Sikandar Amin
Query-Guided Networks for Few-shot Fine-grained Classification and Person Search
Sep 21, 2022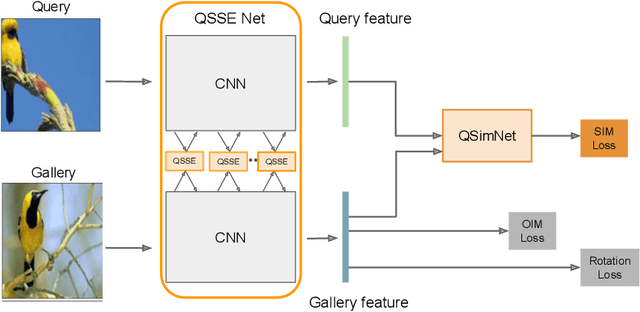
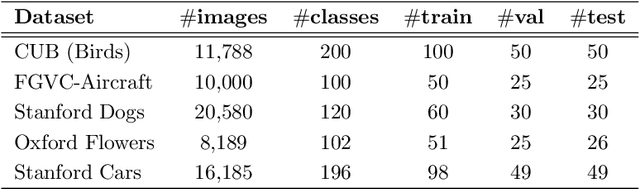
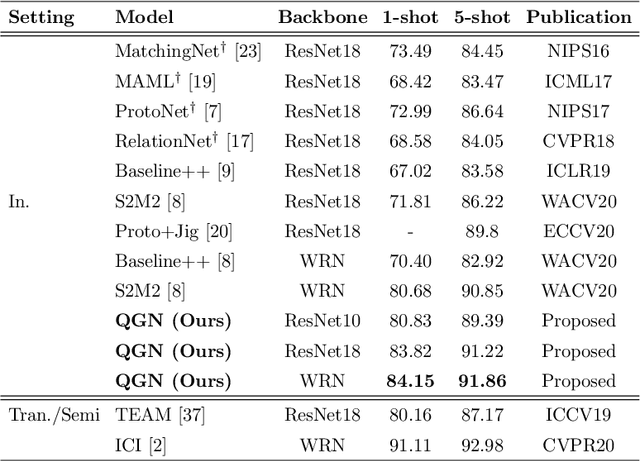
Abstract:Few-shot fine-grained classification and person search appear as distinct tasks and literature has treated them separately. But a closer look unveils important similarities: both tasks target categories that can only be discriminated by specific object details; and the relevant models should generalize to new categories, not seen during training. We propose a novel unified Query-Guided Network (QGN) applicable to both tasks. QGN consists of a Query-guided Siamese-Squeeze-and-Excitation subnetwork which re-weights both the query and gallery features across all network layers, a Query-guided Region Proposal subnetwork for query-specific localisation, and a Query-guided Similarity subnetwork for metric learning. QGN improves on a few recent few-shot fine-grained datasets, outperforming other techniques on CUB by a large margin. QGN also performs competitively on the person search CUHK-SYSU and PRW datasets, where we perform in-depth analysis.
Class Interference Regularization
Sep 04, 2020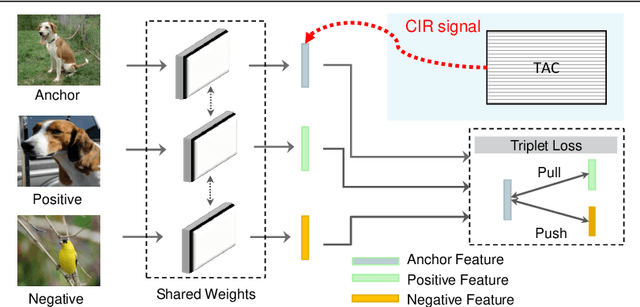
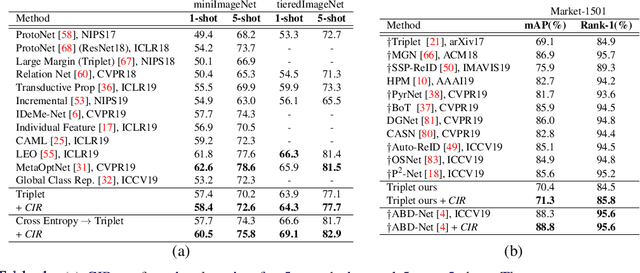

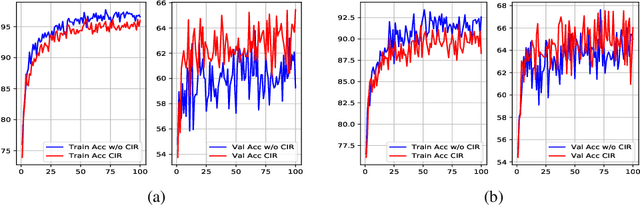
Abstract:Contrastive losses yield state-of-the-art performance for person re-identification, face verification and few shot learning. They have recently outperformed the cross-entropy loss on classification at the ImageNet scale and outperformed all self-supervision prior results by a large margin (SimCLR). Simple and effective regularization techniques such as label smoothing and self-distillation do not apply anymore, because they act on multinomial label distributions, adopted in cross-entropy losses, and not on tuple comparative terms, which characterize the contrastive losses. Here we propose a novel, simple and effective regularization technique, the Class Interference Regularization (CIR), which applies to cross-entropy losses but is especially effective on contrastive losses. CIR perturbs the output features by randomly moving them towards the average embeddings of the negative classes. To the best of our knowledge, CIR is the first regularization technique to act on the output features. In experimental evaluation, the combination of CIR and a plain Siamese-net with triplet loss yields best few-shot learning performance on the challenging tieredImageNet. CIR also improves the state-of-the-art technique in person re-identification on the Market-1501 dataset, based on triplet loss, and the state-of-the-art technique in person search on the CUHK-SYSU dataset, based on a cross-entropy loss. Finally, on the task of classification CIR performs on par with the popular label smoothing, as demonstrated for CIFAR-10 and -100.
Joint Detection and Tracking in Videos with Identification Features
May 25, 2020
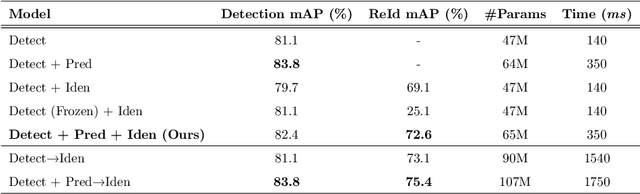
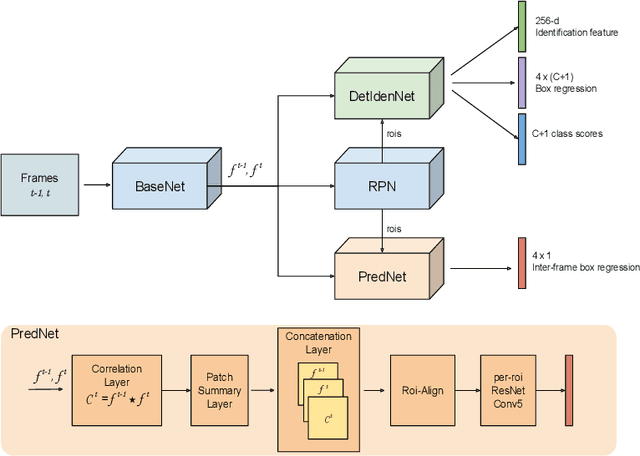
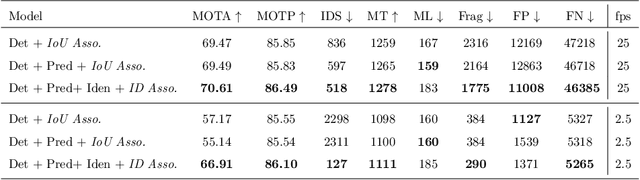
Abstract:Recent works have shown that combining object detection and tracking tasks, in the case of video data, results in higher performance for both tasks, but they require a high frame-rate as a strict requirement for performance. This is assumption is often violated in real-world applications, when models run on embedded devices, often at only a few frames per second. Videos at low frame-rate suffer from large object displacements. Here re-identification features may support to match large-displaced object detections, but current joint detection and re-identification formulations degrade the detector performance, as these two are contrasting tasks. In the real-world application having separate detector and re-id models is often not feasible, as both the memory and runtime effectively double. Towards robust long-term tracking applicable to reduced-computational-power devices, we propose the first joint optimization of detection, tracking and re-identification features for videos. Notably, our joint optimization maintains the detector performance, a typical multi-task challenge. At inference time, we leverage detections for tracking (tracking-by-detection) when the objects are visible, detectable and slowly moving in the image. We leverage instead re-identification features to match objects which disappeared (e.g. due to occlusion) for several frames or were not tracked due to fast motion (or low-frame-rate videos). Our proposed method reaches the state-of-the-art on MOT, it ranks 1st in the UA-DETRAC'18 tracking challenge among online trackers, and 3rd overall.
Knowledge Distillation for End-to-End Person Search
Sep 05, 2019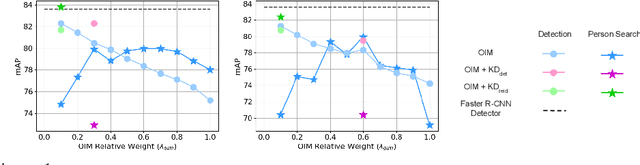
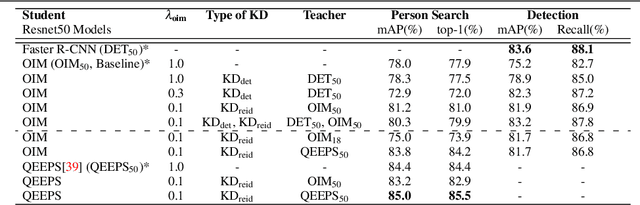
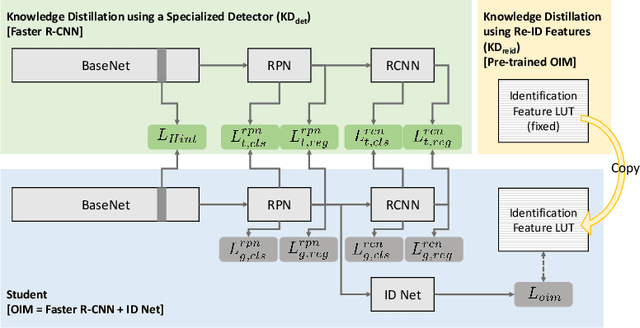
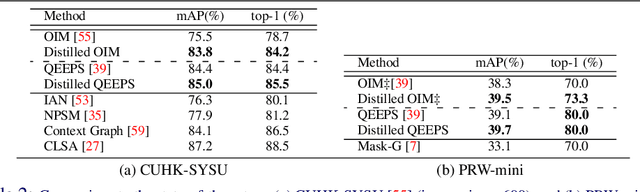
Abstract:We introduce knowledge distillation for end-to-end person search. End-to-End methods are the current state-of-the-art for person search that solve both detection and re-identification jointly. These approaches for joint optimization show their largest drop in performance due to a sub-optimal detector. We propose two distinct approaches for extra supervision of end-to-end person search methods in a teacher-student setting. The first is adopted from state-of-the-art knowledge distillation in object detection. We employ this to supervise the detector of our person search model at various levels using a specialized detector. The second approach is new, simple and yet considerably more effective. This distills knowledge from a teacher re-identification technique via a pre-computed look-up table of ID features. It relaxes the learning of identification features and allows the student to focus on the detection task. This procedure not only helps fixing the sub-optimal detector training in the joint optimization and simultaneously improving the person search, but also closes the performance gap between the teacher and the student for model compression in this case. Overall, we demonstrate significant improvements for two recent state-of-the-art methods using our proposed knowledge distillation approach on two benchmark datasets. Moreover, on the model compression task our approach brings the performance of smaller models on par with the larger models.
Query-guided End-to-End Person Search
May 03, 2019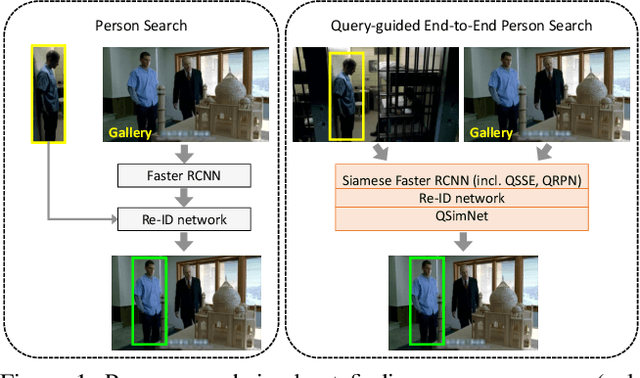
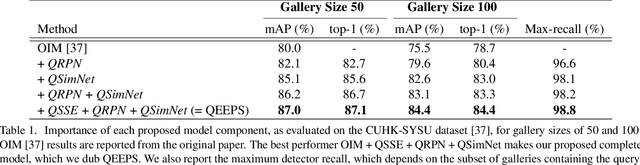
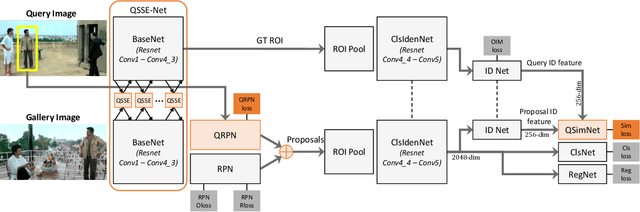
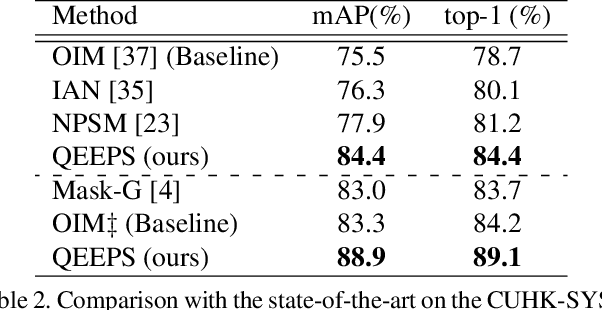
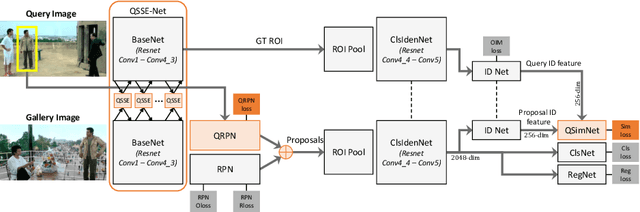
Abstract:Person search has recently gained attention as the novel task of finding a person, provided as a cropped sample, from a gallery of non-cropped images, whereby several other people are also visible. We believe that i. person detection and re-identification should be pursued in a joint optimization framework and that ii. the person search should leverage the query image extensively (e.g. emphasizing unique query patterns). However, so far, no prior art realizes this. We introduce a novel query-guided end-to-end person search network (QEEPS) to address both aspects. We leverage a most recent joint detector and re-identification work, OIM [37]. We extend this with i. a query-guided Siamese squeeze-and-excitation network (QSSE-Net) that uses global context from both the query and gallery images, ii. a query-guided region proposal network (QRPN) to produce query-relevant proposals, and iii. a query-guided similarity subnetwork (QSimNet), to learn a query-guided reidentification score. QEEPS is the first end-to-end query-guided detection and re-id network. On both the most recent CUHK-SYSU [37] and PRW [46] datasets, we outperform the previous state-of-the-art by a large margin.
Forecasting People Trajectories and Head Poses by Jointly Reasoning on Tracklets and Vislets
Jan 07, 2019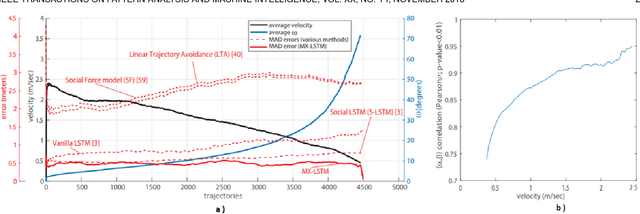
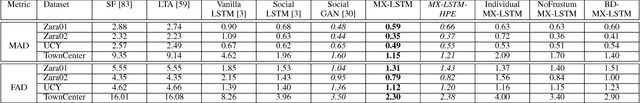
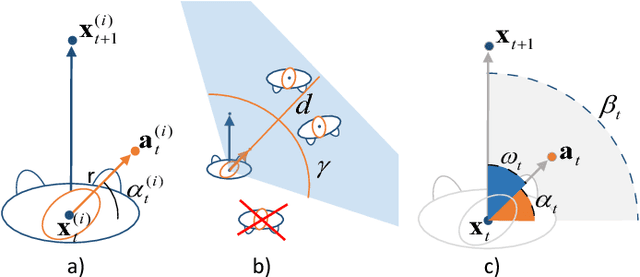
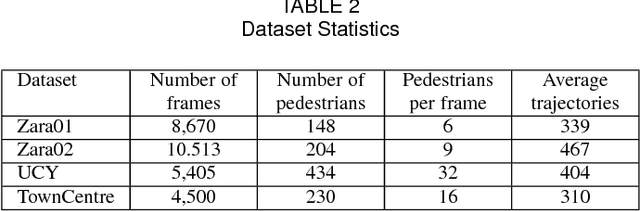
Abstract:In this work, we explore the correlation between people trajectories and their head orientations. We argue that people trajectory and head pose forecasting can be modelled as a joint problem. Recent approaches on trajectory forecasting leverage short-term trajectories (aka tracklets) of pedestrians to predict their future paths. In addition, sociological cues, such as expected destination or pedestrian interaction, are often combined with tracklets. In this paper, we propose MiXing-LSTM (MX-LSTM) to capture the interplay between positions and head orientations (vislets) thanks to a joint unconstrained optimization of full covariance matrices during the LSTM backpropagation. We additionally exploit the head orientations as a proxy for the visual attention, when modeling social interactions. MX-LSTM predicts future pedestrians location and head pose, increasing the standard capabilities of the current approaches on long-term trajectory forecasting. Compared to the state-of-the-art, our approach shows better performances on an extensive set of public benchmarks. MX-LSTM is particularly effective when people move slowly, i.e. the most challenging scenario for all other models. The proposed approach also allows for accurate predictions on a longer time horizon.
Recognizing Fine-Grained and Composite Activities using Hand-Centric Features and Script Data
Oct 15, 2015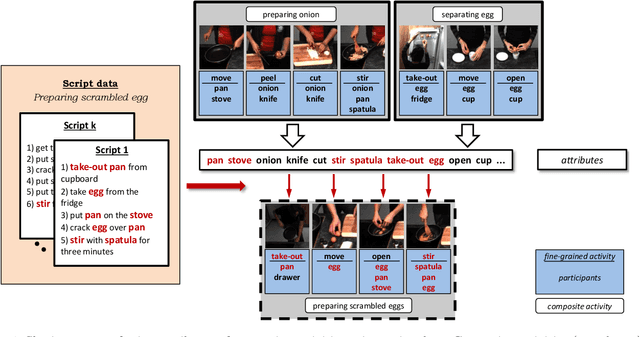
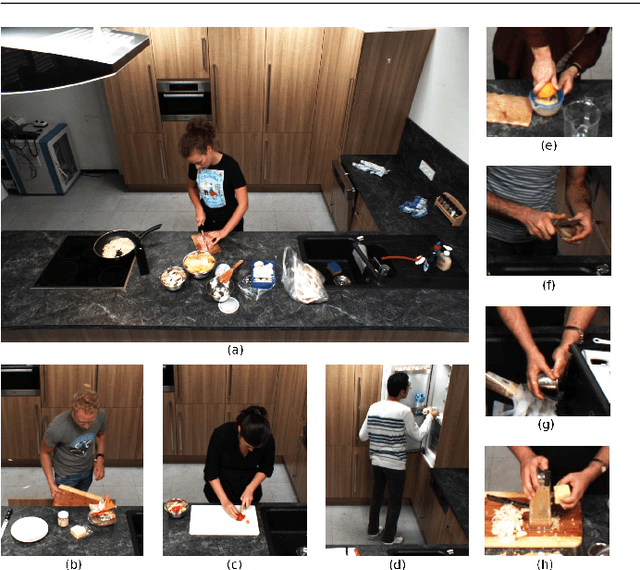
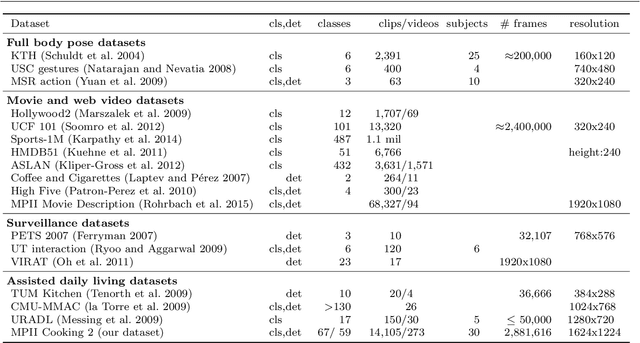

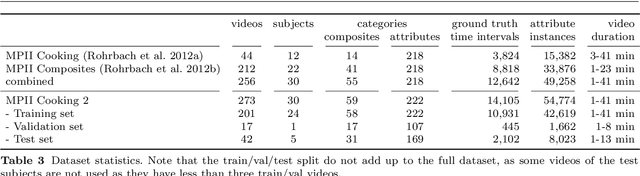
Abstract:Activity recognition has shown impressive progress in recent years. However, the challenges of detecting fine-grained activities and understanding how they are combined into composite activities have been largely overlooked. In this work we approach both tasks and present a dataset which provides detailed annotations to address them. The first challenge is to detect fine-grained activities, which are defined by low inter-class variability and are typically characterized by fine-grained body motions. We explore how human pose and hands can help to approach this challenge by comparing two pose-based and two hand-centric features with state-of-the-art holistic features. To attack the second challenge, recognizing composite activities, we leverage the fact that these activities are compositional and that the essential components of the activities can be obtained from textual descriptions or scripts. We show the benefits of our hand-centric approach for fine-grained activity classification and detection. For composite activity recognition we find that decomposition into attributes allows sharing information across composites and is essential to attack this hard task. Using script data we can recognize novel composites without having training data for them.
Coherent Multi-Sentence Video Description with Variable Level of Detail
Mar 24, 2014
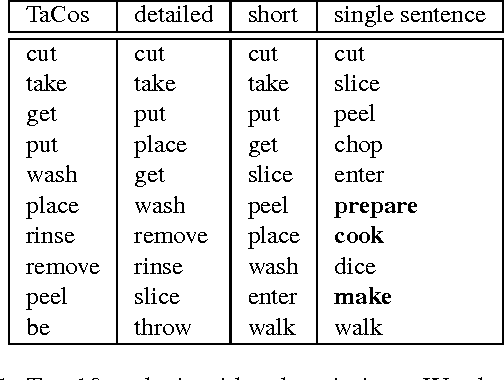
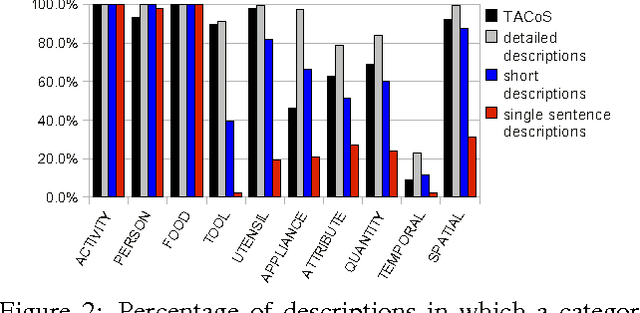
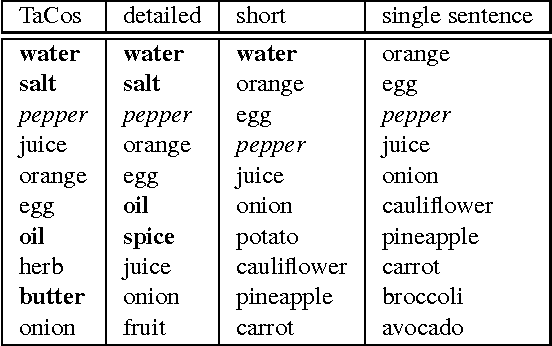
Abstract:Humans can easily describe what they see in a coherent way and at varying level of detail. However, existing approaches for automatic video description are mainly focused on single sentence generation and produce descriptions at a fixed level of detail. In this paper, we address both of these limitations: for a variable level of detail we produce coherent multi-sentence descriptions of complex videos. We follow a two-step approach where we first learn to predict a semantic representation (SR) from video and then generate natural language descriptions from the SR. To produce consistent multi-sentence descriptions, we model across-sentence consistency at the level of the SR by enforcing a consistent topic. We also contribute both to the visual recognition of objects proposing a hand-centric approach as well as to the robust generation of sentences using a word lattice. Human judges rate our multi-sentence descriptions as more readable, correct, and relevant than related work. To understand the difference between more detailed and shorter descriptions, we collect and analyze a video description corpus of three levels of detail.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge