Tobias Elze
FairCLIP: Harnessing Fairness in Vision-Language Learning
Apr 05, 2024



Abstract:Fairness is a critical concern in deep learning, especially in healthcare, where these models influence diagnoses and treatment decisions. Although fairness has been investigated in the vision-only domain, the fairness of medical vision-language (VL) models remains unexplored due to the scarcity of medical VL datasets for studying fairness. To bridge this research gap, we introduce the first fair vision-language medical dataset Harvard-FairVLMed that provides detailed demographic attributes, ground-truth labels, and clinical notes to facilitate an in-depth examination of fairness within VL foundation models. Using Harvard-FairVLMed, we conduct a comprehensive fairness analysis of two widely-used VL models (CLIP and BLIP2), pre-trained on both natural and medical domains, across four different protected attributes. Our results highlight significant biases in all VL models, with Asian, Male, Non-Hispanic, and Spanish being the preferred subgroups across the protected attributes of race, gender, ethnicity, and language, respectively. In order to alleviate these biases, we propose FairCLIP, an optimal-transport-based approach that achieves a favorable trade-off between performance and fairness by reducing the Sinkhorn distance between the overall sample distribution and the distributions corresponding to each demographic group. As the first VL dataset of its kind, Harvard-FairVLMed holds the potential to catalyze advancements in the development of machine learning models that are both ethically aware and clinically effective. Our dataset and code are available at https://ophai.hms.harvard.edu/datasets/harvard-fairvlmed10k.
FairSeg: A Large-scale Medical Image Segmentation Dataset for Fairness Learning with Fair Error-Bound Scaling
Nov 03, 2023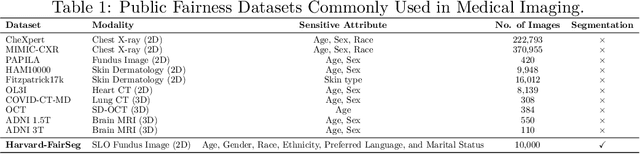
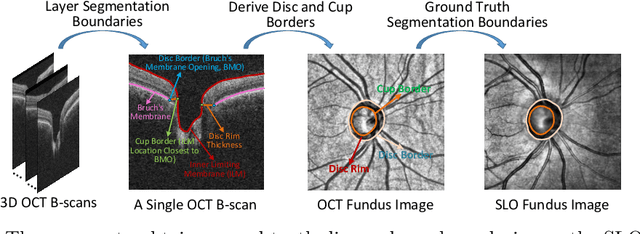
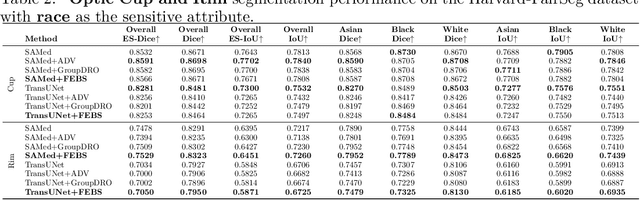
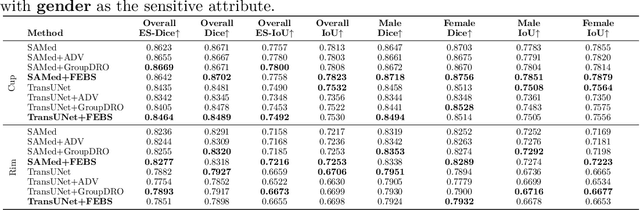
Abstract:Fairness in artificial intelligence models has gained significantly more attention in recent years, especially in the area of medicine, as fairness in medical models is critical to people's well-being and lives. High-quality medical fairness datasets are needed to promote fairness learning research. Existing medical fairness datasets are all for classification tasks, and no fairness datasets are available for medical segmentation, while medical segmentation is an equally important clinical task as classifications, which can provide detailed spatial information on organ abnormalities ready to be assessed by clinicians. In this paper, we propose the first fairness dataset for medical segmentation named FairSeg with 10,000 subject samples. In addition, we propose a fair error-bound scaling approach to reweight the loss function with the upper error-bound in each identity group. We anticipate that the segmentation performance equity can be improved by explicitly tackling the hard cases with high training errors in each identity group. To facilitate fair comparisons, we propose new equity-scaled segmentation performance metrics, such as the equity-scaled Dice coefficient, which is calculated as the overall Dice coefficient divided by one plus the standard deviation of group Dice coefficients. Through comprehensive experiments, we demonstrate that our fair error-bound scaling approach either has superior or comparable fairness performance to the state-of-the-art fairness learning models. The dataset and code are publicly accessible via \url{https://github.com/Harvard-Ophthalmology-AI-Lab/FairSeg}.
Harvard Eye Fairness: A Large-Scale 3D Imaging Dataset for Equitable Eye Diseases Screening and Fair Identity Scaling
Oct 05, 2023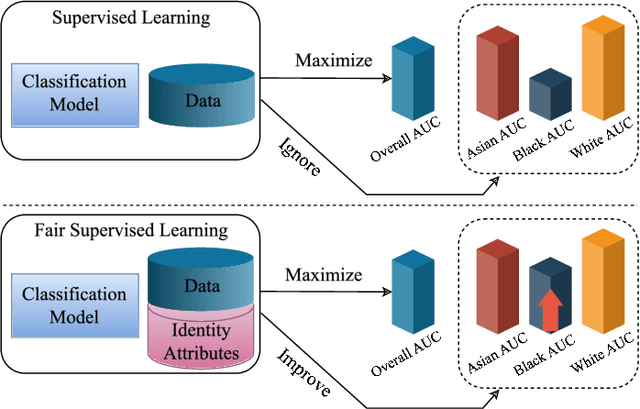
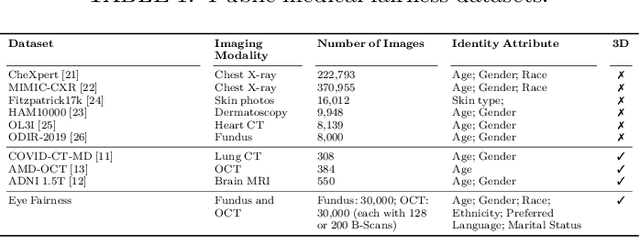
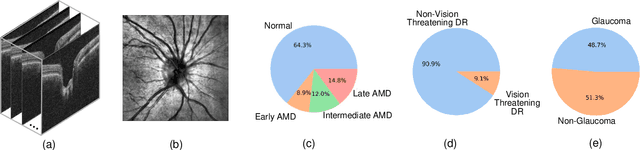
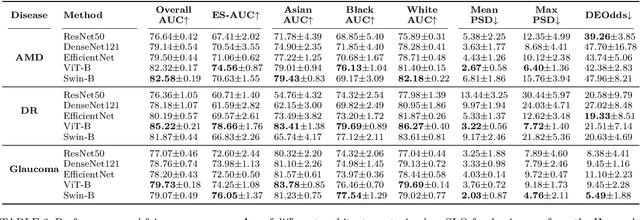
Abstract:Fairness or equity in machine learning is profoundly important for societal well-being, but limited public datasets hinder its progress, especially in the area of medicine. It is undeniable that fairness in medicine is one of the most important areas for fairness learning's applications. Currently, no large-scale public medical datasets with 3D imaging data for fairness learning are available, while 3D imaging data in modern clinics are standard tests for disease diagnosis. In addition, existing medical fairness datasets are actually repurposed datasets, and therefore they typically have limited demographic identity attributes with at most three identity attributes of age, gender, and race for fairness modeling. To address this gap, we introduce our Eye Fairness dataset with 30,000 subjects (Harvard-EF) covering three major eye diseases including age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and glaucoma affecting 380 million patients globally. Our Harvard-EF dataset includes both 2D fundus photos and 3D optical coherence tomography scans with six demographic identity attributes including age, gender, race, ethnicity, preferred language, and marital status. We also propose a fair identity scaling (FIS) approach combining group and individual scaling together to improve model fairness. Our FIS approach is compared with various state-of-the-art fairness learning methods with superior performance in the racial, gender, and ethnicity fairness tasks with 2D and 3D imaging data, which demonstrate the utilities of our Harvard-EF dataset for fairness learning. To facilitate fairness comparisons between different models, we propose performance-scaled disparity measures, which can be used to compare model fairness accounting for overall performance levels. The dataset and code are publicly accessible via https://ophai.hms.harvard.edu/datasets/harvard-ef30k.
Harvard Glaucoma Detection and Progression: A Multimodal Multitask Dataset and Generalization-Reinforced Semi-Supervised Learning
Aug 25, 2023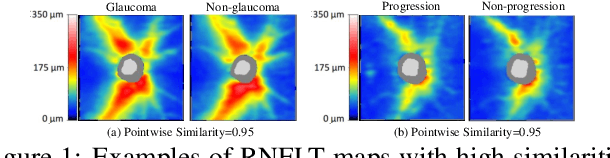
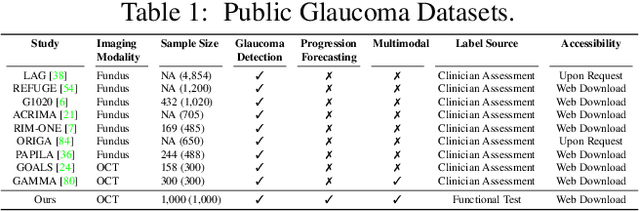
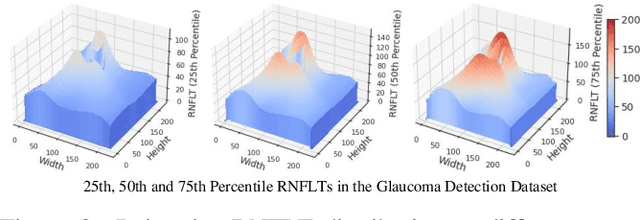
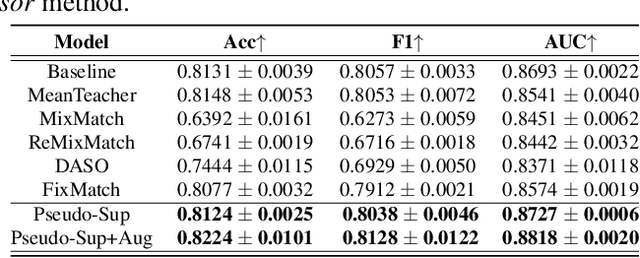
Abstract:Glaucoma is the number one cause of irreversible blindness globally. A major challenge for accurate glaucoma detection and progression forecasting is the bottleneck of limited labeled patients with the state-of-the-art (SOTA) 3D retinal imaging data of optical coherence tomography (OCT). To address the data scarcity issue, this paper proposes two solutions. First, we develop a novel generalization-reinforced semi-supervised learning (SSL) model called pseudo supervisor to optimally utilize unlabeled data. Compared with SOTA models, the proposed pseudo supervisor optimizes the policy of predicting pseudo labels with unlabeled samples to improve empirical generalization. Our pseudo supervisor model is evaluated with two clinical tasks consisting of glaucoma detection and progression forecasting. The progression forecasting task is evaluated both unimodally and multimodally. Our pseudo supervisor model demonstrates superior performance than SOTA SSL comparison models. Moreover, our model also achieves the best results on the publicly available LAG fundus dataset. Second, we introduce the Harvard Glaucoma Detection and Progression (Harvard-GDP) Dataset, a multimodal multitask dataset that includes data from 1,000 patients with OCT imaging data, as well as labels for glaucoma detection and progression. This is the largest glaucoma detection dataset with 3D OCT imaging data and the first glaucoma progression forecasting dataset that is publicly available. Detailed sex and racial analysis are provided, which can be used by interested researchers for fairness learning studies. Our released dataset is benchmarked with several SOTA supervised CNN and transformer deep learning models. The dataset and code are made publicly available via \url{https://ophai.hms.harvard.edu/datasets/harvard-gdp1000}.
Harvard Glaucoma Fairness: A Retinal Nerve Disease Dataset for Fairness Learning and Fair Identity Normalization
Jun 15, 2023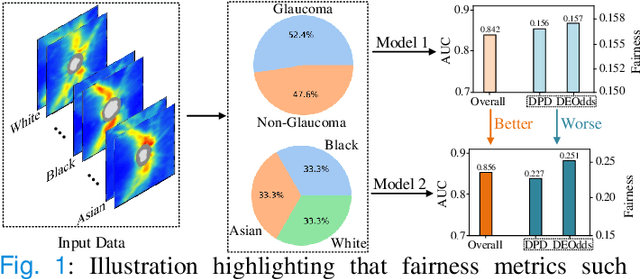
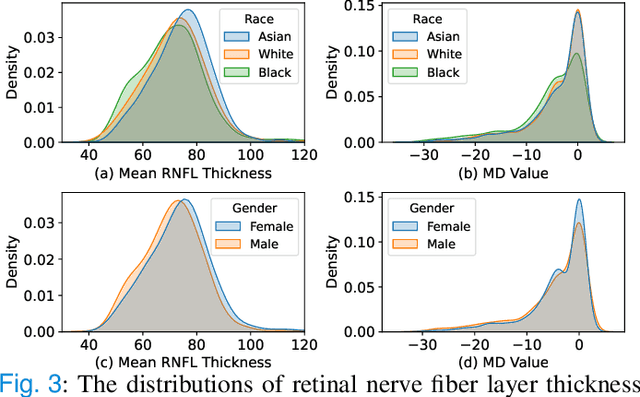
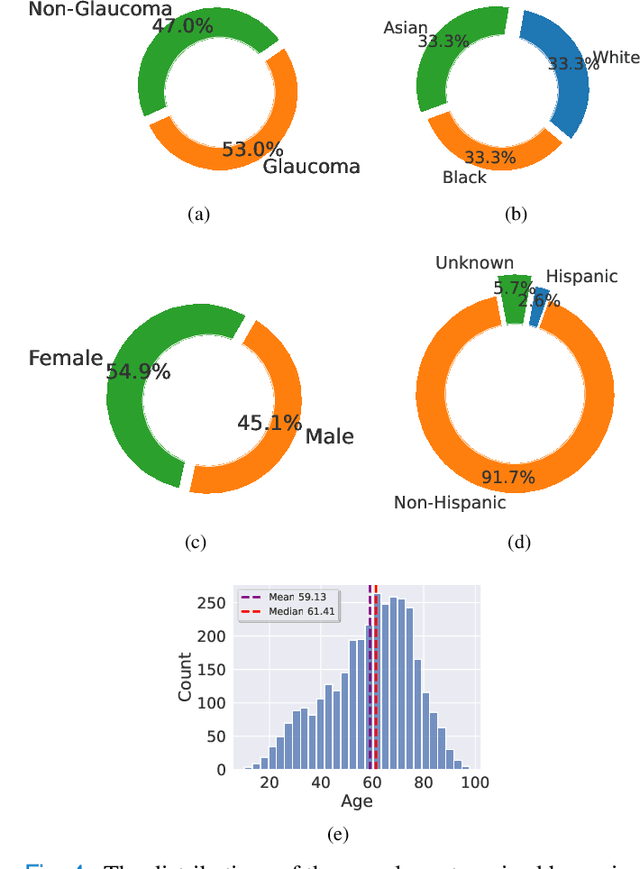
Abstract:Fairness in machine learning is important for societal well-being, but limited public datasets hinder its progress. Currently, no dedicated public medical datasets with imaging data for fairness learning are available, though minority groups suffer from more health issues. To address this gap, we introduce Harvard Glaucoma Fairness (Harvard-GF), a retinal nerve disease dataset with both 2D and 3D imaging data and balanced racial groups for glaucoma detection. Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness globally with Blacks having doubled glaucoma prevalence than other races. We also propose a fair identity normalization (FIN) approach to equalize the feature importance between different identity groups. Our FIN approach is compared with various the-state-of-the-arts fairness learning methods with superior performance in both racial and gender fairness tasks with 2D and 3D imaging data, which demonstrate the utilities of our dataset Harvard-GF for fairness learning. To facilitate fairness comparisons between different models, we propose an equity-scaled performance measure, which can be flexibly used to compare all kinds of performance metrics in the context of fairness. The dataset and code are publicly accessible via https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/A4XMO1 and https://github.com/luoyan407/Harvard-GF, respectively.
Artifact-Tolerant Clustering-Guided Contrastive Embedding Learning for Ophthalmic Images
Sep 02, 2022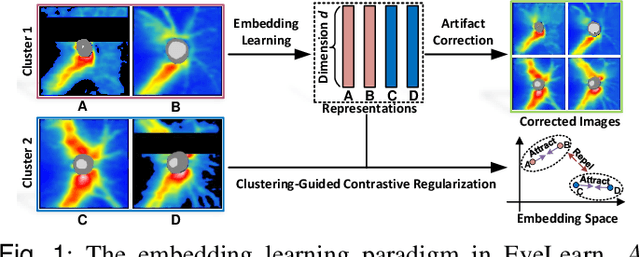
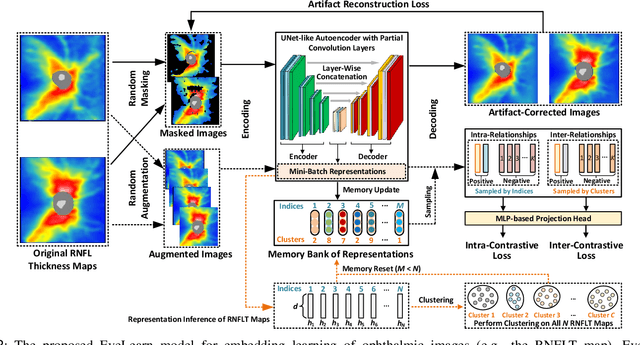
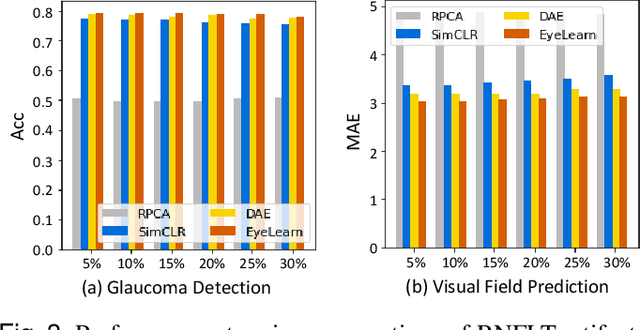
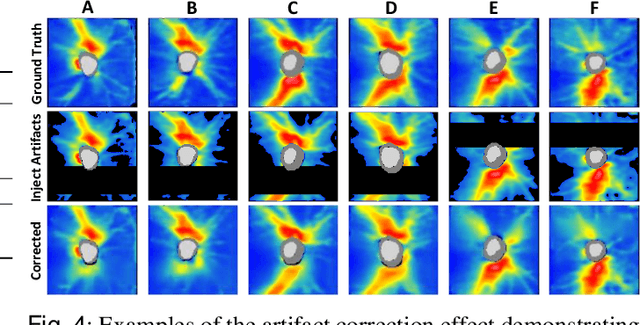
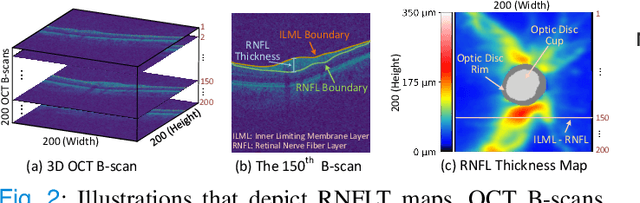
Abstract:Ophthalmic images and derivatives such as the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness map are crucial for detecting and monitoring ophthalmic diseases (e.g., glaucoma). For computer-aided diagnosis of eye diseases, the key technique is to automatically extract meaningful features from ophthalmic images that can reveal the biomarkers (e.g., RNFL thinning patterns) linked to functional vision loss. However, representation learning from ophthalmic images that links structural retinal damage with human vision loss is non-trivial mostly due to large anatomical variations between patients. The task becomes even more challenging in the presence of image artifacts, which are common due to issues with image acquisition and automated segmentation. In this paper, we propose an artifact-tolerant unsupervised learning framework termed EyeLearn for learning representations of ophthalmic images. EyeLearn has an artifact correction module to learn representations that can best predict artifact-free ophthalmic images. In addition, EyeLearn adopts a clustering-guided contrastive learning strategy to explicitly capture the intra- and inter-image affinities. During training, images are dynamically organized in clusters to form contrastive samples in which images in the same or different clusters are encouraged to learn similar or dissimilar representations, respectively. To evaluate EyeLearn, we use the learned representations for visual field prediction and glaucoma detection using a real-world ophthalmic image dataset of glaucoma patients. Extensive experiments and comparisons with state-of-the-art methods verified the effectiveness of EyeLearn for learning optimal feature representations from ophthalmic images.
Affective Medical Estimation and Decision Making via Visualized Learning and Deep Learning
May 09, 2022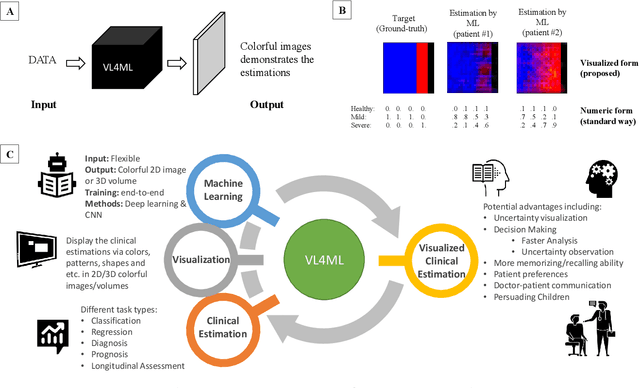
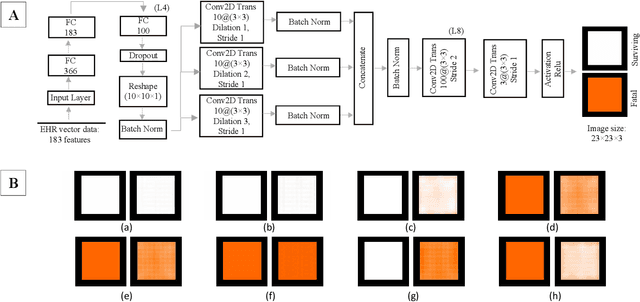
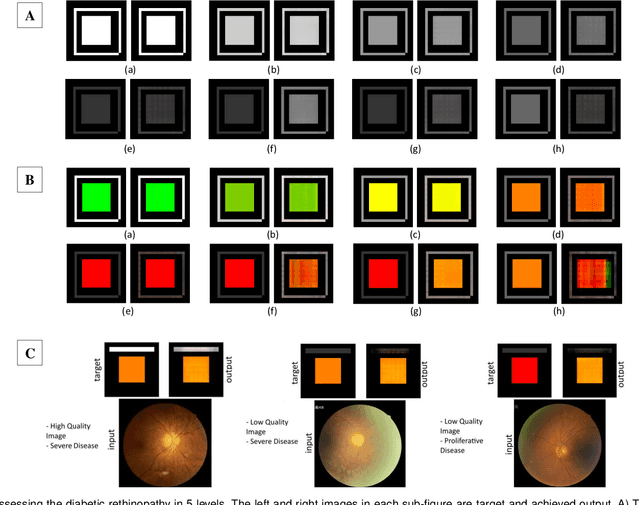
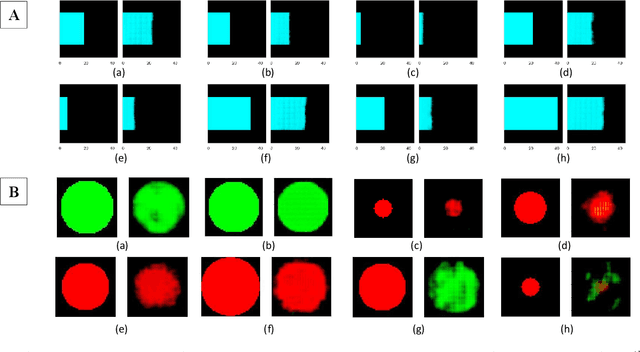
Abstract:With the advent of sophisticated machine learning (ML) techniques and the promising results they yield, especially in medical applications, where they have been investigated for different tasks to enhance the decision-making process. Since visualization is such an effective tool for human comprehension, memorization, and judgment, we have presented a first-of-its-kind estimation approach we refer to as Visualized Learning for Machine Learning (VL4ML) that not only can serve to assist physicians and clinicians in making reasoned medical decisions, but it also allows to appreciate the uncertainty visualization, which could raise incertitude in making the appropriate classification or prediction. For the proof of concept, and to demonstrate the generalized nature of this visualized estimation approach, five different case studies are examined for different types of tasks including classification, regression, and longitudinal prediction. A survey analysis with more than 100 individuals is also conducted to assess users' feedback on this visualized estimation method. The experiments and the survey demonstrate the practical merits of the VL4ML that include: (1) appreciating visually clinical/medical estimations; (2) getting closer to the patients' preferences; (3) improving doctor-patient communication, and (4) visualizing the uncertainty introduced through the black box effect of the deployed ML algorithm. All the source codes are shared via a GitHub repository.
Deep Variational Clustering Framework for Self-labeling of Large-scale Medical Images
Sep 22, 2021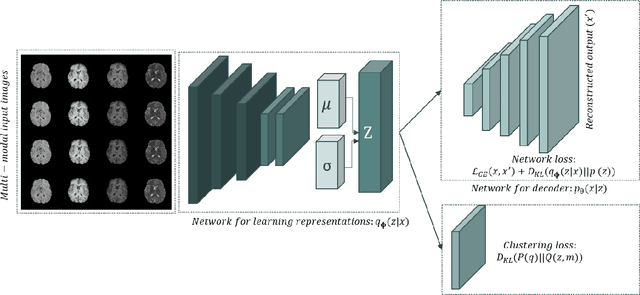
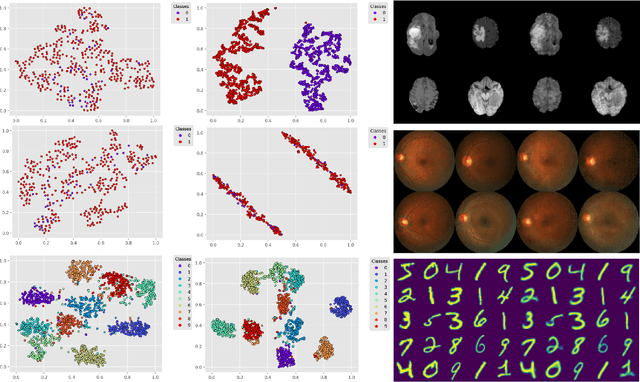
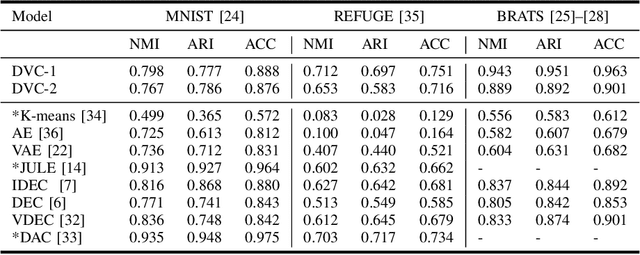
Abstract:We propose a Deep Variational Clustering (DVC) framework for unsupervised representation learning and clustering of large-scale medical images. DVC simultaneously learns the multivariate Gaussian posterior through the probabilistic convolutional encoder and the likelihood distribution with the probabilistic convolutional decoder; and optimizes cluster labels assignment. Here, the learned multivariate Gaussian posterior captures the latent distribution of a large set of unlabeled images. Then, we perform unsupervised clustering on top of the variational latent space using a clustering loss. In this approach, the probabilistic decoder helps to prevent the distortion of data points in the latent space and to preserve the local structure of data generating distribution. The training process can be considered as a self-training process to refine the latent space and simultaneously optimizing cluster assignments iteratively. We evaluated our proposed framework on three public datasets that represented different medical imaging modalities. Our experimental results show that our proposed framework generalizes better across different datasets. It achieves compelling results on several medical imaging benchmarks. Thus, our approach offers potential advantages over conventional deep unsupervised learning in real-world applications. The source code of the method and all the experiments are available publicly at: https://github.com/csfarzin/DVC
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge