Mengxia Yu
Context Selection and Rewriting for Video-based Educational Question Generation
Apr 29, 2025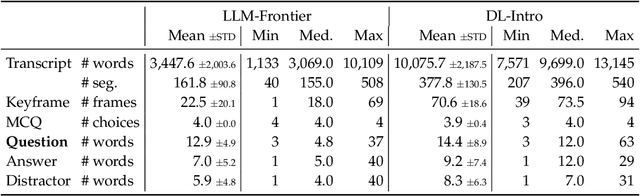
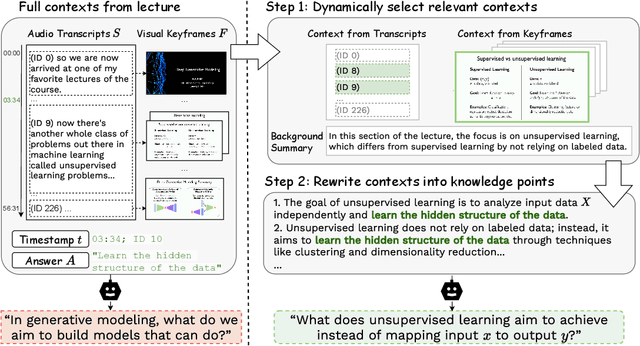
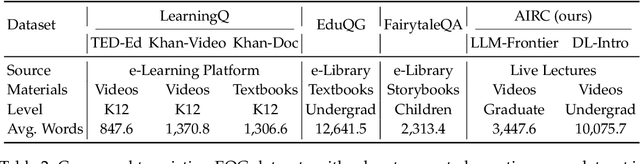
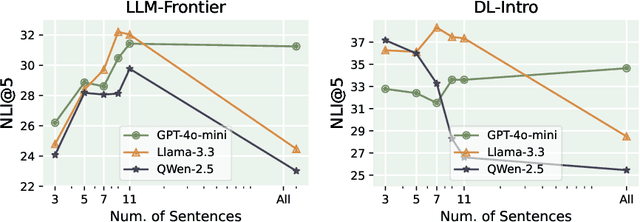
Abstract:Educational question generation (EQG) is a crucial component of intelligent educational systems, significantly aiding self-assessment, active learning, and personalized education. While EQG systems have emerged, existing datasets typically rely on predefined, carefully edited texts, failing to represent real-world classroom content, including lecture speech with a set of complementary slides. To bridge this gap, we collect a dataset of educational questions based on lectures from real-world classrooms. On this realistic dataset, we find that current methods for EQG struggle with accurately generating questions from educational videos, particularly in aligning with specific timestamps and target answers. Common challenges include selecting informative contexts from extensive transcripts and ensuring generated questions meaningfully incorporate the target answer. To address the challenges, we introduce a novel framework utilizing large language models for dynamically selecting and rewriting contexts based on target timestamps and answers. First, our framework selects contexts from both lecture transcripts and video keyframes based on answer relevance and temporal proximity. Then, we integrate the contexts selected from both modalities and rewrite them into answer-containing knowledge statements, to enhance the logical connection between the contexts and the desired answer. This approach significantly improves the quality and relevance of the generated questions. Our dataset and code are released in https://github.com/mengxiayu/COSER.
QG-SMS: Enhancing Test Item Analysis via Student Modeling and Simulation
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:While the Question Generation (QG) task has been increasingly adopted in educational assessments, its evaluation remains limited by approaches that lack a clear connection to the educational values of test items. In this work, we introduce test item analysis, a method frequently used by educators to assess test question quality, into QG evaluation. Specifically, we construct pairs of candidate questions that differ in quality across dimensions such as topic coverage, item difficulty, item discrimination, and distractor efficiency. We then examine whether existing QG evaluation approaches can effectively distinguish these differences. Our findings reveal significant shortcomings in these approaches with respect to accurately assessing test item quality in relation to student performance. To address this gap, we propose a novel QG evaluation framework, QG-SMS, which leverages Large Language Model for Student Modeling and Simulation to perform test item analysis. As demonstrated in our extensive experiments and human evaluation study, the additional perspectives introduced by the simulated student profiles lead to a more effective and robust assessment of test items.
The Super Weight in Large Language Models
Nov 11, 2024
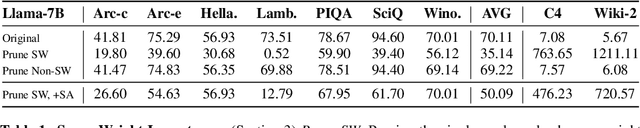
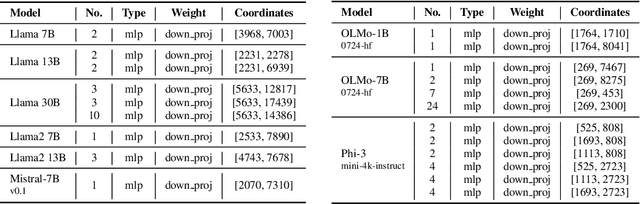
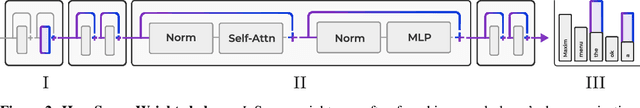
Abstract:Recent works have shown a surprising result: a small fraction of Large Language Model (LLM) parameter outliers are disproportionately important to the quality of the model. LLMs contain billions of parameters, so these small fractions, such as 0.01%, translate to hundreds of thousands of parameters. In this work, we present an even more surprising finding: Pruning as few as a single parameter can destroy an LLM's ability to generate text -- increasing perplexity by 3 orders of magnitude and reducing zero-shot accuracy to guessing. We propose a data-free method for identifying such parameters, termed super weights, using a single forward pass through the model. We additionally find that these super weights induce correspondingly rare and large activation outliers, termed super activations. When preserved with high precision, super activations can improve simple round-to-nearest quantization to become competitive with state-of-the-art methods. For weight quantization, we similarly find that by preserving the super weight and clipping other weight outliers, round-to-nearest quantization can scale to much larger block sizes than previously considered. To facilitate further research into super weights, we provide an index of super weight coordinates for common, openly available LLMs.
Reference-based Metrics Disprove Themselves in Question Generation
Mar 18, 2024Abstract:Reference-based metrics such as BLEU and BERTScore are widely used to evaluate question generation (QG). In this study, on QG benchmarks such as SQuAD and HotpotQA, we find that using human-written references cannot guarantee the effectiveness of the reference-based metrics. Most QG benchmarks have only one reference; we replicated the annotation process and collect another reference. A good metric was expected to grade a human-validated question no worse than generated questions. However, the results of reference-based metrics on our newly collected reference disproved the metrics themselves. We propose a reference-free metric consisted of multi-dimensional criteria such as naturalness, answerability, and complexity, utilizing large language models. These criteria are not constrained to the syntactic or semantic of a single reference question, and the metric does not require a diverse set of references. Experiments reveal that our metric accurately distinguishes between high-quality questions and flawed ones, and achieves state-of-the-art alignment with human judgment.
Pre-training Language Models for Comparative Reasoning
May 23, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel framework to pre-train language models for enhancing their abilities of comparative reasoning over texts. While recent research has developed models for NLP tasks that require comparative reasoning, they suffer from costly manual data labeling and limited generalizability to different tasks. Our approach involves a scalable method for collecting data for text-based entity comparison, which leverages both structured and unstructured data, and the design of three novel pre-training tasks. Evaluation on a range of downstream tasks including comparative question answering, question generation, and summarization shows that our pre-training framework significantly improves the comparative reasoning abilities of language models, especially under low-resource conditions. This work also releases the first integrated benchmark for comparative reasoning over texts.
A Survey of Multi-task Learning in Natural Language Processing: Regarding Task Relatedness and Training Methods
Apr 07, 2022



Abstract:Multi-task learning (MTL) has become increasingly popular in natural language processing (NLP) because it improves the performance of related tasks by exploiting their commonalities and differences. Nevertheless, it is still not understood very well how multi-task learning can be implemented based on the relatedness of training tasks. In this survey, we review recent advances of multi-task learning methods in NLP, with the aim of summarizing them into two general multi-task training methods based on their task relatedness: (i) joint training and (ii) multi-step training. We present examples in various NLP downstream applications, summarize the task relationships and discuss future directions of this promising topic.
Validating Label Consistency in NER Data Annotation
Jan 21, 2021



Abstract:Data annotation plays a crucial role in ensuring your named entity recognition (NER) projects are trained with the right information to learn from. Producing the most accurate labels is a challenge due to the complexity involved with annotation. Label inconsistency between multiple subsets of data annotation (e.g., training set and test set, or multiple training subsets) is an indicator of label mistakes. In this work, we present an empirical method to explore the relationship between label (in-)consistency and NER model performance. It can be used to validate the label consistency (or catches the inconsistency) in multiple sets of NER data annotation. In experiments, our method identified the label inconsistency of test data in SCIERC and CoNLL03 datasets (with 26.7% and 5.4% label mistakes). It validated the consistency in the corrected version of both datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge