Stephanie Chan
Relational reasoning and inductive bias in transformers trained on a transitive inference task
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Transformer-based models have demonstrated remarkable reasoning abilities, but the mechanisms underlying relational reasoning in different learning regimes remain poorly understood. In this work, we investigate how transformers perform a classic relational reasoning task from the Psychology literature, \textit{transitive inference}, which requires inference about indirectly related items by integrating information across observed adjacent item pairs (e.g., if A>B and B>C, then A>C). We compare transitive inference behavior across two distinct learning regimes: in-weights learning (IWL), where models store information in network parameters, and in-context learning (ICL), where models flexibly utilize information presented within the input sequence. Our findings reveal that IWL naturally induces a generalization bias towards transitive inference, despite being trained only on adjacent items, whereas ICL models trained solely on adjacent items do not generalize transitively. Mechanistic analysis shows that ICL models develop induction circuits that implement a simple match-and-copy strategy that performs well at relating adjacent pairs, but does not encoding hierarchical relationships among indirectly related items. Interestingly, when pre-trained on in-context linear regression tasks, transformers successfully exhibit in-context generalizable transitive inference. Moreover, like IWL, they display both \textit{symbolic distance} and \textit{terminal item effects} characteristic of human and animal performance, without forming induction circuits. These results suggest that pre-training on tasks with underlying structure promotes the development of representations that can scaffold in-context relational reasoning.
How do language models learn facts? Dynamics, curricula and hallucinations
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Large language models accumulate vast knowledge during pre-training, yet the dynamics governing this acquisition remain poorly understood. This work investigates the learning dynamics of language models on a synthetic factual recall task, uncovering three key findings: First, language models learn in three phases, exhibiting a performance plateau before acquiring precise factual knowledge. Mechanistically, this plateau coincides with the formation of attention-based circuits that support recall. Second, the training data distribution significantly impacts learning dynamics, as imbalanced distributions lead to shorter plateaus. Finally, hallucinations emerge simultaneously with knowledge, and integrating new knowledge into the model through fine-tuning is challenging, as it quickly corrupts its existing parametric memories. Our results emphasize the importance of data distribution in knowledge acquisition and suggest novel data scheduling strategies to accelerate neural network training.
LearnLM: Improving Gemini for Learning
Dec 21, 2024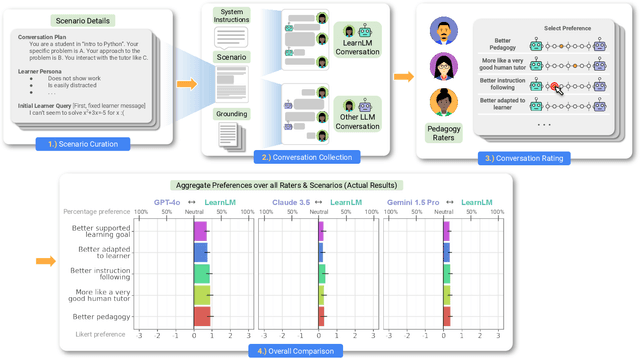
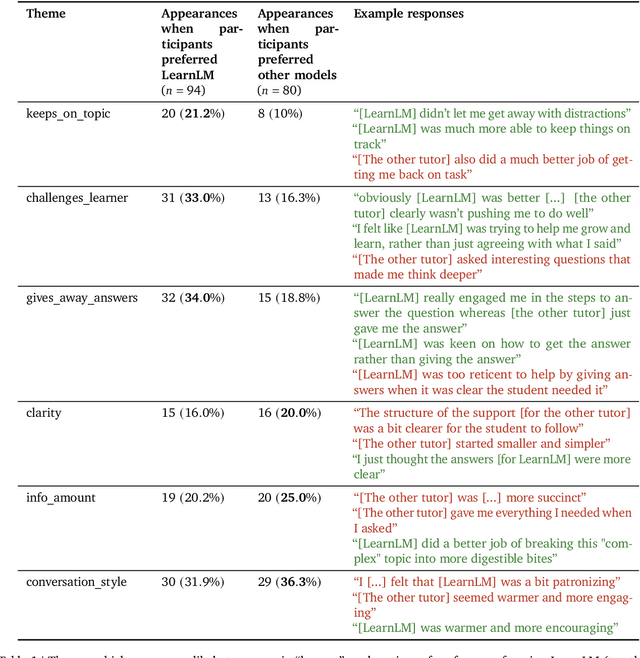
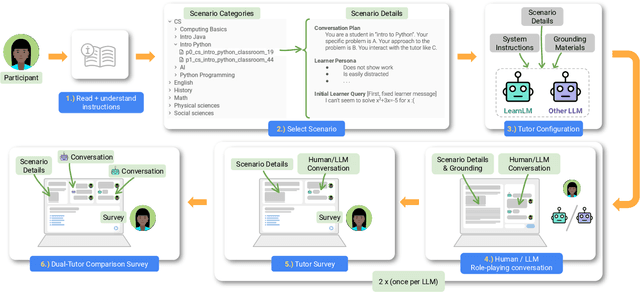
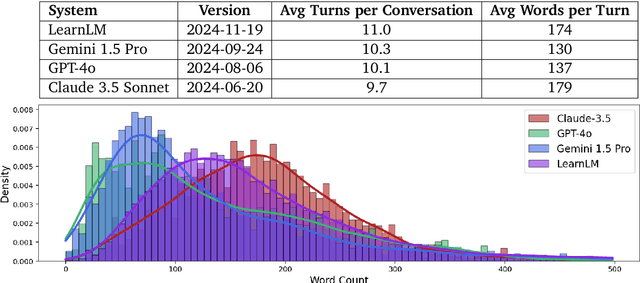
Abstract:Today's generative AI systems are tuned to present information by default rather than engage users in service of learning as a human tutor would. To address the wide range of potential education use cases for these systems, we reframe the challenge of injecting pedagogical behavior as one of \textit{pedagogical instruction following}, where training and evaluation examples include system-level instructions describing the specific pedagogy attributes present or desired in subsequent model turns. This framing avoids committing our models to any particular definition of pedagogy, and instead allows teachers or developers to specify desired model behavior. It also clears a path to improving Gemini models for learning -- by enabling the addition of our pedagogical data to post-training mixtures -- alongside their rapidly expanding set of capabilities. Both represent important changes from our initial tech report. We show how training with pedagogical instruction following produces a LearnLM model (available on Google AI Studio) that is preferred substantially by expert raters across a diverse set of learning scenarios, with average preference strengths of 31\% over GPT-4o, 11\% over Claude 3.5, and 13\% over the Gemini 1.5 Pro model LearnLM was based on.
Many-Shot In-Context Learning
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel at few-shot in-context learning (ICL) -- learning from a few examples provided in context at inference, without any weight updates. Newly expanded context windows allow us to investigate ICL with hundreds or thousands of examples -- the many-shot regime. Going from few-shot to many-shot, we observe significant performance gains across a wide variety of generative and discriminative tasks. While promising, many-shot ICL can be bottlenecked by the available amount of human-generated examples. To mitigate this limitation, we explore two new settings: Reinforced and Unsupervised ICL. Reinforced ICL uses model-generated chain-of-thought rationales in place of human examples. Unsupervised ICL removes rationales from the prompt altogether, and prompts the model only with domain-specific questions. We find that both Reinforced and Unsupervised ICL can be quite effective in the many-shot regime, particularly on complex reasoning tasks. Finally, we demonstrate that, unlike few-shot learning, many-shot learning is effective at overriding pretraining biases and can learn high-dimensional functions with numerical inputs. Our analysis also reveals the limitations of next-token prediction loss as an indicator of downstream ICL performance.
Genie: Generative Interactive Environments
Feb 23, 2024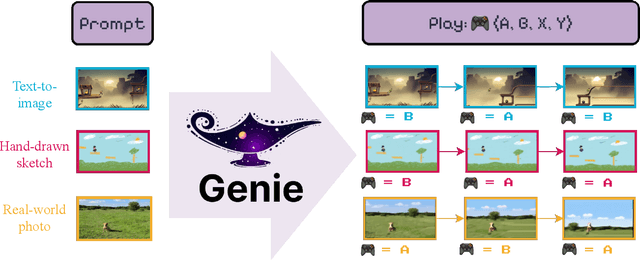
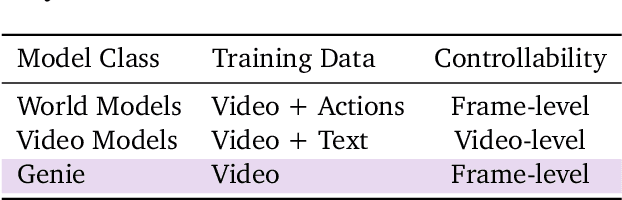
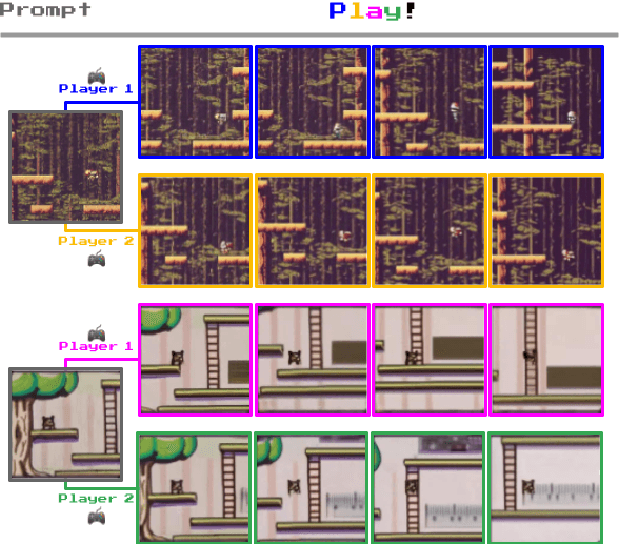
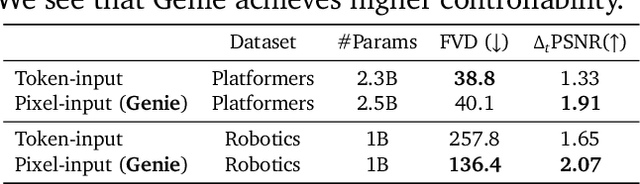
Abstract:We introduce Genie, the first generative interactive environment trained in an unsupervised manner from unlabelled Internet videos. The model can be prompted to generate an endless variety of action-controllable virtual worlds described through text, synthetic images, photographs, and even sketches. At 11B parameters, Genie can be considered a foundation world model. It is comprised of a spatiotemporal video tokenizer, an autoregressive dynamics model, and a simple and scalable latent action model. Genie enables users to act in the generated environments on a frame-by-frame basis despite training without any ground-truth action labels or other domain-specific requirements typically found in the world model literature. Further the resulting learned latent action space facilitates training agents to imitate behaviors from unseen videos, opening the path for training generalist agents of the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge