Shivani Kumar
Are Rules Meant to be Broken? Understanding Multilingual Moral Reasoning as a Computational Pipeline with UniMoral
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Moral reasoning is a complex cognitive process shaped by individual experiences and cultural contexts and presents unique challenges for computational analysis. While natural language processing (NLP) offers promising tools for studying this phenomenon, current research lacks cohesion, employing discordant datasets and tasks that examine isolated aspects of moral reasoning. We bridge this gap with UniMoral, a unified dataset integrating psychologically grounded and social-media-derived moral dilemmas annotated with labels for action choices, ethical principles, contributing factors, and consequences, alongside annotators' moral and cultural profiles. Recognizing the cultural relativity of moral reasoning, UniMoral spans six languages, Arabic, Chinese, English, Hindi, Russian, and Spanish, capturing diverse socio-cultural contexts. We demonstrate UniMoral's utility through a benchmark evaluations of three large language models (LLMs) across four tasks: action prediction, moral typology classification, factor attribution analysis, and consequence generation. Key findings reveal that while implicitly embedded moral contexts enhance the moral reasoning capability of LLMs, there remains a critical need for increasingly specialized approaches to further advance moral reasoning in these models.
Real or Robotic? Assessing Whether LLMs Accurately Simulate Qualities of Human Responses in Dialogue
Sep 16, 2024Abstract:Studying and building datasets for dialogue tasks is both expensive and time-consuming due to the need to recruit, train, and collect data from study participants. In response, much recent work has sought to use large language models (LLMs) to simulate both human-human and human-LLM interactions, as they have been shown to generate convincingly human-like text in many settings. However, to what extent do LLM-based simulations \textit{actually} reflect human dialogues? In this work, we answer this question by generating a large-scale dataset of 100,000 paired LLM-LLM and human-LLM dialogues from the WildChat dataset and quantifying how well the LLM simulations align with their human counterparts. Overall, we find relatively low alignment between simulations and human interactions, demonstrating a systematic divergence along the multiple textual properties, including style and content. Further, in comparisons of English, Chinese, and Russian dialogues, we find that models perform similarly. Our results suggest that LLMs generally perform better when the human themself writes in a way that is more similar to the LLM's own style.
SemEval 2024 -- Task 10: Emotion Discovery and Reasoning its Flip in Conversation
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:We present SemEval-2024 Task 10, a shared task centred on identifying emotions and finding the rationale behind their flips within monolingual English and Hindi-English code-mixed dialogues. This task comprises three distinct subtasks - emotion recognition in conversation for code-mixed dialogues, emotion flip reasoning for code-mixed dialogues, and emotion flip reasoning for English dialogues. Participating systems were tasked to automatically execute one or more of these subtasks. The datasets for these tasks comprise manually annotated conversations focusing on emotions and triggers for emotion shifts (The task data is available at https://github.com/LCS2-IIITD/EDiReF-SemEval2024.git). A total of 84 participants engaged in this task, with the most adept systems attaining F1-scores of 0.70, 0.79, and 0.76 for the respective subtasks. This paper summarises the results and findings from 24 teams alongside their system descriptions.
Exploring the Efficacy of Large Language Models in Summarizing Mental Health Counseling Sessions: A Benchmark Study
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:Comprehensive summaries of sessions enable an effective continuity in mental health counseling, facilitating informed therapy planning. Yet, manual summarization presents a significant challenge, diverting experts' attention from the core counseling process. This study evaluates the effectiveness of state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs) in selectively summarizing various components of therapy sessions through aspect-based summarization, aiming to benchmark their performance. We introduce MentalCLOUDS, a counseling-component guided summarization dataset consisting of 191 counseling sessions with summaries focused on three distinct counseling components (aka counseling aspects). Additionally, we assess the capabilities of 11 state-of-the-art LLMs in addressing the task of component-guided summarization in counseling. The generated summaries are evaluated quantitatively using standard summarization metrics and verified qualitatively by mental health professionals. Our findings demonstrate the superior performance of task-specific LLMs such as MentalLlama, Mistral, and MentalBART in terms of standard quantitative metrics such as Rouge-1, Rouge-2, Rouge-L, and BERTScore across all aspects of counseling components. Further, expert evaluation reveals that Mistral supersedes both MentalLlama and MentalBART based on six parameters -- affective attitude, burden, ethicality, coherence, opportunity costs, and perceived effectiveness. However, these models share the same weakness by demonstrating a potential for improvement in the opportunity costs and perceived effectiveness metrics.
Harmonizing Code-mixed Conversations: Personality-assisted Code-mixed Response Generation in Dialogues
Jan 18, 2024Abstract:Code-mixing, the blending of multiple languages within a single conversation, introduces a distinctive challenge, particularly in the context of response generation. Capturing the intricacies of code-mixing proves to be a formidable task, given the wide-ranging variations influenced by individual speaking styles and cultural backgrounds. In this study, we explore response generation within code-mixed conversations. We introduce a novel approach centered on harnessing the Big Five personality traits acquired in an unsupervised manner from the conversations to bolster the performance of response generation. These inferred personality attributes are seamlessly woven into the fabric of the dialogue context, using a novel fusion mechanism, PA3. It uses an effective two-step attention formulation to fuse the dialogue and personality information. This fusion not only enhances the contextual relevance of generated responses but also elevates the overall performance of the model. Our experimental results, grounded in a dataset comprising of multi-party Hindi-English code-mix conversations, highlight the substantial advantages offered by personality-infused models over their conventional counterparts. This is evident in the increase observed in ROUGE and BLUE scores for the response generation task when the identified personality is seamlessly integrated into the dialogue context. Qualitative assessment for personality identification and response generation aligns well with our quantitative results.
From Multilingual Complexity to Emotional Clarity: Leveraging Commonsense to Unveil Emotions in Code-Mixed Dialogues
Oct 19, 2023Abstract:Understanding emotions during conversation is a fundamental aspect of human communication, driving NLP research for Emotion Recognition in Conversation (ERC). While considerable research has focused on discerning emotions of individual speakers in monolingual dialogues, understanding the emotional dynamics in code-mixed conversations has received relatively less attention. This motivates our undertaking of ERC for code-mixed conversations in this study. Recognizing that emotional intelligence encompasses a comprehension of worldly knowledge, we propose an innovative approach that integrates commonsense information with dialogue context to facilitate a deeper understanding of emotions. To achieve this, we devise an efficient pipeline that extracts relevant commonsense from existing knowledge graphs based on the code-mixed input. Subsequently, we develop an advanced fusion technique that seamlessly combines the acquired commonsense information with the dialogue representation obtained from a dedicated dialogue understanding module. Our comprehensive experimentation showcases the substantial performance improvement obtained through the systematic incorporation of commonsense in ERC. Both quantitative assessments and qualitative analyses further corroborate the validity of our hypothesis, reaffirming the pivotal role of commonsense integration in enhancing ERC.
Dialogue Agents 101: A Beginner's Guide to Critical Ingredients for Designing Effective Conversational Systems
Jul 14, 2023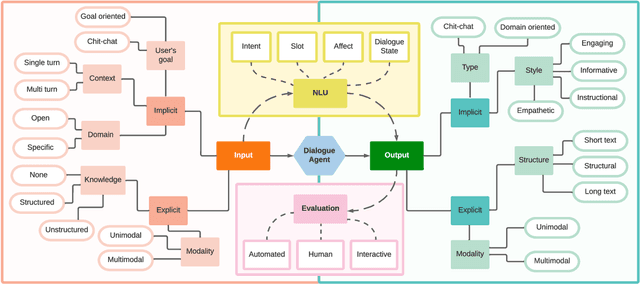
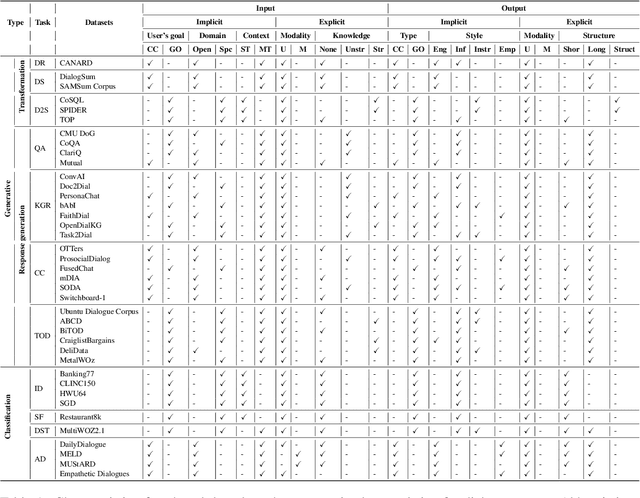
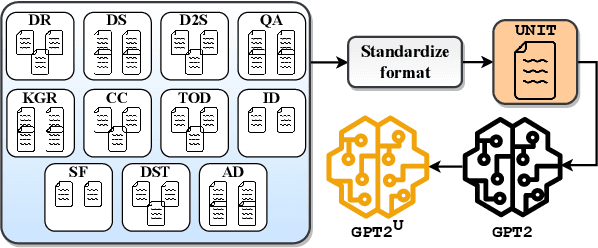
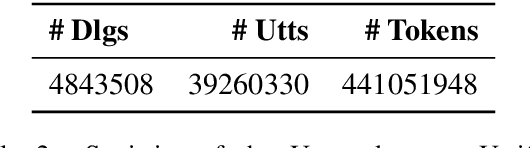
Abstract:Sharing ideas through communication with peers is the primary mode of human interaction. Consequently, extensive research has been conducted in the area of conversational AI, leading to an increase in the availability and diversity of conversational tasks, datasets, and methods. However, with numerous tasks being explored simultaneously, the current landscape of conversational AI becomes fragmented. Therefore, initiating a well-thought-out model for a dialogue agent can pose significant challenges for a practitioner. Towards highlighting the critical ingredients needed for a practitioner to design a dialogue agent from scratch, the current study provides a comprehensive overview of the primary characteristics of a dialogue agent, the supporting tasks, their corresponding open-domain datasets, and the methods used to benchmark these datasets. We observe that different methods have been used to tackle distinct dialogue tasks. However, building separate models for each task is costly and does not leverage the correlation among the several tasks of a dialogue agent. As a result, recent trends suggest a shift towards building unified foundation models. To this end, we propose UNIT, a UNified dIalogue dataseT constructed from conversations of existing datasets for different dialogue tasks capturing the nuances for each of them. We also examine the evaluation strategies used to measure the performance of dialogue agents and highlight the scope for future research in the area of conversational AI.
Emotion Flip Reasoning in Multiparty Conversations
Jun 24, 2023Abstract:In a conversational dialogue, speakers may have different emotional states and their dynamics play an important role in understanding dialogue's emotional discourse. However, simply detecting emotions is not sufficient to entirely comprehend the speaker-specific changes in emotion that occur during a conversation. To understand the emotional dynamics of speakers in an efficient manner, it is imperative to identify the rationale or instigator behind any changes or flips in emotion expressed by the speaker. In this paper, we explore the task called Instigator based Emotion Flip Reasoning (EFR), which aims to identify the instigator behind a speaker's emotion flip within a conversation. For example, an emotion flip from joy to anger could be caused by an instigator like threat. To facilitate this task, we present MELD-I, a dataset that includes ground-truth EFR instigator labels, which are in line with emotional psychology. To evaluate the dataset, we propose a novel neural architecture called TGIF, which leverages Transformer encoders and stacked GRUs to capture the dialogue context, speaker dynamics, and emotion sequence in a conversation. Our evaluation demonstrates state-of-the-art performance (+4-12% increase in F1-score) against five baselines used for the task. Further, we establish the generalizability of TGIF on an unseen dataset in a zero-shot setting. Additionally, we provide a detailed analysis of the competing models, highlighting the advantages and limitations of our neural architecture.
Speaker Profiling in Multiparty Conversations
Apr 19, 2023Abstract:In conversational settings, individuals exhibit unique behaviors, rendering a one-size-fits-all approach insufficient for generating responses by dialogue agents. Although past studies have aimed to create personalized dialogue agents using speaker persona information, they have relied on the assumption that the speaker's persona is already provided. However, this assumption is not always valid, especially when it comes to chatbots utilized in industries like banking, hotel reservations, and airline bookings. This research paper aims to fill this gap by exploring the task of Speaker Profiling in Conversations (SPC). The primary objective of SPC is to produce a summary of persona characteristics for each individual speaker present in a dialogue. To accomplish this, we have divided the task into three subtasks: persona discovery, persona-type identification, and persona-value extraction. Given a dialogue, the first subtask aims to identify all utterances that contain persona information. Subsequently, the second task evaluates these utterances to identify the type of persona information they contain, while the third subtask identifies the specific persona values for each identified type. To address the task of SPC, we have curated a new dataset named SPICE, which comes with specific labels. We have evaluated various baselines on this dataset and benchmarked it with a new neural model, SPOT, which we introduce in this paper. Furthermore, we present a comprehensive analysis of SPOT, examining the limitations of individual modules both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Explaining (Sarcastic) Utterances to Enhance Affect Understanding in Multimodal Dialogues
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:Conversations emerge as the primary media for exchanging ideas and conceptions. From the listener's perspective, identifying various affective qualities, such as sarcasm, humour, and emotions, is paramount for comprehending the true connotation of the emitted utterance. However, one of the major hurdles faced in learning these affect dimensions is the presence of figurative language, viz. irony, metaphor, or sarcasm. We hypothesize that any detection system constituting the exhaustive and explicit presentation of the emitted utterance would improve the overall comprehension of the dialogue. To this end, we explore the task of Sarcasm Explanation in Dialogues, which aims to unfold the hidden irony behind sarcastic utterances. We propose MOSES, a deep neural network, which takes a multimodal (sarcastic) dialogue instance as an input and generates a natural language sentence as its explanation. Subsequently, we leverage the generated explanation for various natural language understanding tasks in a conversational dialogue setup, such as sarcasm detection, humour identification, and emotion recognition. Our evaluation shows that MOSES outperforms the state-of-the-art system for SED by an average of ~2% on different evaluation metrics, such as ROUGE, BLEU, and METEOR. Further, we observe that leveraging the generated explanation advances three downstream tasks for affect classification - an average improvement of ~14% F1-score in the sarcasm detection task and ~2% in the humour identification and emotion recognition task. We also perform extensive analyses to assess the quality of the results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge