Siwei Fu
Accelerating High-Efficiency Organic Photovoltaic Discovery via Pretrained Graph Neural Networks and Generative Reinforcement Learning
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Organic photovoltaic (OPV) materials offer a promising avenue toward cost-effective solar energy utilization. However, optimizing donor-acceptor (D-A) combinations to achieve high power conversion efficiency (PCE) remains a significant challenge. In this work, we propose a framework that integrates large-scale pretraining of graph neural networks (GNNs) with a GPT-2 (Generative Pretrained Transformer 2)-based reinforcement learning (RL) strategy to design OPV molecules with potentially high PCE. This approach produces candidate molecules with predicted efficiencies approaching 21\%, although further experimental validation is required. Moreover, we conducted a preliminary fragment-level analysis to identify structural motifs recognized by the RL model that may contribute to enhanced PCE, thus providing design guidelines for the broader research community. To facilitate continued discovery, we are building the largest open-source OPV dataset to date, expected to include nearly 3,000 donor-acceptor pairs. Finally, we discuss plans to collaborate with experimental teams on synthesizing and characterizing AI-designed molecules, which will provide new data to refine and improve our predictive and generative models.
VisImages: A Large-scale, High-quality Image Corpus in Visualization Publications
Jul 10, 2020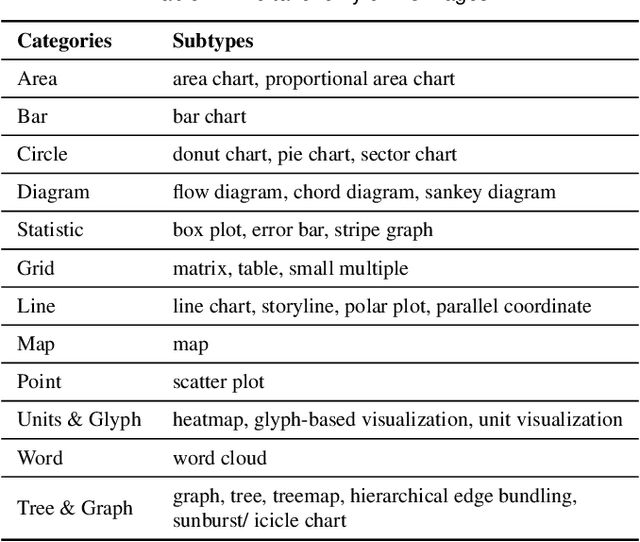
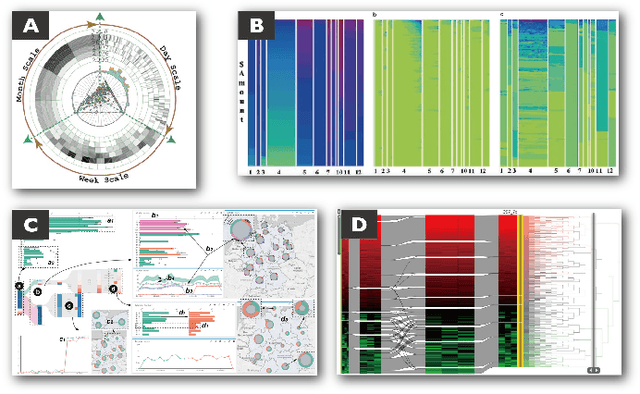

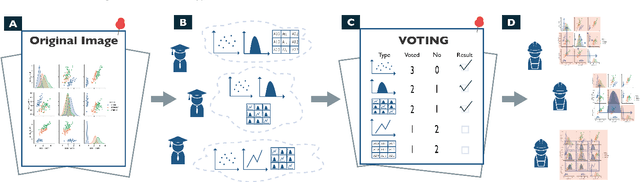
Abstract:Images in visualization publications contain rich information, such as novel visual designs, model details, and experiment results. Constructing such an image corpus can contribute to the community in many aspects, including literature analysis from the perspective of visual representations, empirical studies on visual memorability, and machine learning research for chart detection. This study presents VisImages, a high-quality and large-scale image corpus collected from visualization publications. VisImages contain fruitful and diverse annotations for each image, including captions, types of visual representations, and bounding boxes. First, we algorithmically extract the images associated with captions and manually correct the errors. Second, to categorize visualizations in publications, we extend and iteratively refine the existing taxonomy through a multi-round pilot study. Third, guided by this taxonomy, we invite senior visualization practitioners to annotate visual representations that appear in each image. In this process, we borrow techniques such as "gold standards" and majority voting for quality control. Finally, we recruit the crowd to draw bounding boxes for visual representations in the images. The resulting corpus contains 35,096 annotated visualizations from 12,267 images with 12,057 captions in 1397 papers from VAST and InfoVis. We demonstrate the usefulness of VisImages through the following four use cases: 1) analysis of color usage in VAST and InfoVis papers across years, 2) discussion of the researcher preference on visualization types, 3) spatial distribution analysis of visualizations in visual analytic systems, and 4) training visualization detection models.
Quda: Natural Language Queries for Visual Data Analytics
May 13, 2020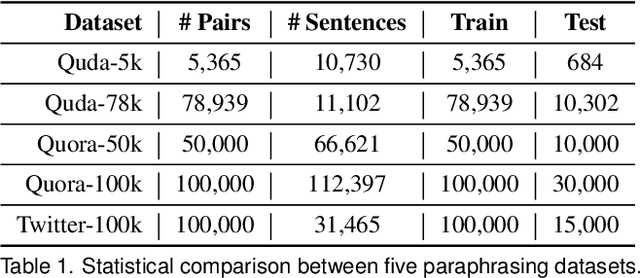
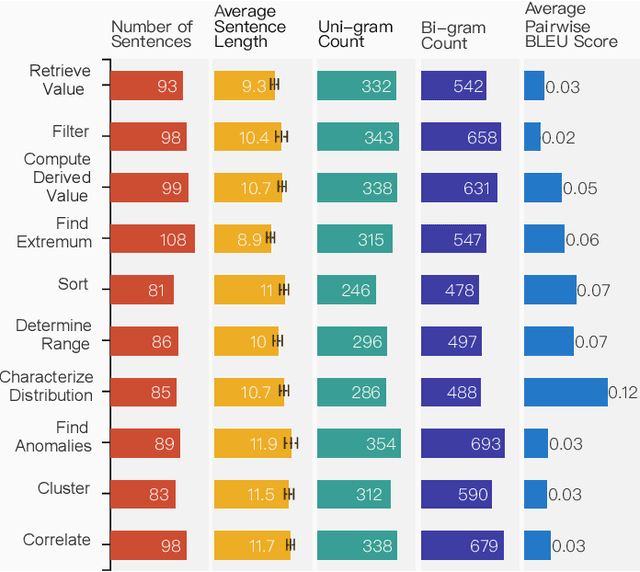
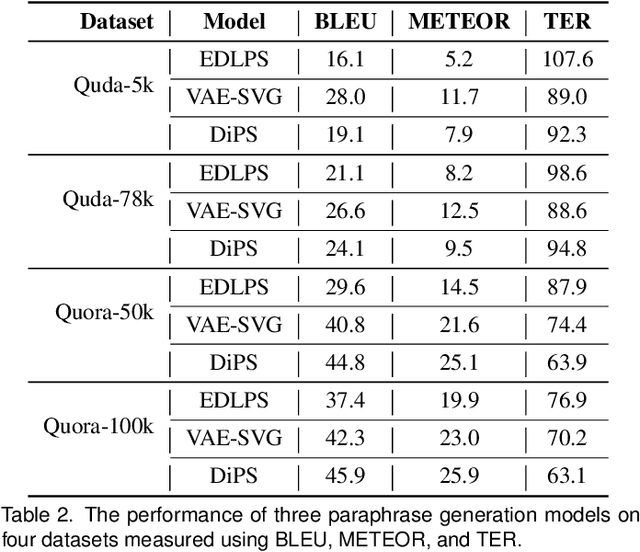
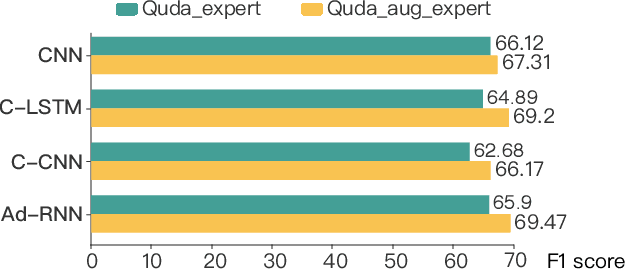
Abstract:Visualization-oriented natural language interfaces (V-NLIs) have been explored and developed in recent years. One challenge faced by V-NLIs is in the formation of effective design decisions that usually requires a deep understanding of user queries. Learning-based approaches have shown potential in V-NLIs and reached state-of-the-art performance in various NLP tasks. However, because of the lack of sufficient training samples that cater to visual data analytics, cutting-edge techniques have rarely been employed to facilitate the development of V-NLIs. We present a new dataset, called Quda, to help V-NLIs understand free-form natural language. Our dataset contains 14;035 diverse user queries annotated with 10 low-level analytic tasks that assist in the deployment of state-of-the-art techniques for parsing complex human language. We achieve this goal by first gathering seed queries with data analysts who are target users of V-NLIs. Then we employ extensive crowd force for paraphrase generation and validation. We demonstrate the usefulness of Quda in building V-NLIs by creating a prototype that makes effective design decisions for free-form user queries. We also show that Quda can be beneficial for a wide range of applications in the visualization community by analyzing the design tasks described in academic publications.
Task-Oriented Optimal Sequencing of Visualization Charts
Aug 07, 2019
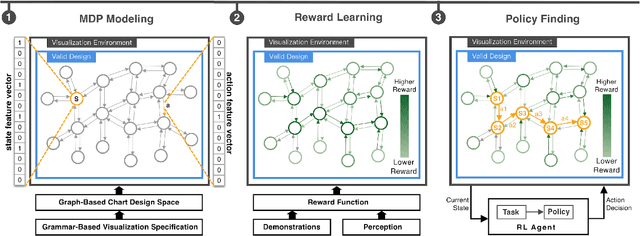
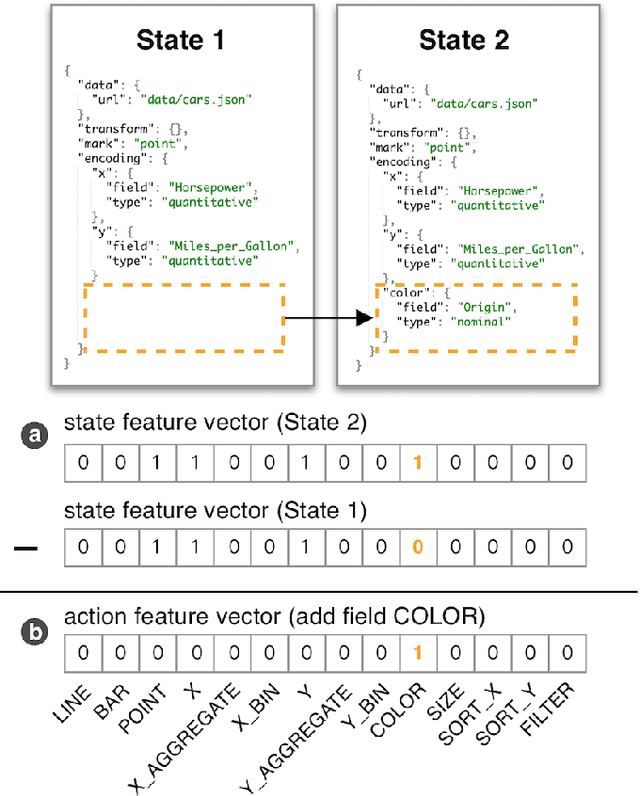
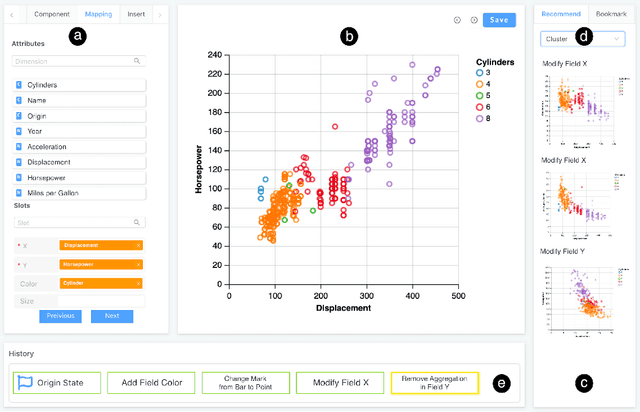
Abstract:A chart sequence is used to describe a series of visualization charts generated in the exploratory analysis by data analysts. It provides information details in each chart as well as a logical relationship among charts. While existing research targets on generating chart sequences that match human's perceptions, little attention has been paid to formulate task-oriented connections between charts in a chart design space. We present a novel chart sequencing method based on reinforcement learning to capture the connections between charts in the context of three major analysis tasks, including correlation analysis, anomaly detection, and cluster analysis. The proposed method formulates a chart sequencing procedure as an optimization problem, which seeks an optimal policy to sequencing charts for the specific analysis task. In our method, a novel reward function is introduced, which takes both the analysis task and the factor of human cognition into consideration. We conducted one case study and two user studies to evaluate the effectiveness of our method under the application scenarios of visualization demonstration, sequencing charts for reasoning analysis results, and making a chart design choice. The study results showed the power of our method.
Challenge AI Mind: A Crowd System for Proactive AI Testing
Oct 21, 2018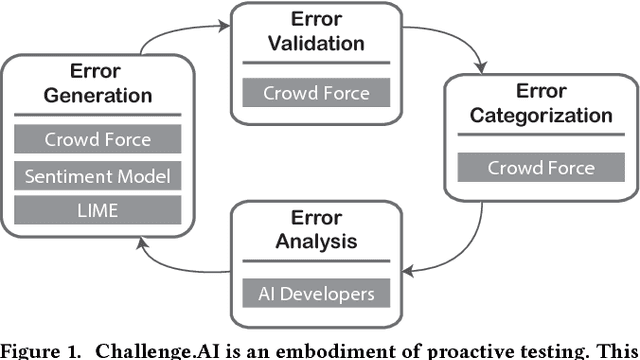
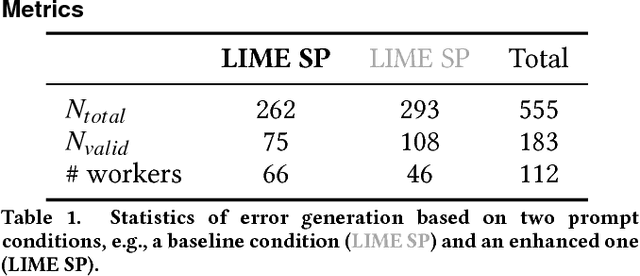
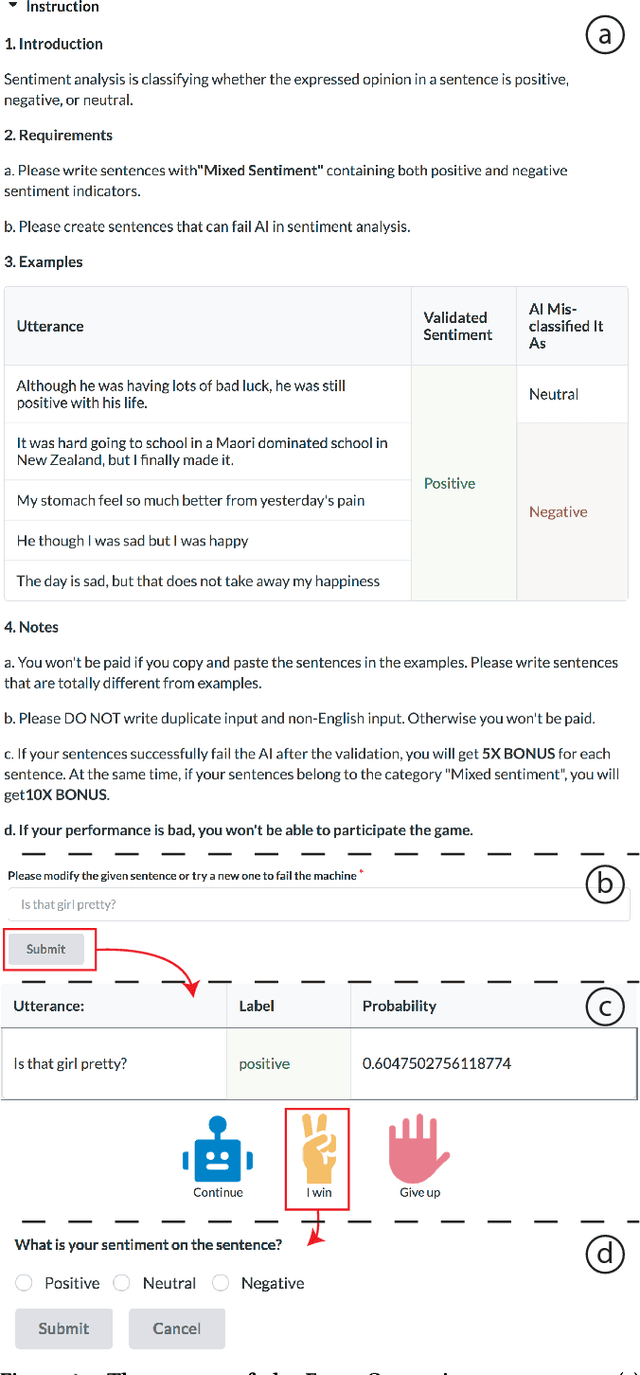
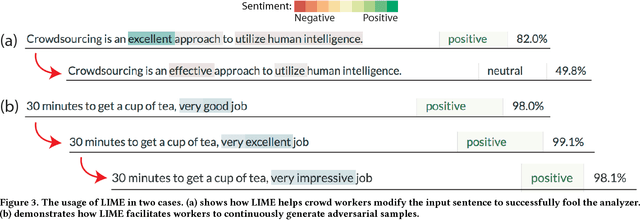
Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) has burrowed into our lives in various aspects; however, without appropriate testing, deployed AI systems are often being criticized to fail in critical and embarrassing cases. Existing testing approaches mainly depend on fixed and pre-defined datasets, providing a limited testing coverage. In this paper, we propose the concept of proactive testing to dynamically generate testing data and evaluate the performance of AI systems. We further introduce Challenge.AI, a new crowd system that features the integration of crowdsourcing and machine learning techniques in the process of error generation, error validation, error categorization, and error analysis. We present experiences and insights into a participatory design with AI developers. The evaluation shows that the crowd workflow is more effective with the help of machine learning techniques. AI developers found that our system can help them discover unknown errors made by the AI models, and engage in the process of proactive testing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge