Md Shad Akhtar
MAMA-Memeia! Multi-Aspect Multi-Agent Collaboration for Depressive Symptoms Identification in Memes
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Over the past years, memes have evolved from being exclusively a medium of humorous exchanges to one that allows users to express a range of emotions freely and easily. With the ever-growing utilization of memes in expressing depressive sentiments, we conduct a study on identifying depressive symptoms exhibited by memes shared by users of online social media platforms. We introduce RESTOREx as a vital resource for detecting depressive symptoms in memes on social media through the Large Language Model (LLM) generated and human-annotated explanations. We introduce MAMAMemeia, a collaborative multi-agent multi-aspect discussion framework grounded in the clinical psychology method of Cognitive Analytic Therapy (CAT) Competencies. MAMAMemeia improves upon the current state-of-the-art by 7.55% in macro-F1 and is established as the new benchmark compared to over 30 methods.
Target-Augmented Shared Fusion-based Multimodal Sarcasm Explanation Generation
Feb 11, 2025
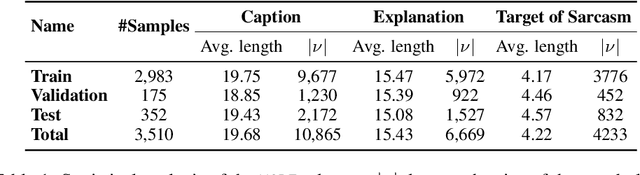
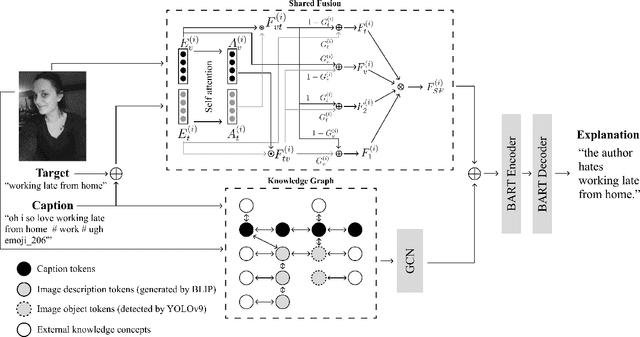
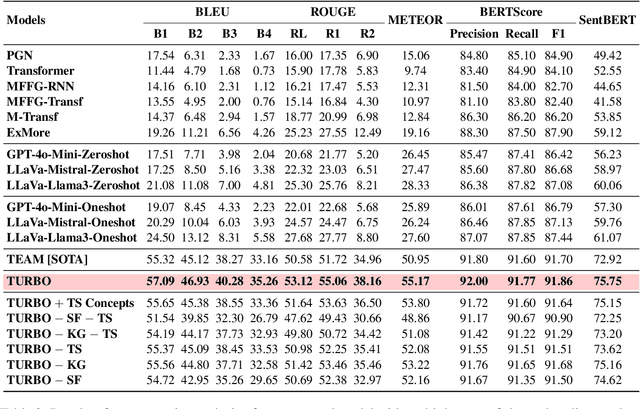
Abstract:Sarcasm is a linguistic phenomenon that intends to ridicule a target (e.g., entity, event, or person) in an inherent way. Multimodal Sarcasm Explanation (MuSE) aims at revealing the intended irony in a sarcastic post using a natural language explanation. Though important, existing systems overlooked the significance of the target of sarcasm in generating explanations. In this paper, we propose a Target-aUgmented shaRed fusion-Based sarcasm explanatiOn model, aka. TURBO. We design a novel shared-fusion mechanism to leverage the inter-modality relationships between an image and its caption. TURBO assumes the target of the sarcasm and guides the multimodal shared fusion mechanism in learning intricacies of the intended irony for explanations. We evaluate our proposed TURBO model on the MORE+ dataset. Comparison against multiple baselines and state-of-the-art models signifies the performance improvement of TURBO by an average margin of $+3.3\%$. Moreover, we explore LLMs in zero and one-shot settings for our task and observe that LLM-generated explanation, though remarkable, often fails to capture the critical nuances of the sarcasm. Furthermore, we supplement our study with extensive human evaluation on TURBO's generated explanations and find them out to be comparatively better than other systems.
Incongruence Identification in Eyewitness Testimony
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:Incongruence detection in eyewitness narratives is critical for understanding the reliability of testimonies, yet traditional approaches often fail to address the nuanced inconsistencies inherent in such accounts. In this paper, we introduce a novel task of incongruence detection in eyewitness testimonies. Given a pair of testimonies containing of multiple pairs of question and answer by two subjects, we identify contextually related incongruence between the two subjects. We also mark the span of incongruences in the utterances. To achieve this, we developed MIND(MultI-EyewitNess Deception) - a comprehensive dataset consisting of 2927 pairs of contextually related answers designed to capture both explicit and implicit contradictions. INstruction - TunEd iNcongruity Detection framework based on 6W and multi-hop reasoning approach, aka. INTEND. Drawing from investigative techniques, INTEND address the task as a close-style problem, contradicting on the who, what, when, where and why aspect of the content. Our findings shows that prompt tuning, especially when utilizing our framework, enhances the detection of incongruences by a margin of +5.63 percent. We compare our approach with multiple fine-tuning and prompt tuning techniques on MLMs and LLMs. Emperical results demonstrate convincing performance improvement in F1-score over fine-tuned and regular prompt-tuning techniques, highlighting the effectiveness of our approach.
Figurative-cum-Commonsense Knowledge Infusion for Multimodal Mental Health Meme Classification
Jan 25, 2025Abstract:The expression of mental health symptoms through non-traditional means, such as memes, has gained remarkable attention over the past few years, with users often highlighting their mental health struggles through figurative intricacies within memes. While humans rely on commonsense knowledge to interpret these complex expressions, current Multimodal Language Models (MLMs) struggle to capture these figurative aspects inherent in memes. To address this gap, we introduce a novel dataset, AxiOM, derived from the GAD anxiety questionnaire, which categorizes memes into six fine-grained anxiety symptoms. Next, we propose a commonsense and domain-enriched framework, M3H, to enhance MLMs' ability to interpret figurative language and commonsense knowledge. The overarching goal remains to first understand and then classify the mental health symptoms expressed in memes. We benchmark M3H against 6 competitive baselines (with 20 variations), demonstrating improvements in both quantitative and qualitative metrics, including a detailed human evaluation. We observe a clear improvement of 4.20% and 4.66% on weighted-F1 metric. To assess the generalizability, we perform extensive experiments on a public dataset, RESTORE, for depressive symptom identification, presenting an extensive ablation study that highlights the contribution of each module in both datasets. Our findings reveal limitations in existing models and the advantage of employing commonsense to enhance figurative understanding.
Trust Modeling in Counseling Conversations: A Benchmark Study
Jan 06, 2025Abstract:In mental health counseling, a variety of earlier studies have focused on dialogue modeling. However, most of these studies give limited to no emphasis on the quality of interaction between a patient and a therapist. The therapeutic bond between a patient and a therapist directly correlates with effective mental health counseling. It involves developing the patient's trust on the therapist over the course of counseling. To assess the therapeutic bond in counseling, we introduce trust as a therapist-assistive metric. Our definition of trust involves patients' willingness and openness to express themselves and, consequently, receive better care. We conceptualize it as a dynamic trajectory observable through textual interactions during the counseling. To facilitate trust modeling, we present MENTAL-TRUST, a novel counseling dataset comprising manual annotation of 212 counseling sessions with first-of-its-kind seven expert-verified ordinal trust levels. We project our problem statement as an ordinal classification task for trust quantification and propose a new benchmark, TrustBench, comprising a suite of classical and state-of-the-art language models on MENTAL-TRUST. We evaluate the performance across a suite of metrics and lay out an exhaustive set of findings. Our study aims to unfold how trust evolves in therapeutic interactions.
Crowd Intelligence for Early Misinformation Prediction on Social Media
Aug 08, 2024



Abstract:Misinformation spreads rapidly on social media, causing serious damage by influencing public opinion, promoting dangerous behavior, or eroding trust in reliable sources. It spreads too fast for traditional fact-checking, stressing the need for predictive methods. We introduce CROWDSHIELD, a crowd intelligence-based method for early misinformation prediction. We hypothesize that the crowd's reactions to misinformation reveal its accuracy. Furthermore, we hinge upon exaggerated assertions/claims and replies with particular positions/stances on the source post within a conversation thread. We employ Q-learning to capture the two dimensions -- stances and claims. We utilize deep Q-learning due to its proficiency in navigating complex decision spaces and effectively learning network properties. Additionally, we use a transformer-based encoder to develop a comprehensive understanding of both content and context. This multifaceted approach helps ensure the model pays attention to user interaction and stays anchored in the communication's content. We propose MIST, a manually annotated misinformation detection Twitter corpus comprising nearly 200 conversation threads with more than 14K replies. In experiments, CROWDSHIELD outperformed ten baseline systems, achieving an improvement of ~4% macro-F1 score. We conduct an ablation study and error analysis to validate our proposed model's performance. The source code and dataset are available at https://github.com/LCS2-IIITD/CrowdShield.git.
Tox-BART: Leveraging Toxicity Attributes for Explanation Generation of Implicit Hate Speech
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Employing language models to generate explanations for an incoming implicit hate post is an active area of research. The explanation is intended to make explicit the underlying stereotype and aid content moderators. The training often combines top-k relevant knowledge graph (KG) tuples to provide world knowledge and improve performance on standard metrics. Interestingly, our study presents conflicting evidence for the role of the quality of KG tuples in generating implicit explanations. Consequently, simpler models incorporating external toxicity signals outperform KG-infused models. Compared to the KG-based setup, we observe a comparable performance for SBIC (LatentHatred) datasets with a performance variation of +0.44 (+0.49), +1.83 (-1.56), and -4.59 (+0.77) in BLEU, ROUGE-L, and BERTScore. Further human evaluation and error analysis reveal that our proposed setup produces more precise explanations than zero-shot GPT-3.5, highlighting the intricate nature of the task.
Synthetic Data Generation and Joint Learning for Robust Code-Mixed Translation
Mar 25, 2024Abstract:The widespread online communication in a modern multilingual world has provided opportunities to blend more than one language (aka code-mixed language) in a single utterance. This has resulted a formidable challenge for the computational models due to the scarcity of annotated data and presence of noise. A potential solution to mitigate the data scarcity problem in low-resource setup is to leverage existing data in resource-rich language through translation. In this paper, we tackle the problem of code-mixed (Hinglish and Bengalish) to English machine translation. First, we synthetically develop HINMIX, a parallel corpus of Hinglish to English, with ~4.2M sentence pairs. Subsequently, we propose RCMT, a robust perturbation based joint-training model that learns to handle noise in the real-world code-mixed text by parameter sharing across clean and noisy words. Further, we show the adaptability of RCMT in a zero-shot setup for Bengalish to English translation. Our evaluation and comprehensive analyses qualitatively and quantitatively demonstrate the superiority of RCMT over state-of-the-art code-mixed and robust translation methods.
Intent-conditioned and Non-toxic Counterspeech Generation using Multi-Task Instruction Tuning with RLAIF
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Counterspeech, defined as a response to mitigate online hate speech, is increasingly used as a non-censorial solution. Addressing hate speech effectively involves dispelling the stereotypes, prejudices, and biases often subtly implied in brief, single-sentence statements or abuses. These implicit expressions challenge language models, especially in seq2seq tasks, as model performance typically excels with longer contexts. Our study introduces CoARL, a novel framework enhancing counterspeech generation by modeling the pragmatic implications underlying social biases in hateful statements. CoARL's first two phases involve sequential multi-instruction tuning, teaching the model to understand intents, reactions, and harms of offensive statements, and then learning task-specific low-rank adapter weights for generating intent-conditioned counterspeech. The final phase uses reinforcement learning to fine-tune outputs for effectiveness and non-toxicity. CoARL outperforms existing benchmarks in intent-conditioned counterspeech generation, showing an average improvement of 3 points in intent-conformity and 4 points in argument-quality metrics. Extensive human evaluation supports CoARL's efficacy in generating superior and more context-appropriate responses compared to existing systems, including prominent LLMs like ChatGPT.
SemEval 2024 -- Task 10: Emotion Discovery and Reasoning its Flip in Conversation
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:We present SemEval-2024 Task 10, a shared task centred on identifying emotions and finding the rationale behind their flips within monolingual English and Hindi-English code-mixed dialogues. This task comprises three distinct subtasks - emotion recognition in conversation for code-mixed dialogues, emotion flip reasoning for code-mixed dialogues, and emotion flip reasoning for English dialogues. Participating systems were tasked to automatically execute one or more of these subtasks. The datasets for these tasks comprise manually annotated conversations focusing on emotions and triggers for emotion shifts (The task data is available at https://github.com/LCS2-IIITD/EDiReF-SemEval2024.git). A total of 84 participants engaged in this task, with the most adept systems attaining F1-scores of 0.70, 0.79, and 0.76 for the respective subtasks. This paper summarises the results and findings from 24 teams alongside their system descriptions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge