T. Lucas Makinen
Hybrid Summary Statistics
Oct 10, 2024Abstract:We present a way to capture high-information posteriors from training sets that are sparsely sampled over the parameter space for robust simulation-based inference. In physical inference problems, we can often apply domain knowledge to define traditional summary statistics to capture some of the information in a dataset. We show that augmenting these statistics with neural network outputs to maximise the mutual information improves information extraction compared to neural summaries alone or their concatenation to existing summaries and makes inference robust in settings with low training data. We introduce 1) two loss formalisms to achieve this and 2) apply the technique to two different cosmological datasets to extract non-Gaussian parameter information.
CHARM: Creating Halos with Auto-Regressive Multi-stage networks
Sep 13, 2024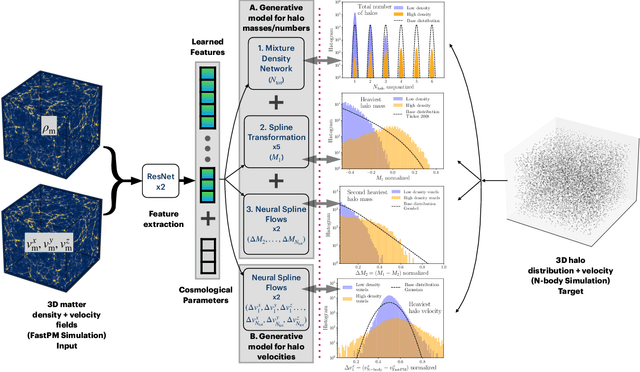
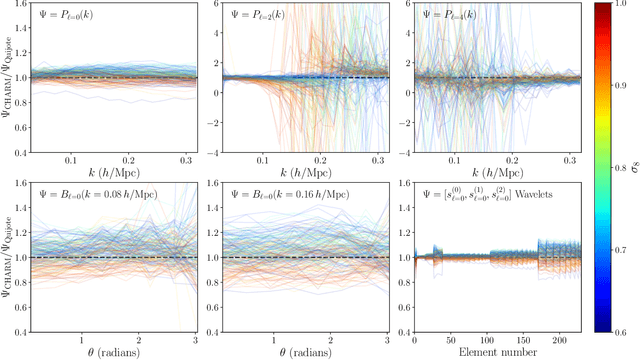
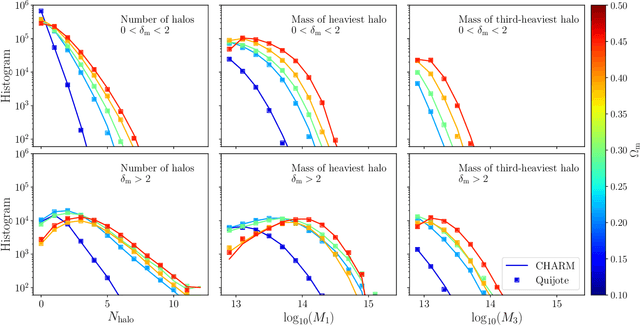
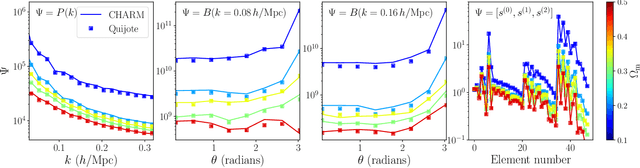
Abstract:To maximize the amount of information extracted from cosmological datasets, simulations that accurately represent these observations are necessary. However, traditional simulations that evolve particles under gravity by estimating particle-particle interactions (N-body simulations) are computationally expensive and prohibitive to scale to the large volumes and resolutions necessary for the upcoming datasets. Moreover, modeling the distribution of galaxies typically involves identifying virialized dark matter halos, which is also a time- and memory-consuming process for large N-body simulations, further exacerbating the computational cost. In this study, we introduce CHARM, a novel method for creating mock halo catalogs by matching the spatial, mass, and velocity statistics of halos directly from the large-scale distribution of the dark matter density field. We develop multi-stage neural spline flow-based networks to learn this mapping at redshift z=0.5 directly with computationally cheaper low-resolution particle mesh simulations instead of relying on the high-resolution N-body simulations. We show that the mock halo catalogs and painted galaxy catalogs have the same statistical properties as obtained from $N$-body simulations in both real space and redshift space. Finally, we use these mock catalogs for cosmological inference using redshift-space galaxy power spectrum, bispectrum, and wavelet-based statistics using simulation-based inference, performing the first inference with accelerated forward model simulations and finding unbiased cosmological constraints with well-calibrated posteriors. The code was developed as part of the Simons Collaboration on Learning the Universe and is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/shivampcosmo/CHARM}.
Hybrid summary statistics: neural weak lensing inference beyond the power spectrum
Jul 26, 2024Abstract:In inference problems, we often have domain knowledge which allows us to define summary statistics that capture most of the information content in a dataset. In this paper, we present a hybrid approach, where such physics-based summaries are augmented by a set of compressed neural summary statistics that are optimised to extract the extra information that is not captured by the predefined summaries. The resulting statistics are very powerful inputs to simulation-based or implicit inference of model parameters. We apply this generalisation of Information Maximising Neural Networks (IMNNs) to parameter constraints from tomographic weak gravitational lensing convergence maps to find summary statistics that are explicitly optimised to complement angular power spectrum estimates. We study several dark matter simulation resolutions in low- and high-noise regimes. We show that i) the information-update formalism extracts at least $3\times$ and up to $8\times$ as much information as the angular power spectrum in all noise regimes, ii) the network summaries are highly complementary to existing 2-point summaries, and iii) our formalism allows for networks with smaller, physically-informed architectures to match much larger regression networks with far fewer simulations needed to obtain asymptotically optimal inference.
LtU-ILI: An All-in-One Framework for Implicit Inference in Astrophysics and Cosmology
Feb 06, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents the Learning the Universe Implicit Likelihood Inference (LtU-ILI) pipeline, a codebase for rapid, user-friendly, and cutting-edge machine learning (ML) inference in astrophysics and cosmology. The pipeline includes software for implementing various neural architectures, training schema, priors, and density estimators in a manner easily adaptable to any research workflow. It includes comprehensive validation metrics to assess posterior estimate coverage, enhancing the reliability of inferred results. Additionally, the pipeline is easily parallelizable, designed for efficient exploration of modeling hyperparameters. To demonstrate its capabilities, we present real applications across a range of astrophysics and cosmology problems, such as: estimating galaxy cluster masses from X-ray photometry; inferring cosmology from matter power spectra and halo point clouds; characterising progenitors in gravitational wave signals; capturing physical dust parameters from galaxy colors and luminosities; and establishing properties of semi-analytic models of galaxy formation. We also include exhaustive benchmarking and comparisons of all implemented methods as well as discussions about the challenges and pitfalls of ML inference in astronomical sciences. All code and examples are made publicly available at https://github.com/maho3/ltu-ili.
Fishnets: Information-Optimal, Scalable Aggregation for Sets and Graphs
Oct 05, 2023Abstract:Set-based learning is an essential component of modern deep learning and network science. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and their edge-free counterparts Deepsets have proven remarkably useful on ragged and topologically challenging datasets. The key to learning informative embeddings for set members is a specified aggregation function, usually a sum, max, or mean. We propose Fishnets, an aggregation strategy for learning information-optimal embeddings for sets of data for both Bayesian inference and graph aggregation. We demonstrate that i) Fishnets neural summaries can be scaled optimally to an arbitrary number of data objects, ii) Fishnets aggregations are robust to changes in data distribution, unlike standard deepsets, iii) Fishnets saturate Bayesian information content and extend to regimes where MCMC techniques fail and iv) Fishnets can be used as a drop-in aggregation scheme within GNNs. We show that by adopting a Fishnets aggregation scheme for message passing, GNNs can achieve state-of-the-art performance versus architecture size on ogbn-protein data over existing benchmarks with a fraction of learnable parameters and faster training time.
The Cosmic Graph: Optimal Information Extraction from Large-Scale Structure using Catalogues
Jul 11, 2022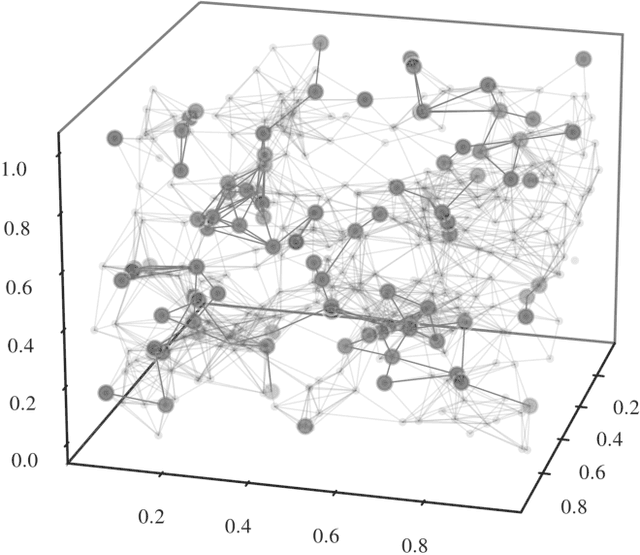
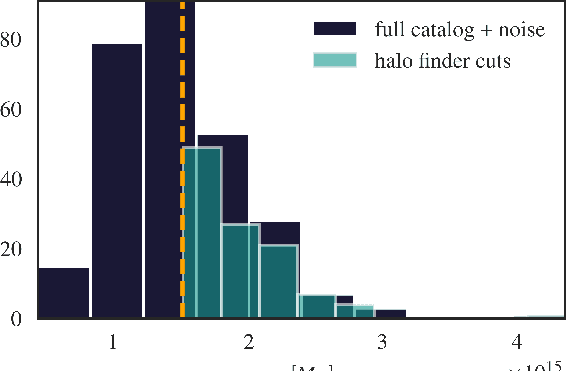
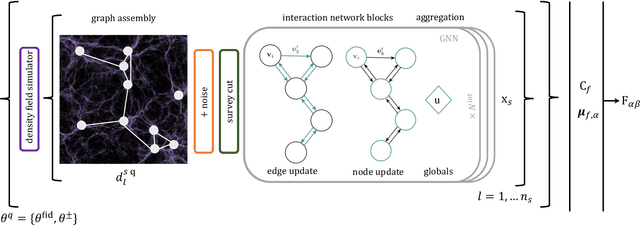
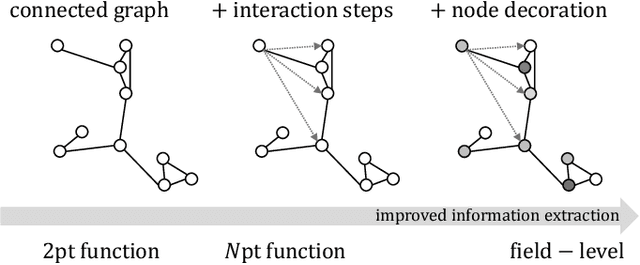
Abstract:We present an implicit likelihood approach to quantifying cosmological information over discrete catalogue data, assembled as graphs. To do so, we explore cosmological inference using mock dark matter halo catalogues. We employ Information Maximising Neural Networks (IMNNs) to quantify Fisher information extraction as a function of graph representation. We a) demonstrate the high sensitivity of modular graph structure to the underlying cosmology in the noise-free limit, b) show that networks automatically combine mass and clustering information through comparisons to traditional statistics, c) demonstrate that graph neural networks can still extract information when catalogues are subject to noisy survey cuts, and d) illustrate how nonlinear IMNN summaries can be used as asymptotically optimal compressed statistics for Bayesian implicit likelihood inference. We reduce the area of joint $\Omega_m, \sigma_8$ parameter constraints with small ($\sim$100 object) halo catalogues by a factor of 42 over the two-point correlation function, and demonstrate that the networks automatically combine mass and clustering information. This work utilises a new IMNN implementation over graph data in Jax, which can take advantage of either numerical or auto-differentiability. We also show that graph IMNNs successfully compress simulations far from the fiducial model at which the network is fitted, indicating a promising alternative to $n$-point statistics in catalogue-based analyses.
$\texttt{deep21}$: a Deep Learning Method for 21cm Foreground Removal
Oct 29, 2020



Abstract:We seek to remove foreground contaminants from 21cm intensity mapping observations. We demonstrate that a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) with a UNet architecture and three-dimensional convolutions, trained on simulated observations, can effectively separate frequency and spatial patterns of the cosmic neutral hydrogen (HI) signal from foregrounds in the presence of noise. Cleaned maps recover cosmological clustering statistics within 10% at all relevant angular scales and frequencies. This amounts to a reduction in prediction variance of over an order of magnitude on small angular scales ($\ell > 300$), and improved accuracy for small radial scales ($k_{\parallel} > 0.17\ \rm h\ Mpc^{-1})$ compared to standard Principal Component Analysis (PCA) methods. We estimate posterior confidence intervals for the network's prediction by training an ensemble of UNets. Our approach demonstrates the feasibility of analyzing 21cm intensity maps, as opposed to derived summary statistics, for upcoming radio experiments, as long as the simulated foreground model is sufficiently realistic. We provide the code used for this analysis on $\href{https://github.com/tlmakinen/deep21}{\rm GitHub}$, as well as a browser-based tutorial for the experiment and UNet model via the accompanying $\href{http://bit.ly/deep21-colab}{\rm Colab\ notebook}$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge