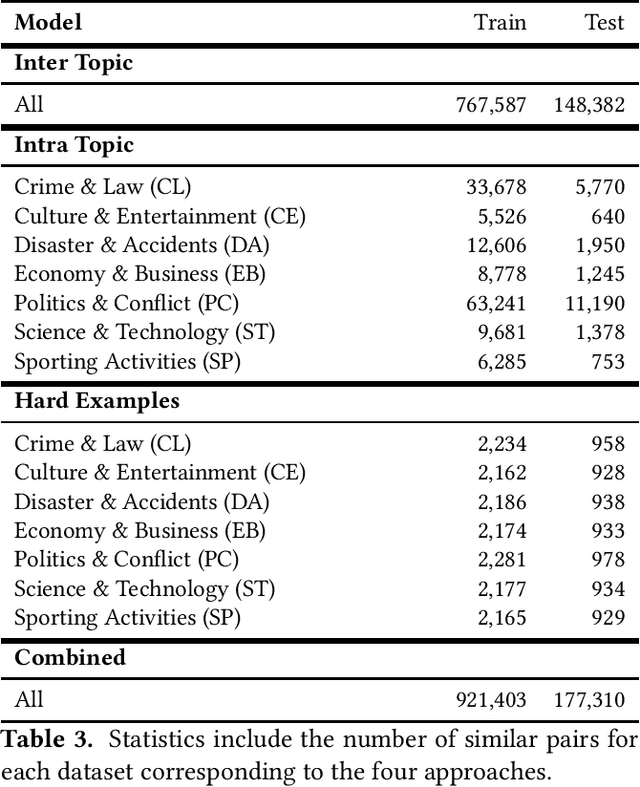
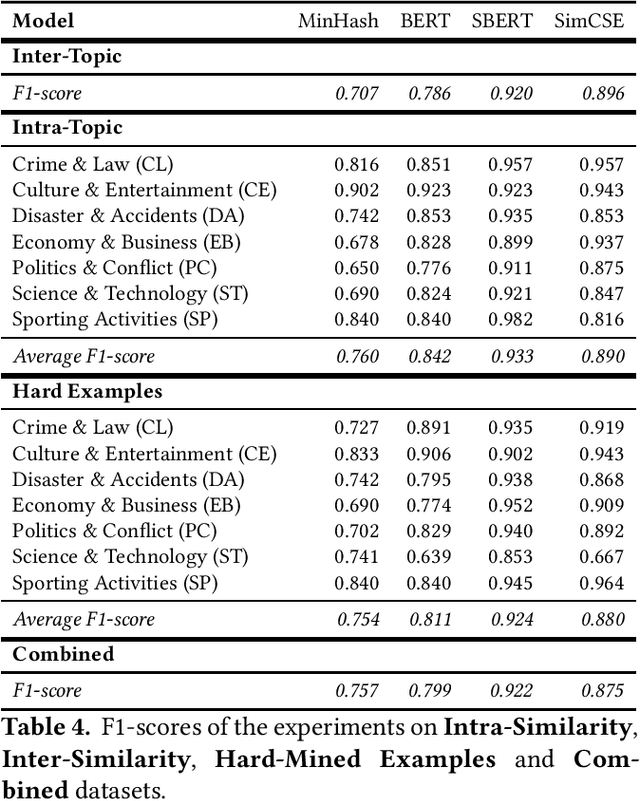
Abstract:Nowadays, the use of intelligent systems to detect redundant information in news articles has become especially prevalent with the proliferation of news media outlets in order to enhance user experience. However, the heterogeneous nature of news can lead to spurious findings in these systems: Simple heuristics such as whether a pair of news are both about politics can provide strong but deceptive downstream performance. Segmenting news similarity datasets into topics improves the training of these models by forcing them to learn how to distinguish salient characteristics under more narrow domains. However, this requires the existence of topic-specific datasets, which are currently lacking. In this article, we propose a new dataset of similar news, SPICED, which includes seven topics: Crime & Law, Culture & Entertainment, Disasters & Accidents, Economy & Business, Politics & Conflicts, Science & Technology, and Sports. Futhermore, we present four distinct approaches for generating news pairs, which are used in the creation of datasets specifically designed for news similarity detection task. We benchmarked the created datasets using MinHash, BERT, SBERT, and SimCSE models.
STA: Self-controlled Text Augmentation for Improving Text Classifications
Feb 24, 2023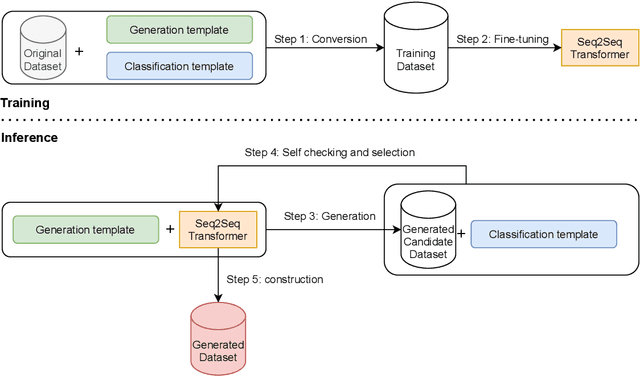

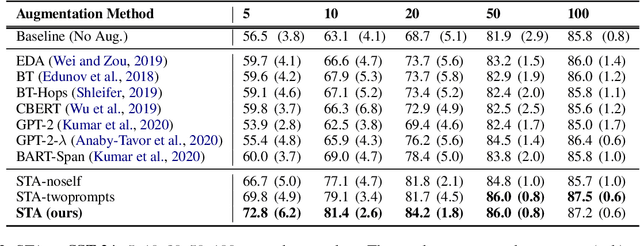
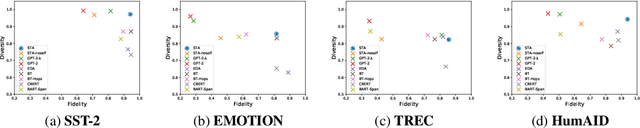
Abstract:Despite recent advancements in Machine Learning, many tasks still involve working in low-data regimes which can make solving natural language problems difficult. Recently, a number of text augmentation techniques have emerged in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) which can enrich the training data with new examples, though they are not without their caveats. For instance, simple rule-based heuristic methods are effective, but lack variation in semantic content and syntactic structure with respect to the original text. On the other hand, more complex deep learning approaches can cause extreme shifts in the intrinsic meaning of the text and introduce unwanted noise into the training data. To more reliably control the quality of the augmented examples, we introduce a state-of-the-art approach for Self-Controlled Text Augmentation (STA). Our approach tightly controls the generation process by introducing a self-checking procedure to ensure that generated examples retain the semantic content of the original text. Experimental results on multiple benchmarking datasets demonstrate that STA substantially outperforms existing state-of-the-art techniques, whilst qualitative analysis reveals that the generated examples are both lexically diverse and semantically reliable.
Topics as Entity Clusters: Entity-based Topics from Language Models and Graph Neural Networks
Jan 06, 2023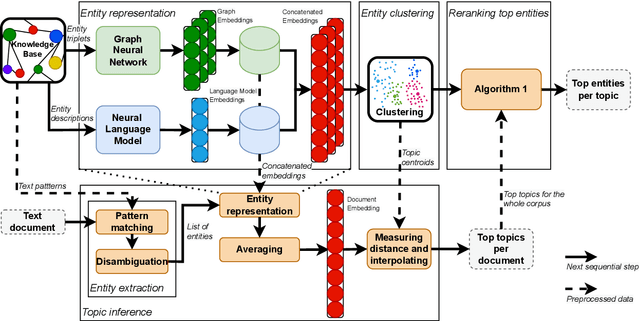
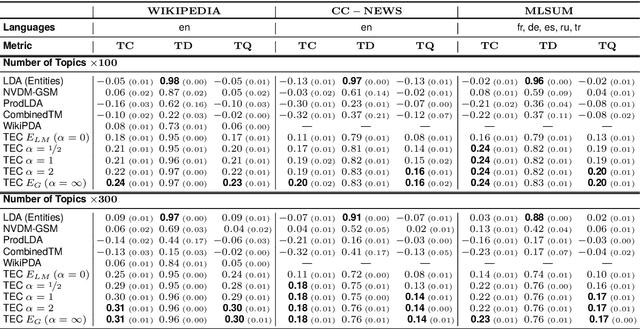
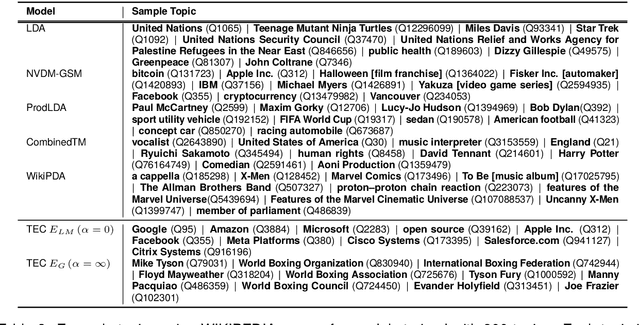
Abstract:Topic models aim to reveal the latent structure behind a corpus, typically conducted over a bag-of-words representation of documents. In the context of topic modeling, most vocabulary is either irrelevant for uncovering underlying topics or contains strong relationships with relevant concepts, impacting the interpretability of these topics. Furthermore, their limited expressiveness and dependency on language demand considerable computation resources. Hence, we propose a novel approach for cluster-based topic modeling that employs conceptual entities. Entities are language-agnostic representations of real-world concepts rich in relational information. To this end, we extract vector representations of entities from (i) an encyclopedic corpus using a language model; and (ii) a knowledge base using a graph neural network. We demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms other state-of-the-art topic models across coherency metrics and find that the explicit knowledge encoded in the graph-based embeddings provides more coherent topics than the implicit knowledge encoded with the contextualized embeddings of language models.
Multilingual News Location Detection using an Entity-Based Siamese Network with Semi-Supervised Contrastive Learning and Knowledge Base
Dec 22, 2022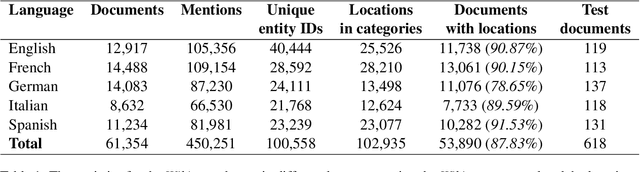
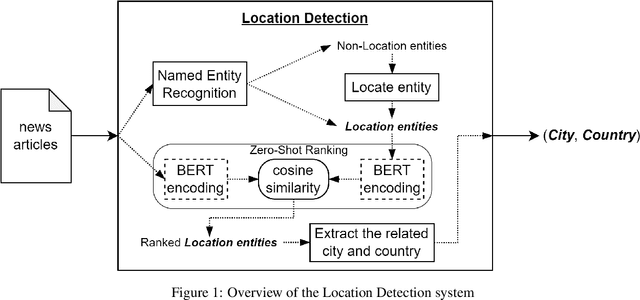

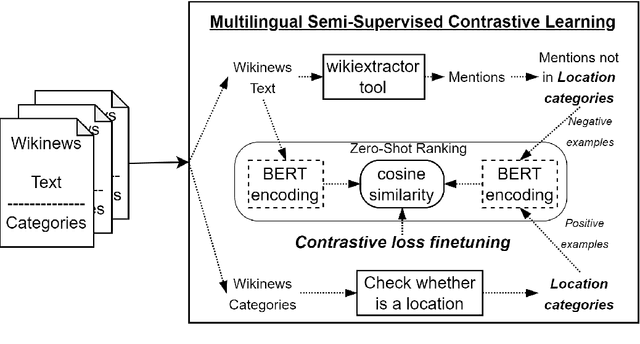
Abstract:Early detection of relevant locations in a piece of news is especially important in extreme events such as environmental disasters, war conflicts, disease outbreaks, or political turmoils. Additionally, this detection also helps recommender systems to promote relevant news based on user locations. Note that, when the relevant locations are not mentioned explicitly in the text, state-of-the-art methods typically fail to recognize them because these methods rely on syntactic recognition. In contrast, by incorporating a knowledge base and connecting entities with their locations, our system successfully infers the relevant locations even when they are not mentioned explicitly in the text. To evaluate the effectiveness of our approach, and due to the lack of datasets in this area, we also contribute to the research community with a gold-standard multilingual news-location dataset, NewsLOC. It contains the annotation of the relevant locations (and their WikiData IDs) of 600+ Wikinews articles in five different languages: English, French, German, Italian, and Spanish. Through experimental evaluations, we show that our proposed system outperforms the baselines and the fine-tuned version of the model using semi-supervised data that increases the classification rate. The source code and the NewsLOC dataset are publicly available for being used by the research community at https://github.com/vsuarezpaniagua/NewsLocation.
Feature2Vec: Distributional semantic modelling of human property knowledge
Aug 29, 2019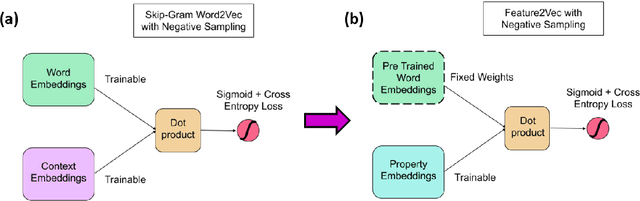
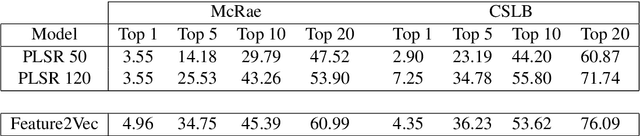
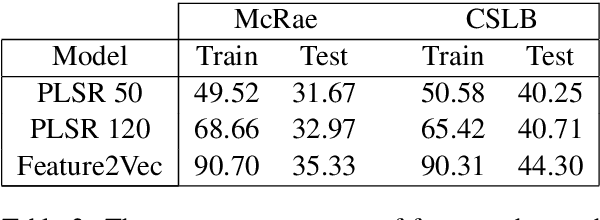

Abstract:Feature norm datasets of human conceptual knowledge, collected in surveys of human volunteers, yield highly interpretable models of word meaning and play an important role in neurolinguistic research on semantic cognition. However, these datasets are limited in size due to practical obstacles associated with exhaustively listing properties for a large number of words. In contrast, the development of distributional modelling techniques and the availability of vast text corpora have allowed researchers to construct effective vector space models of word meaning over large lexicons. However, this comes at the cost of interpretable, human-like information about word meaning. We propose a method for mapping human property knowledge onto a distributional semantic space, which adapts the word2vec architecture to the task of modelling concept features. Our approach gives a measure of concept and feature affinity in a single semantic space, which makes for easy and efficient ranking of candidate human-derived semantic properties for arbitrary words. We compare our model with a previous approach, and show that it performs better on several evaluation tasks. Finally, we discuss how our method could be used to develop efficient sampling techniques to extend existing feature norm datasets in a reliable way.
* 7 pages, Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP 2019)
Using Sparse Semantic Embeddings Learned from Multimodal Text and Image Data to Model Human Conceptual Knowledge
Sep 18, 2018
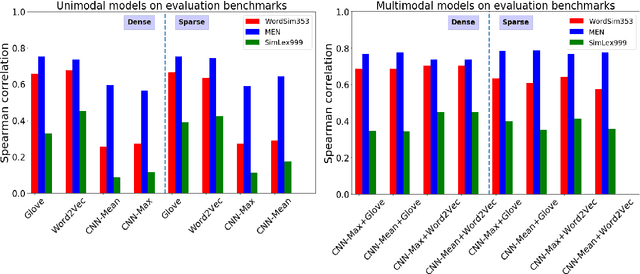

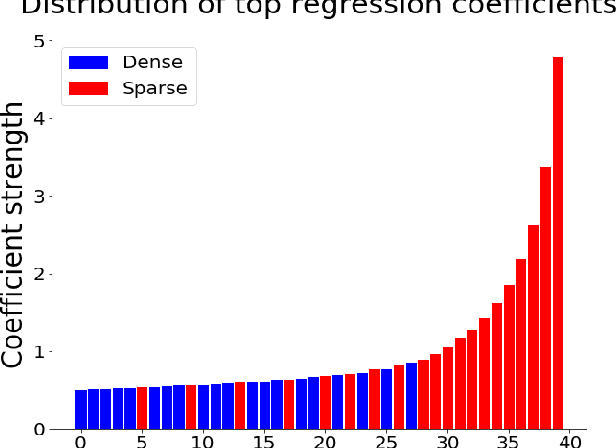
Abstract:Distributional models provide a convenient way to model semantics using dense embedding spaces derived from unsupervised learning algorithms. However, the dimensions of dense embedding spaces are not designed to resemble human semantic knowledge. Moreover, embeddings are often built from a single source of information (typically text data), even though neurocognitive research suggests that semantics is deeply linked to both language and perception. In this paper, we combine multimodal information from both text and image-based representations derived from state-of-the-art distributional models to produce sparse, interpretable vectors using Joint Non-Negative Sparse Embedding. Through in-depth analyses comparing these sparse models to human-derived behavioural and neuroimaging data, we demonstrate their ability to predict interpretable linguistic descriptions of human ground-truth semantic knowledge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge