Tianwen Jiang
FailureAtlas:Mapping the Failure Landscape of T2I Models via Active Exploration
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Static benchmarks have provided a valuable foundation for comparing Text-to-Image (T2I) models. However, their passive design offers limited diagnostic power, struggling to uncover the full landscape of systematic failures or isolate their root causes. We argue for a complementary paradigm: active exploration. We introduce FailureAtlas, the first framework designed to autonomously explore and map the vast failure landscape of T2I models at scale. FailureAtlas frames error discovery as a structured search for minimal, failure-inducing concepts. While it is a computationally explosive problem, we make it tractable with novel acceleration techniques. When applied to Stable Diffusion models, our method uncovers hundreds of thousands of previously unknown error slices (over 247,000 in SD1.5 alone) and provides the first large-scale evidence linking these failures to data scarcity in the training set. By providing a principled and scalable engine for deep model auditing, FailureAtlas establishes a new, diagnostic-first methodology to guide the development of more robust generative AI. The code is available at https://github.com/cure-lab/FailureAtlas
VEM$^2$L: A Plug-and-play Framework for Fusing Text and Structure Knowledge on Sparse Knowledge Graph Completion
Jul 12, 2022
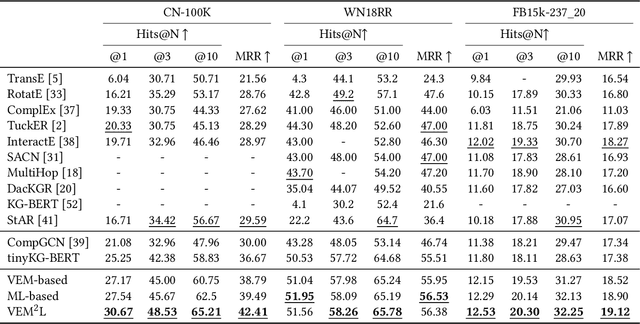
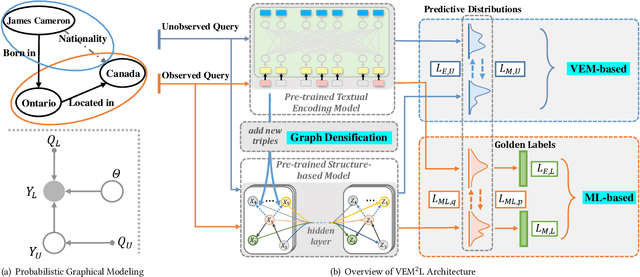
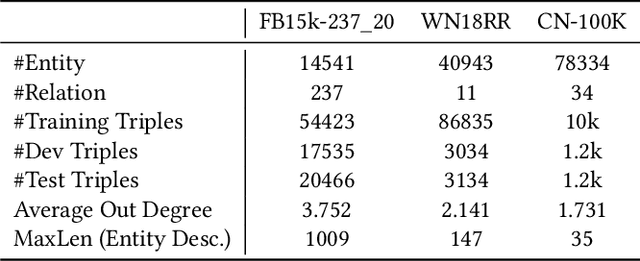
Abstract:Knowledge Graph Completion has been widely studied recently to complete missing elements within triples via mainly modeling graph structural features, but performs sensitive to the sparsity of graph structure. Relevant texts like entity names and descriptions, acting as another expression form for Knowledge Graphs (KGs), are expected to solve this challenge. Several methods have been proposed to utilize both structure and text messages with two encoders, but only achieved limited improvements due to the failure to balance weights between them. And reserving both structural and textual encoders during inference also suffers from heavily overwhelmed parameters. Motivated by Knowledge Distillation, we view knowledge as mappings from input to output probabilities and propose a plug-and-play framework VEM2L over sparse KGs to fuse knowledge extracted from text and structure messages into a unity. Specifically, we partition knowledge acquired by models into two nonoverlapping parts: one part is relevant to the fitting capacity upon training triples, which could be fused by motivating two encoders to learn from each other on training sets; the other reflects the generalization ability upon unobserved queries. And correspondingly, we propose a new fusion strategy proved by Variational EM algorithm to fuse the generalization ability of models, during which we also apply graph densification operations to further alleviate the sparse graph problem. By combining these two fusion methods, we propose VEM2L framework finally. Both detailed theoretical evidence, as well as quantitative and qualitative experiments, demonstrates the effectiveness and efficiency of our proposed framework.
Validating Label Consistency in NER Data Annotation
Jan 21, 2021



Abstract:Data annotation plays a crucial role in ensuring your named entity recognition (NER) projects are trained with the right information to learn from. Producing the most accurate labels is a challenge due to the complexity involved with annotation. Label inconsistency between multiple subsets of data annotation (e.g., training set and test set, or multiple training subsets) is an indicator of label mistakes. In this work, we present an empirical method to explore the relationship between label (in-)consistency and NER model performance. It can be used to validate the label consistency (or catches the inconsistency) in multiple sets of NER data annotation. In experiments, our method identified the label inconsistency of test data in SCIERC and CoNLL03 datasets (with 26.7% and 5.4% label mistakes). It validated the consistency in the corrected version of both datasets.
Learning Attribute-Structure Co-Evolutions in Dynamic Graphs
Jul 25, 2020



Abstract:Most graph neural network models learn embeddings of nodes in static attributed graphs for predictive analysis. Recent attempts have been made to learn temporal proximity of the nodes. We find that real dynamic attributed graphs exhibit complex co-evolution of node attributes and graph structure. Learning node embeddings for forecasting change of node attributes and birth and death of links over time remains an open problem. In this work, we present a novel framework called CoEvoGNN for modeling dynamic attributed graph sequence. It preserves the impact of earlier graphs on the current graph by embedding generation through the sequence. It has a temporal self-attention mechanism to model long-range dependencies in the evolution. Moreover, CoEvoGNN optimizes model parameters jointly on two dynamic tasks, attribute inference and link prediction over time. So the model can capture the co-evolutionary patterns of attribute change and link formation. This framework can adapt to any graph neural algorithms so we implemented and investigated three methods based on it: CoEvoGCN, CoEvoGAT, and CoEvoSAGE. Experiments demonstrate the framework (and its methods) outperform strong baselines on predicting an entire unseen graph snapshot of personal attributes and interpersonal links in dynamic social graphs and financial graphs.
Canonicalizing Open Knowledge Bases with Multi-Layered Meta-Graph Neural Network
Jun 17, 2020



Abstract:Noun phrases and relational phrases in Open Knowledge Bases are often not canonical, leading to redundant and ambiguous facts. In this work, we integrate structural information (from which tuple, which sentence) and semantic information (semantic similarity) to do the canonicalization. We represent the two types of information as a multi-layered graph: the structural information forms the links across the sentence, relational phrase, and noun phrase layers; the semantic information forms weighted intra-layer links for each layer. We propose a graph neural network model to aggregate the representations of noun phrases and relational phrases through the multi-layered meta-graph structure. Experiments show that our model outperforms existing approaches on a public datasets in general domain.
Constructing Information-Lossless Biological Knowledge Graphs from Conditional Statements
Jun 26, 2019
Abstract:Conditions are essential in the statements of biological literature. Without the conditions (e.g., environment, equipment) that were precisely specified, the facts (e.g., observations) in the statements may no longer be valid. One biological statement has one or multiple fact(s) and/or condition(s). Their subject and object can be either a concept or a concept's attribute. Existing information extraction methods do not consider the role of condition in the biological statement nor the role of attribute in the subject/object. In this work, we design a new tag schema and propose a deep sequence tagging framework to structure conditional statement into fact and condition tuples from biological text. Experiments demonstrate that our method yields a information-lossless structure of the literature.
Towards Time-Aware Distant Supervision for Relation Extraction
Mar 08, 2019



Abstract:Distant supervision for relation extraction heavily suffers from the wrong labeling problem. To alleviate this issue in news data with the timestamp, we take a new factor time into consideration and propose a novel time-aware distant supervision framework (Time-DS). Time-DS is composed of a time series instance-popularity and two strategies. Instance-popularity is to encode the strong relevance of time and true relation mention. Therefore, instance-popularity would be an effective clue to reduce the noises generated through distant supervision labeling. The two strategies, i.e., hard filter and curriculum learning are both ways to implement instance-popularity for better relation extraction in the manner of Time-DS. The curriculum learning is a more sophisticated and flexible way to exploit instance-popularity to eliminate the bad effects of noises, thus get better relation extraction performance. Experiments on our collected multi-source news corpus show that Time-DS achieves significant improvements for relation extraction.
Attribute Acquisition in Ontology based on Representation Learning of Hierarchical Classes and Attributes
Mar 08, 2019



Abstract:Attribute acquisition for classes is a key step in ontology construction, which is often achieved by community members manually. This paper investigates an attention-based automatic paradigm called TransATT for attribute acquisition, by learning the representation of hierarchical classes and attributes in Chinese ontology. The attributes of an entity can be acquired by merely inspecting its classes, because the entity can be regard as the instance of its classes and inherit their attributes. For explicitly describing of the class of an entity unambiguously, we propose class-path to represent the hierarchical classes in ontology, instead of the terminal class word of the hypernym-hyponym relation (i.e., is-a relation) based hierarchy. The high performance of TransATT on attribute acquisition indicates the promising ability of the learned representation of class-paths and attributes. Moreover, we construct a dataset named \textbf{BigCilin11k}. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first Chinese dataset with abundant hierarchical classes and entities with attributes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge