Joy Prakash Sain
A Variational Approach for Mitigating Entity Bias in Relation Extraction
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Mitigating entity bias is a critical challenge in Relation Extraction (RE), where models often rely excessively on entities, resulting in poor generalization. This paper presents a novel approach to address this issue by adapting a Variational Information Bottleneck (VIB) framework. Our method compresses entity-specific information while preserving task-relevant features. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on relation extraction datasets across general, financial, and biomedical domains, in both indomain (original test sets) and out-of-domain (modified test sets with type-constrained entity replacements) settings. Our approach offers a robust, interpretable, and theoretically grounded methodology.
Identifying Depressive Symptoms from Tweets: Figurative Language Enabled Multitask Learning Framework
Nov 12, 2020
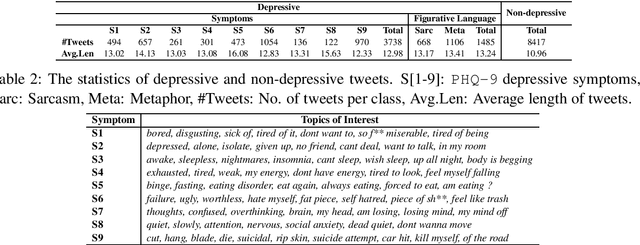
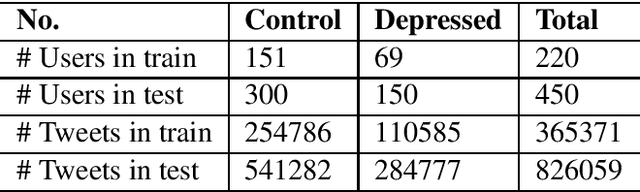
Abstract:Existing studies on using social media for deriving mental health status of users focus on the depression detection task. However, for case management and referral to psychiatrists, healthcare workers require practical and scalable depressive disorder screening and triage system. This study aims to design and evaluate a decision support system (DSS) to reliably determine the depressive triage level by capturing fine-grained depressive symptoms expressed in user tweets through the emulation of Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) that is routinely used in clinical practice. The reliable detection of depressive symptoms from tweets is challenging because the 280-character limit on tweets incentivizes the use of creative artifacts in the utterances and figurative usage contributes to effective expression. We propose a novel BERT based robust multi-task learning framework to accurately identify the depressive symptoms using the auxiliary task of figurative usage detection. Specifically, our proposed novel task sharing mechanism, co-task aware attention, enables automatic selection of optimal information across the BERT layers and tasks by soft-sharing of parameters. Our results show that modeling figurative usage can demonstrably improve the model's robustness and reliability for distinguishing the depression symptoms.
Assessing the Severity of Health States based on Social Media Posts
Sep 21, 2020



Abstract:The unprecedented growth of Internet users has resulted in an abundance of unstructured information on social media including health forums, where patients request health-related information or opinions from other users. Previous studies have shown that online peer support has limited effectiveness without expert intervention. Therefore, a system capable of assessing the severity of health state from the patients' social media posts can help health professionals (HP) in prioritizing the user's post. In this study, we inspect the efficacy of different aspects of Natural Language Understanding (NLU) to identify the severity of the user's health state in relation to two perspectives(tasks) (a) Medical Condition (i.e., Recover, Exist, Deteriorate, Other) and (b) Medication (i.e., Effective, Ineffective, Serious Adverse Effect, Other) in online health communities. We propose a multiview learning framework that models both the textual content as well as contextual-information to assess the severity of the user's health state. Specifically, our model utilizes the NLU views such as sentiment, emotions, personality, and use of figurative language to extract the contextual information. The diverse NLU views demonstrate its effectiveness on both the tasks and as well as on the individual disease to assess a user's health.
Towards Geocoding Spatial Expressions
Jun 12, 2019

Abstract:Imprecise composite location references formed using ad hoc spatial expressions in English text makes the geocoding task challenging for both inference and evaluation. Typically such spatial expressions fill in unestablished areas with new toponyms for finer spatial referents. For example, the spatial extent of the ad hoc spatial expression "north of" or "50 minutes away from" in relation to the toponym "Dayton, OH" refers to an ambiguous, imprecise area, requiring translation from this qualitative representation to a quantitative one with precise semantics using systems such as WGS84. Here we highlight the challenges of geocoding such referents and propose a formal representation that employs background knowledge, semantic approximations and rules, and fuzzy linguistic variables. We also discuss an appropriate evaluation technique for the task that is based on human contextualized and subjective judgment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge