Jingrun Zhang
BigCilin: An Automatic Chinese Open-domain Knowledge Graph with Fine-grained Hypernym-Hyponym Relations
Nov 07, 2022Abstract:This paper presents BigCilin, the first Chinese open-domain knowledge graph with fine-grained hypernym-hyponym re-lations which are extracted automatically from multiple sources for Chinese named entities. With the fine-grained hypernym-hyponym relations, BigCilin owns flexible semantic hierarchical structure. Since the hypernym-hyponym paths are automati-cally generated and one entity may have several senses, we provide a path disambi-guation solution to map a hypernym-hyponym path of one entity to its one sense on the condition that the path and the sense express the same meaning. In order to conveniently access our BigCilin Knowle-dge graph, we provide web interface in two ways. One is that it supports querying any Chinese named entity and browsing the extracted hypernym-hyponym paths surro-unding the query entity. The other is that it gives a top-down browsing view to illust-rate the overall hierarchical structure of our BigCilin knowledge graph over some sam-pled entities.
VEM$^2$L: A Plug-and-play Framework for Fusing Text and Structure Knowledge on Sparse Knowledge Graph Completion
Jul 12, 2022
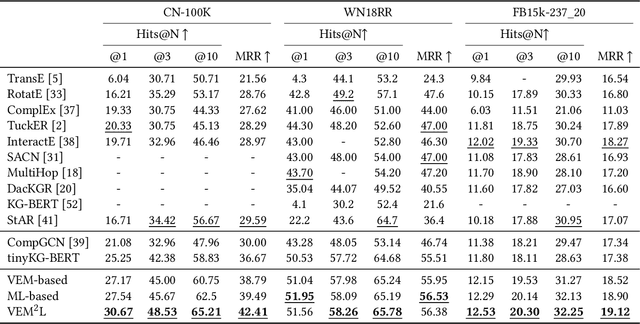
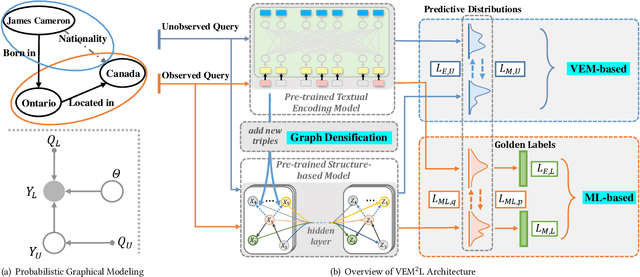
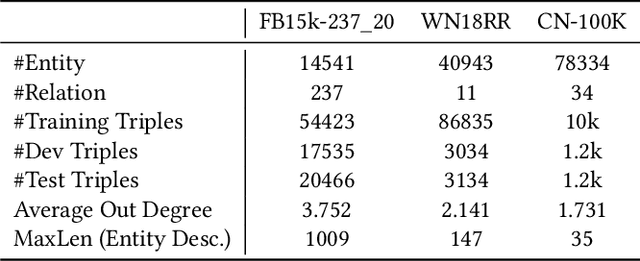
Abstract:Knowledge Graph Completion has been widely studied recently to complete missing elements within triples via mainly modeling graph structural features, but performs sensitive to the sparsity of graph structure. Relevant texts like entity names and descriptions, acting as another expression form for Knowledge Graphs (KGs), are expected to solve this challenge. Several methods have been proposed to utilize both structure and text messages with two encoders, but only achieved limited improvements due to the failure to balance weights between them. And reserving both structural and textual encoders during inference also suffers from heavily overwhelmed parameters. Motivated by Knowledge Distillation, we view knowledge as mappings from input to output probabilities and propose a plug-and-play framework VEM2L over sparse KGs to fuse knowledge extracted from text and structure messages into a unity. Specifically, we partition knowledge acquired by models into two nonoverlapping parts: one part is relevant to the fitting capacity upon training triples, which could be fused by motivating two encoders to learn from each other on training sets; the other reflects the generalization ability upon unobserved queries. And correspondingly, we propose a new fusion strategy proved by Variational EM algorithm to fuse the generalization ability of models, during which we also apply graph densification operations to further alleviate the sparse graph problem. By combining these two fusion methods, we propose VEM2L framework finally. Both detailed theoretical evidence, as well as quantitative and qualitative experiments, demonstrates the effectiveness and efficiency of our proposed framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge