Shweta Yadav
MAMA-Memeia! Multi-Aspect Multi-Agent Collaboration for Depressive Symptoms Identification in Memes
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Over the past years, memes have evolved from being exclusively a medium of humorous exchanges to one that allows users to express a range of emotions freely and easily. With the ever-growing utilization of memes in expressing depressive sentiments, we conduct a study on identifying depressive symptoms exhibited by memes shared by users of online social media platforms. We introduce RESTOREx as a vital resource for detecting depressive symptoms in memes on social media through the Large Language Model (LLM) generated and human-annotated explanations. We introduce MAMAMemeia, a collaborative multi-agent multi-aspect discussion framework grounded in the clinical psychology method of Cognitive Analytic Therapy (CAT) Competencies. MAMAMemeia improves upon the current state-of-the-art by 7.55% in macro-F1 and is established as the new benchmark compared to over 30 methods.
A Dataset and Benchmark for Consumer Healthcare Question Summarization
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:The quest for seeking health information has swamped the web with consumers health-related questions. Generally, consumers use overly descriptive and peripheral information to express their medical condition or other healthcare needs, contributing to the challenges of natural language understanding. One way to address this challenge is to summarize the questions and distill the key information of the original question. Recently, large-scale datasets have significantly propelled the development of several summarization tasks, such as multi-document summarization and dialogue summarization. However, a lack of a domain-expert annotated dataset for the consumer healthcare questions summarization task inhibits the development of an efficient summarization system. To address this issue, we introduce a new dataset, CHQ-Sum,m that contains 1507 domain-expert annotated consumer health questions and corresponding summaries. The dataset is derived from the community question answering forum and therefore provides a valuable resource for understanding consumer health-related posts on social media. We benchmark the dataset on multiple state-of-the-art summarization models to show the effectiveness of the dataset
Figurative-cum-Commonsense Knowledge Infusion for Multimodal Mental Health Meme Classification
Jan 25, 2025Abstract:The expression of mental health symptoms through non-traditional means, such as memes, has gained remarkable attention over the past few years, with users often highlighting their mental health struggles through figurative intricacies within memes. While humans rely on commonsense knowledge to interpret these complex expressions, current Multimodal Language Models (MLMs) struggle to capture these figurative aspects inherent in memes. To address this gap, we introduce a novel dataset, AxiOM, derived from the GAD anxiety questionnaire, which categorizes memes into six fine-grained anxiety symptoms. Next, we propose a commonsense and domain-enriched framework, M3H, to enhance MLMs' ability to interpret figurative language and commonsense knowledge. The overarching goal remains to first understand and then classify the mental health symptoms expressed in memes. We benchmark M3H against 6 competitive baselines (with 20 variations), demonstrating improvements in both quantitative and qualitative metrics, including a detailed human evaluation. We observe a clear improvement of 4.20% and 4.66% on weighted-F1 metric. To assess the generalizability, we perform extensive experiments on a public dataset, RESTORE, for depressive symptom identification, presenting an extensive ablation study that highlights the contribution of each module in both datasets. Our findings reveal limitations in existing models and the advantage of employing commonsense to enhance figurative understanding.
No perspective, no perception!! Perspective-aware Healthcare Answer Summarization
Jun 13, 2024

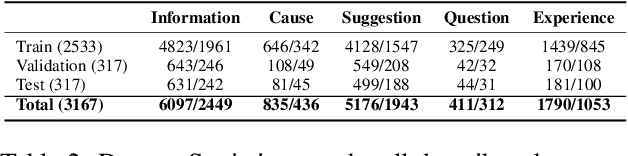

Abstract:Healthcare Community Question Answering (CQA) forums offer an accessible platform for individuals seeking information on various healthcare-related topics. People find such platforms suitable for self-disclosure, seeking medical opinions, finding simplified explanations for their medical conditions, and answering others' questions. However, answers on these forums are typically diverse and prone to off-topic discussions. It can be challenging for readers to sift through numerous answers and extract meaningful insights, making answer summarization a crucial task for CQA forums. While several efforts have been made to summarize the community answers, most of them are limited to the open domain and overlook the different perspectives offered by these answers. To address this problem, this paper proposes a novel task of perspective-specific answer summarization. We identify various perspectives, within healthcare-related responses and frame a perspective-driven abstractive summary covering all responses. To achieve this, we annotate 3167 CQA threads with 6193 perspective-aware summaries in our PUMA dataset. Further, we propose PLASMA, a prompt-driven controllable summarization model. To encapsulate the perspective-specific conditions, we design an energy-controlled loss function for the optimization. We also leverage the prefix tuner to learn the intricacies of the health-care perspective summarization. Our evaluation against five baselines suggests the superior performance of PLASMA by a margin of 1.5-21% improvement. We supplement our experiments with ablation and qualitative analysis.
Aspect-oriented Consumer Health Answer Summarization
May 10, 2024Abstract:Community Question-Answering (CQA) forums have revolutionized how people seek information, especially those related to their healthcare needs, placing their trust in the collective wisdom of the public. However, there can be several answers in response to a single query, which makes it hard to grasp the key information related to the specific health concern. Typically, CQA forums feature a single top-voted answer as a representative summary for each query. However, a single answer overlooks the alternative solutions and other information frequently offered in other responses. Our research focuses on aspect-based summarization of health answers to address this limitation. Summarization of responses under different aspects such as suggestions, information, personal experiences, and questions can enhance the usability of the platforms. We formalize a multi-stage annotation guideline and contribute a unique dataset comprising aspect-based human-written health answer summaries. We build an automated multi-faceted answer summarization pipeline with this dataset based on task-specific fine-tuning of several state-of-the-art models. The pipeline leverages question similarity to retrieve relevant answer sentences, subsequently classifying them into the appropriate aspect type. Following this, we employ several recent abstractive summarization models to generate aspect-based summaries. Finally, we present a comprehensive human analysis and find that our summaries rank high in capturing relevant content and a wide range of solutions.
Towards Enhancing Health Coaching Dialogue in Low-Resource Settings
Apr 13, 2024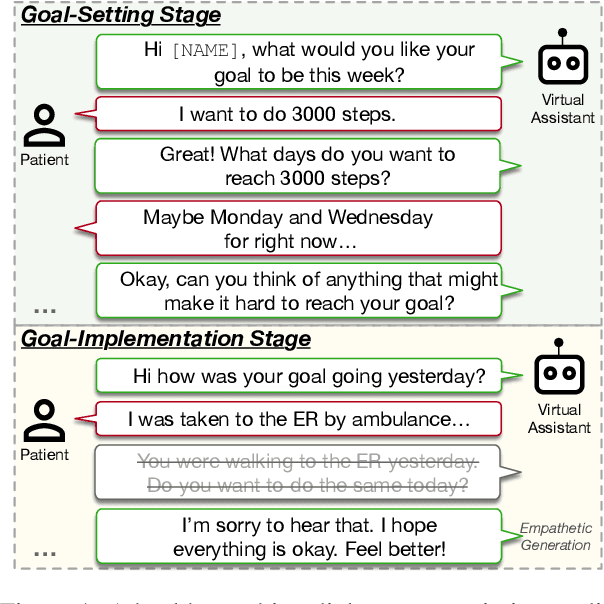
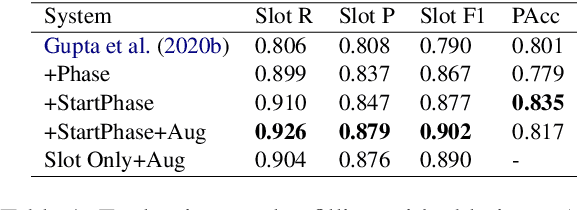
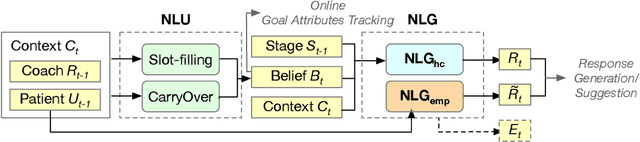
Abstract:Health coaching helps patients identify and accomplish lifestyle-related goals, effectively improving the control of chronic diseases and mitigating mental health conditions. However, health coaching is cost-prohibitive due to its highly personalized and labor-intensive nature. In this paper, we propose to build a dialogue system that converses with the patients, helps them create and accomplish specific goals, and can address their emotions with empathy. However, building such a system is challenging since real-world health coaching datasets are limited and empathy is subtle. Thus, we propose a modularized health coaching dialogue system with simplified NLU and NLG frameworks combined with mechanism-conditioned empathetic response generation. Through automatic and human evaluation, we show that our system generates more empathetic, fluent, and coherent responses and outperforms the state-of-the-art in NLU tasks while requiring less annotation. We view our approach as a key step towards building automated and more accessible health coaching systems.
CHQ-Summ: A Dataset for Consumer Healthcare Question Summarization
Jun 15, 2022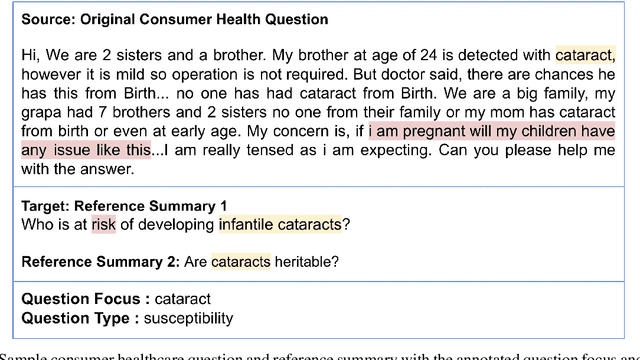
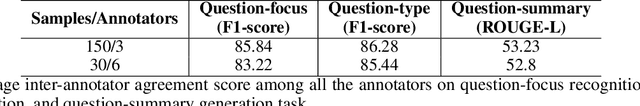
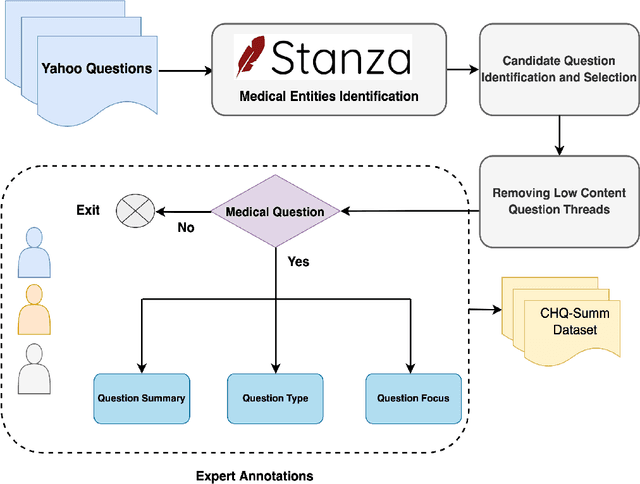
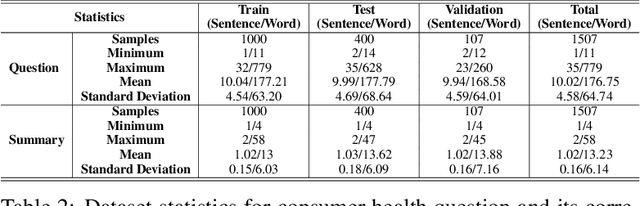
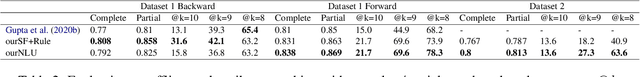
Abstract:The quest for seeking health information has swamped the web with consumers' health-related questions. Generally, consumers use overly descriptive and peripheral information to express their medical condition or other healthcare needs, contributing to the challenges of natural language understanding. One way to address this challenge is to summarize the questions and distill the key information of the original question. To address this issue, we introduce a new dataset, CHQ-Summ that contains 1507 domain-expert annotated consumer health questions and corresponding summaries. The dataset is derived from the community question-answering forum and therefore provides a valuable resource for understanding consumer health-related posts on social media. We benchmark the dataset on multiple state-of-the-art summarization models to show the effectiveness of the dataset.
Multimodal Graph-based Transformer Framework for Biomedical Relation Extraction
Jul 01, 2021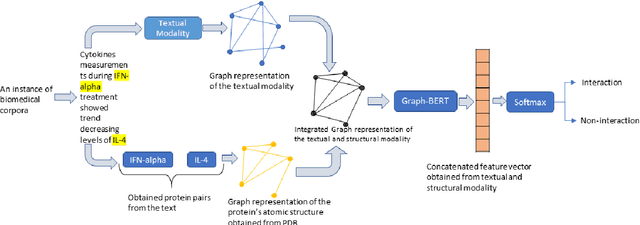
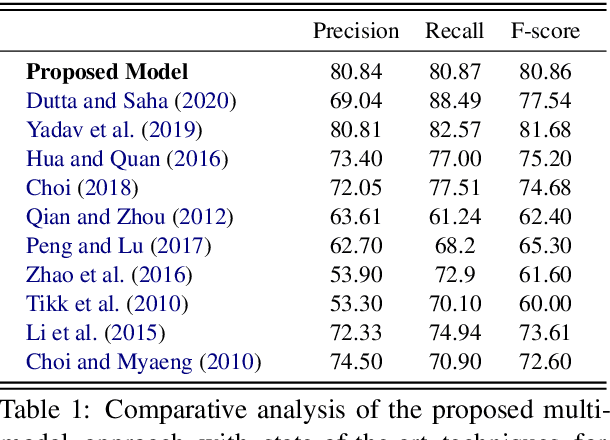
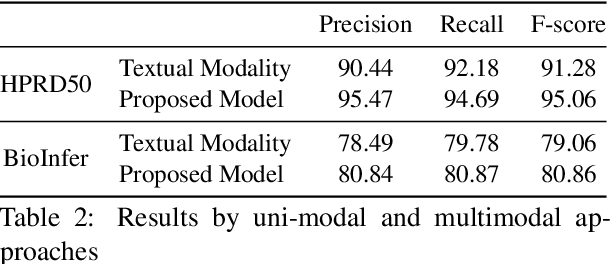
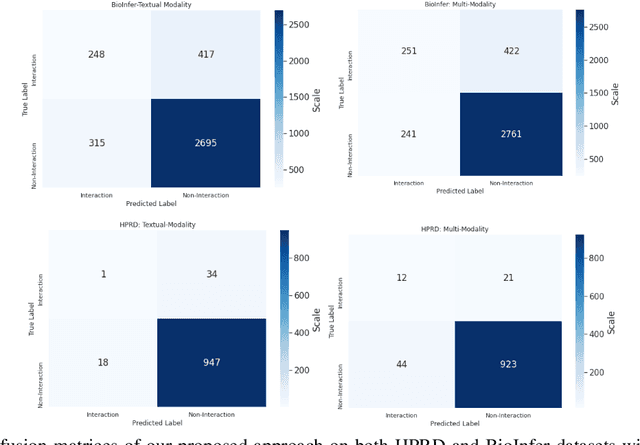
Abstract:The recent advancement of pre-trained Transformer models has propelled the development of effective text mining models across various biomedical tasks. However, these models are primarily learned on the textual data and often lack the domain knowledge of the entities to capture the context beyond the sentence. In this study, we introduced a novel framework that enables the model to learn multi-omnics biological information about entities (proteins) with the help of additional multi-modal cues like molecular structure. Towards this, rather developing modality-specific architectures, we devise a generalized and optimized graph based multi-modal learning mechanism that utilizes the GraphBERT model to encode the textual and molecular structure information and exploit the underlying features of various modalities to enable end-to-end learning. We evaluated our proposed method on ProteinProtein Interaction task from the biomedical corpus, where our proposed generalized approach is observed to be benefited by the additional domain-specific modality.
Reinforcement Learning for Abstractive Question Summarization with Question-aware Semantic Rewards
Jul 01, 2021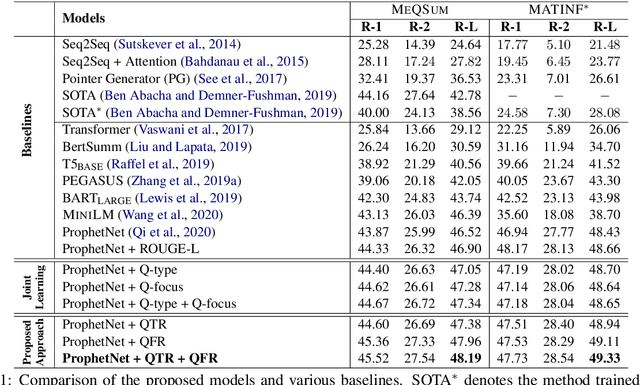

Abstract:The growth of online consumer health questions has led to the necessity for reliable and accurate question answering systems. A recent study showed that manual summarization of consumer health questions brings significant improvement in retrieving relevant answers. However, the automatic summarization of long questions is a challenging task due to the lack of training data and the complexity of the related subtasks, such as the question focus and type recognition. In this paper, we introduce a reinforcement learning-based framework for abstractive question summarization. We propose two novel rewards obtained from the downstream tasks of (i) question-type identification and (ii) question-focus recognition to regularize the question generation model. These rewards ensure the generation of semantically valid questions and encourage the inclusion of key medical entities/foci in the question summary. We evaluated our proposed method on two benchmark datasets and achieved higher performance over state-of-the-art models. The manual evaluation of the summaries reveals that the generated questions are more diverse and have fewer factual inconsistencies than the baseline summaries
Question-aware Transformer Models for Consumer Health Question Summarization
Jun 01, 2021
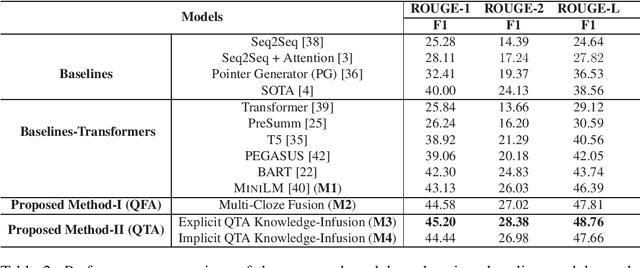

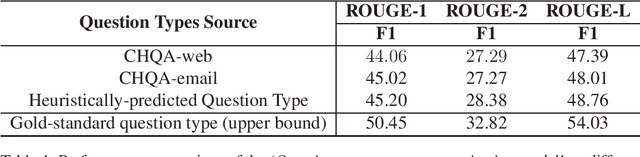
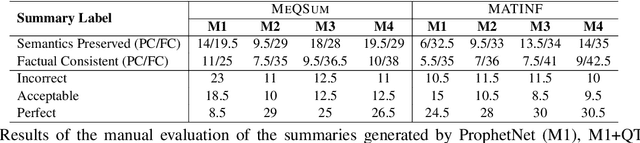
Abstract:Searching for health information online is becoming customary for more and more consumers every day, which makes the need for efficient and reliable question answering systems more pressing. An important contributor to the success rates of these systems is their ability to fully understand the consumers' questions. However, these questions are frequently longer than needed and mention peripheral information that is not useful in finding relevant answers. Question summarization is one of the potential solutions to simplifying long and complex consumer questions before attempting to find an answer. In this paper, we study the task of abstractive summarization for real-world consumer health questions. We develop an abstractive question summarization model that leverages the semantic interpretation of a question via recognition of medical entities, which enables the generation of informative summaries. Towards this, we propose multiple Cloze tasks (i.e. the task of filing missing words in a given context) to identify the key medical entities that enforce the model to have better coverage in question-focus recognition. Additionally, we infuse the decoder inputs with question-type information to generate question-type driven summaries. When evaluated on the MeQSum benchmark corpus, our framework outperformed the state-of-the-art method by 10.2 ROUGE-L points. We also conducted a manual evaluation to assess the correctness of the generated summaries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge