Tharun Suresh
Grin
Characterizing the Entities in Harmful Memes: Who is the Hero, the Villain, the Victim?
Jan 26, 2023



Abstract:Memes can sway people's opinions over social media as they combine visual and textual information in an easy-to-consume manner. Since memes instantly turn viral, it becomes crucial to infer their intent and potentially associated harmfulness to take timely measures as needed. A common problem associated with meme comprehension lies in detecting the entities referenced and characterizing the role of each of these entities. Here, we aim to understand whether the meme glorifies, vilifies, or victimizes each entity it refers to. To this end, we address the task of role identification of entities in harmful memes, i.e., detecting who is the 'hero', the 'villain', and the 'victim' in the meme, if any. We utilize HVVMemes - a memes dataset on US Politics and Covid-19 memes, released recently as part of the CONSTRAINT@ACL-2022 shared-task. It contains memes, entities referenced, and their associated roles: hero, villain, victim, and other. We further design VECTOR (Visual-semantic role dEteCToR), a robust multi-modal framework for the task, which integrates entity-based contextual information in the multi-modal representation and compare it to several standard unimodal (text-only or image-only) or multi-modal (image+text) models. Our experimental results show that our proposed model achieves an improvement of 4% over the best baseline and 1% over the best competing stand-alone submission from the shared-task. Besides divulging an extensive experimental setup with comparative analyses, we finally highlight the challenges encountered in addressing the complex task of semantic role labeling within memes.
What do you MEME? Generating Explanations for Visual Semantic Role Labelling in Memes
Dec 20, 2022



Abstract:Memes are powerful means for effective communication on social media. Their effortless amalgamation of viral visuals and compelling messages can have far-reaching implications with proper marketing. Previous research on memes has primarily focused on characterizing their affective spectrum and detecting whether the meme's message insinuates any intended harm, such as hate, offense, racism, etc. However, memes often use abstraction, which can be elusive. Here, we introduce a novel task - EXCLAIM, generating explanations for visual semantic role labeling in memes. To this end, we curate ExHVV, a novel dataset that offers natural language explanations of connotative roles for three types of entities - heroes, villains, and victims, encompassing 4,680 entities present in 3K memes. We also benchmark ExHVV with several strong unimodal and multimodal baselines. Moreover, we posit LUMEN, a novel multimodal, multi-task learning framework that endeavors to address EXCLAIM optimally by jointly learning to predict the correct semantic roles and correspondingly to generate suitable natural language explanations. LUMEN distinctly outperforms the best baseline across 18 standard natural language generation evaluation metrics. Our systematic evaluation and analyses demonstrate that characteristic multimodal cues required for adjudicating semantic roles are also helpful for generating suitable explanations.
Predicting Hate Intensity of Twitter Conversation Threads
Jun 20, 2022
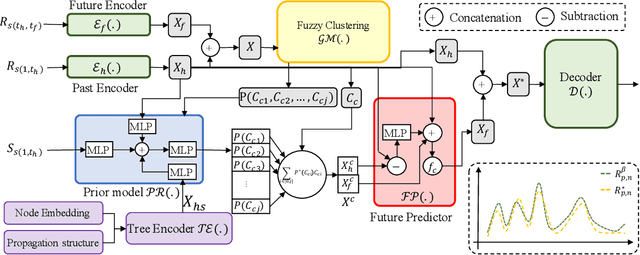

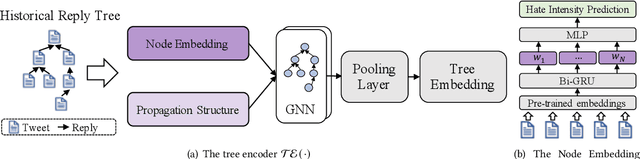
Abstract:Tweets are the most concise form of communication in online social media, wherein a single tweet has the potential to make or break the discourse of the conversation. Online hate speech is more accessible than ever, and stifling its propagation is of utmost importance for social media companies and users for congenial communication. Most of the research barring a recent few has focused on classifying an individual tweet regardless of the tweet thread/context leading up to that point. One of the classical approaches to curb hate speech is to adopt a reactive strategy after the hate speech postage. The ex-post facto strategy results in neglecting subtle posts that do not show the potential to instigate hate speech on their own but may portend in the subsequent discussion ensuing in the post's replies. In this paper, we propose DRAGNET++, which aims to predict the intensity of hatred that a tweet can bring in through its reply chain in the future. It uses the semantic and propagating structure of the tweet threads to maximize the contextual information leading up to and the fall of hate intensity at each subsequent tweet. We explore three publicly available Twitter datasets -- Anti-Racism contains the reply tweets of a collection of social media discourse on racist remarks during US political and Covid-19 background; Anti-Social presents a dataset of 40 million tweets amidst the COVID-19 pandemic on anti-social behaviours; and Anti-Asian presents Twitter datasets collated based on anti-Asian behaviours during COVID-19 pandemic. All the curated datasets consist of structural graph information of the Tweet threads. We show that DRAGNET++ outperforms all the state-of-the-art baselines significantly. It beats the best baseline by an 11% margin on the Person correlation coefficient and a decrease of 25% on RMSE for the Anti-Racism dataset with a similar performance on the other two datasets.
Counseling Summarization using Mental Health Knowledge Guided Utterance Filtering
Jun 08, 2022



Abstract:The psychotherapy intervention technique is a multifaceted conversation between a therapist and a patient. Unlike general clinical discussions, psychotherapy's core components (viz. symptoms) are hard to distinguish, thus becoming a complex problem to summarize later. A structured counseling conversation may contain discussions about symptoms, history of mental health issues, or the discovery of the patient's behavior. It may also contain discussion filler words irrelevant to a clinical summary. We refer to these elements of structured psychotherapy as counseling components. In this paper, the aim is mental health counseling summarization to build upon domain knowledge and to help clinicians quickly glean meaning. We create a new dataset after annotating 12.9K utterances of counseling components and reference summaries for each dialogue. Further, we propose ConSum, a novel counseling-component guided summarization model. ConSum undergoes three independent modules. First, to assess the presence of depressive symptoms, it filters utterances utilizing the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), while the second and third modules aim to classify counseling components. At last, we propose a problem-specific Mental Health Information Capture (MHIC) evaluation metric for counseling summaries. Our comparative study shows that we improve on performance and generate cohesive, semantic, and coherent summaries. We comprehensively analyze the generated summaries to investigate the capturing of psychotherapy elements. Human and clinical evaluations on the summary show that ConSum generates quality summary. Further, mental health experts validate the clinical acceptability of the ConSum. Lastly, we discuss the uniqueness in mental health counseling summarization in the real world and show evidences of its deployment on an online application with the support of mpathic.ai
A Comprehensive Understanding of Code-mixed Language Semantics using Hierarchical Transformer
Apr 27, 2022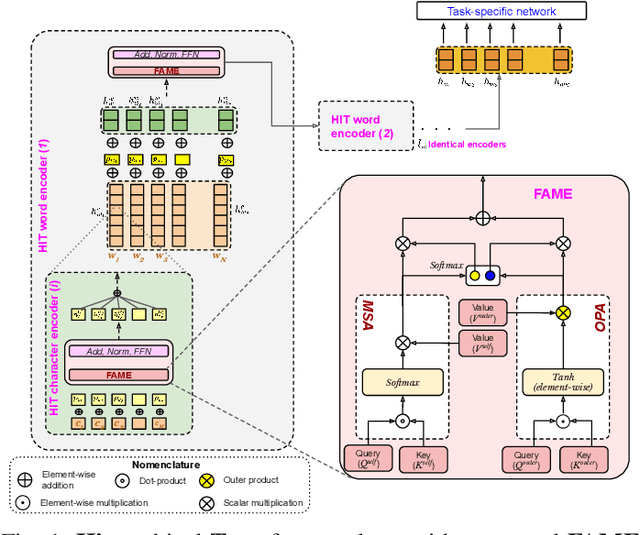


Abstract:Being a popular mode of text-based communication in multilingual communities, code-mixing in online social media has became an important subject to study. Learning the semantics and morphology of code-mixed language remains a key challenge, due to scarcity of data and unavailability of robust and language-invariant representation learning technique. Any morphologically-rich language can benefit from character, subword, and word-level embeddings, aiding in learning meaningful correlations. In this paper, we explore a hierarchical transformer-based architecture (HIT) to learn the semantics of code-mixed languages. HIT consists of multi-headed self-attention and outer product attention components to simultaneously comprehend the semantic and syntactic structures of code-mixed texts. We evaluate the proposed method across 6 Indian languages (Bengali, Gujarati, Hindi, Tamil, Telugu and Malayalam) and Spanish for 9 NLP tasks on 17 datasets. The HIT model outperforms state-of-the-art code-mixed representation learning and multilingual language models in all tasks. We further demonstrate the generalizability of the HIT architecture using masked language modeling-based pre-training, zero-shot learning, and transfer learning approaches. Our empirical results show that the pre-training objectives significantly improve the performance on downstream tasks.
Handling Bias in Toxic Speech Detection: A Survey
Feb 02, 2022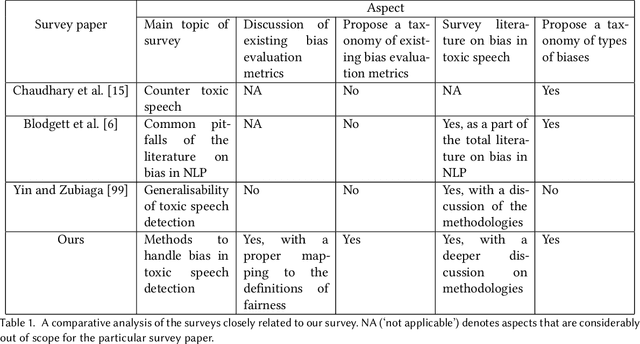
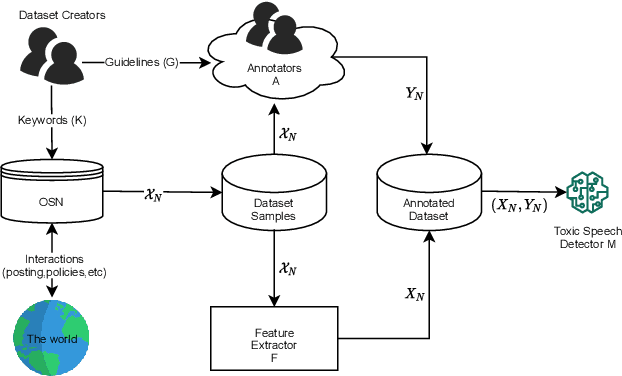
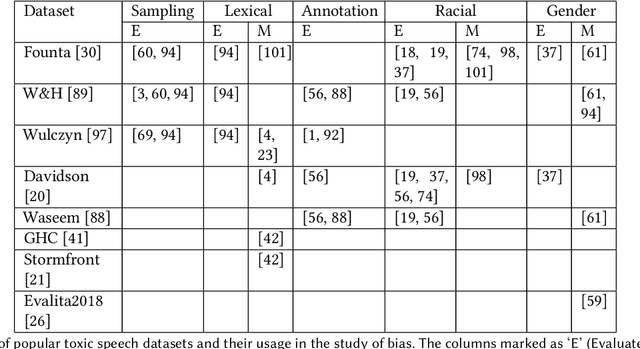
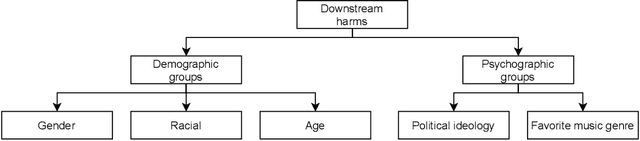
Abstract:The massive growth of social media usage has witnessed a tsunami of online toxicity in teams of hate speech, abusive posts, cyberbullying, etc. Detecting online toxicity is challenging due to its inherent subjectivity. Factors such as the context of the speech, geography, socio-political climate, and background of the producers and consumers of the posts play a crucial role in determining if the content can be flagged as toxic. Adoption of automated toxicity detection models in production can lead to a sidelining of the various demographic and psychographic groups they aim to help in the first place. It has piqued researchers' interest in examining unintended biases and their mitigation. Due to the nascent and multi-faceted nature of the work, complete literature is chaotic in its terminologies, techniques, and findings. In this paper, we put together a systematic study to discuss the limitations and challenges of existing methods. We start by developing a taxonomy for categorising various unintended biases and a suite of evaluation metrics proposed to quantify such biases. We take a closer look at each proposed method for evaluating and mitigating bias in toxic speech detection. To examine the limitations of existing methods, we also conduct a case study to introduce the concept of bias shift due to knowledge-based bias mitigation methods. The survey concludes with an overview of the critical challenges, research gaps and future directions. While reducing toxicity on online platforms continues to be an active area of research, a systematic study of various biases and their mitigation strategies will help the research community produce robust and fair models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge