Michaela Regneri
LLMs Explain't: A Post-Mortem on Semantic Interpretability in Transformer Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are becoming increasingly popular in pervasive computing due to their versatility and strong performance. However, despite their ubiquitous use, the exact mechanisms underlying their outstanding performance remain unclear. Different methods for LLM explainability exist, and many are, as a method, not fully understood themselves. We started with the question of how linguistic abstraction emerges in LLMs, aiming to detect it across different LLM modules (attention heads and input embeddings). For this, we used methods well-established in the literature: (1) probing for token-level relational structures, and (2) feature-mapping using embeddings as carriers of human-interpretable properties. Both attempts failed for different methodological reasons: Attention-based explanations collapsed once we tested the core assumption that later-layer representations still correspond to tokens. Property-inference methods applied to embeddings also failed because their high predictive scores were driven by methodological artifacts and dataset structure rather than meaningful semantic knowledge. These failures matter because both techniques are widely treated as evidence for what LLMs supposedly understand, yet our results show such conclusions are unwarranted. These limitations are particularly relevant in pervasive and distributed computing settings where LLMs are deployed as system components and interpretability methods are relied upon for debugging, compression, and explaining models.
Automating Violence Detection and Categorization from Ancient Texts
Mar 11, 2025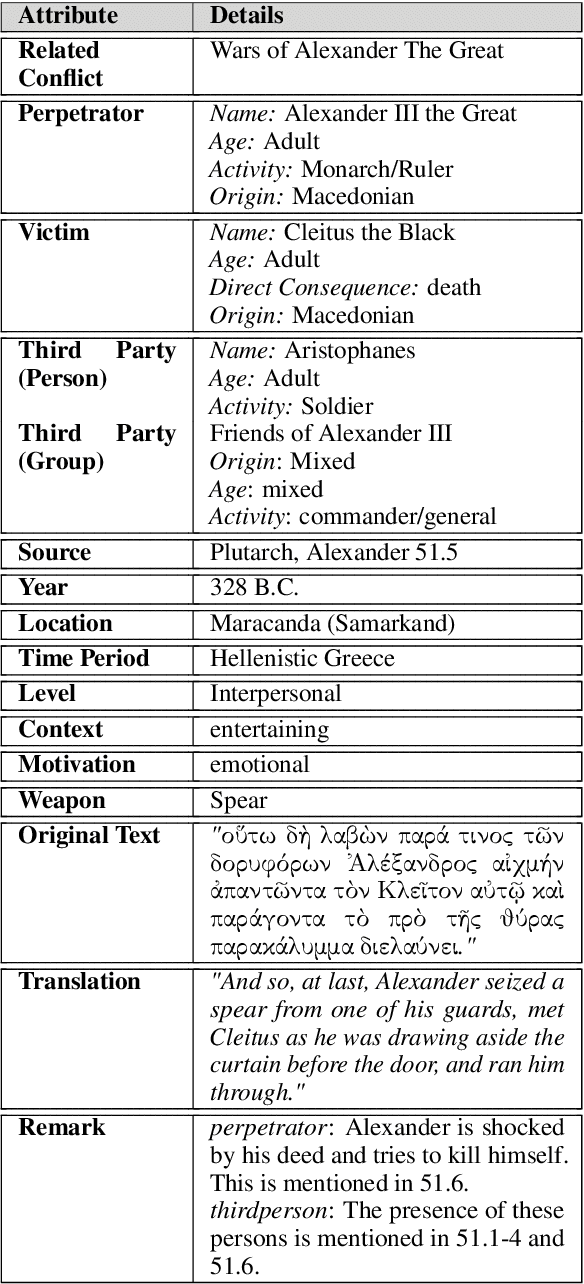
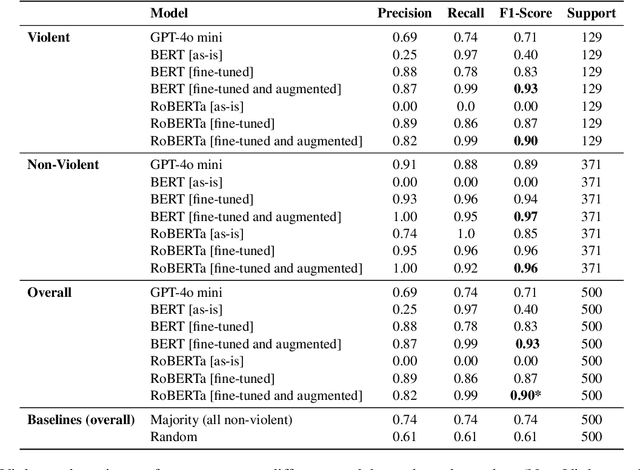
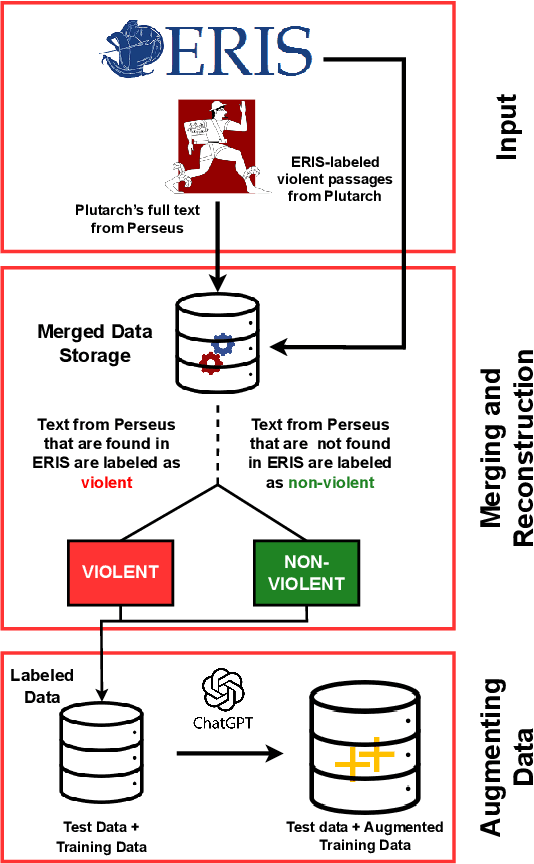
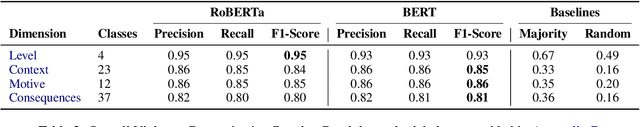
Abstract:Violence descriptions in literature offer valuable insights for a wide range of research in the humanities. For historians, depictions of violence are of special interest for analyzing the societal dynamics surrounding large wars and individual conflicts of influential people. Harvesting data for violence research manually is laborious and time-consuming. This study is the first one to evaluate the effectiveness of large language models (LLMs) in identifying violence in ancient texts and categorizing it across multiple dimensions. Our experiments identify LLMs as a valuable tool to scale up the accurate analysis of historical texts and show the effect of fine-tuning and data augmentation, yielding an F1-score of up to 0.93 for violence detection and 0.86 for fine-grained violence categorization.
Detecting Conceptual Abstraction in LLMs
Apr 25, 2024Abstract:We present a novel approach to detecting noun abstraction within a large language model (LLM). Starting from a psychologically motivated set of noun pairs in taxonomic relationships, we instantiate surface patterns indicating hypernymy and analyze the attention matrices produced by BERT. We compare the results to two sets of counterfactuals and show that we can detect hypernymy in the abstraction mechanism, which cannot solely be related to the distributional similarity of noun pairs. Our findings are a first step towards the explainability of conceptual abstraction in LLMs.
Computing the Value of Data: Towards Applied Data Minimalism
Jul 29, 2019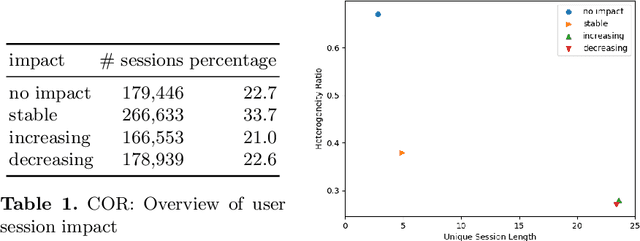
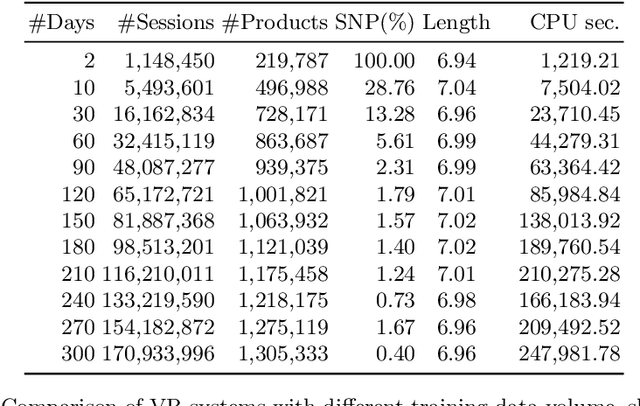
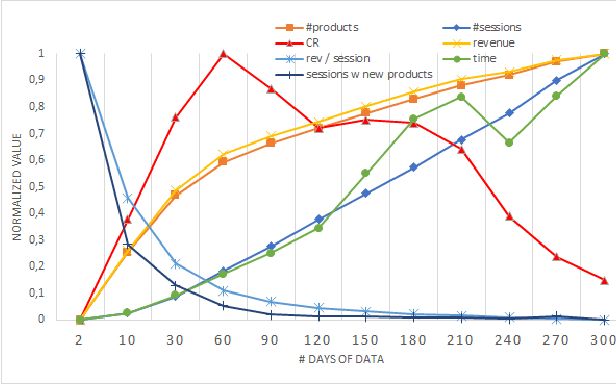
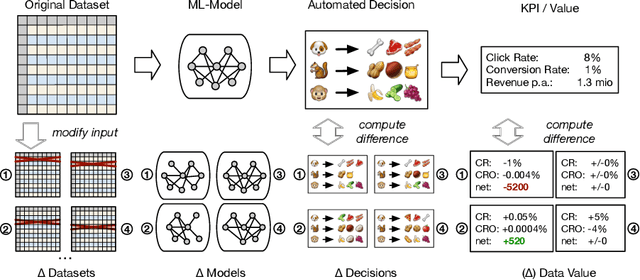
Abstract:We present an approach to compute the monetary value of individual data points, in context of an automated decision system. The proposed method enables us to explore and implement a paradigm of data minimalism for large-scale machine learning systems. Data minimalistic implementations enhance scalability, while maintaining or even optimizing a system's performance. Using two types of recommender systems, we first demonstrate how much data is ineffective in both settings. We then present a general account of computing data value via sensitivity analysis, and how, in theory, individual data points can be priced according to their informational contribution to automated decisions. We further exemplify this method to lab-scale recommender systems and outline further steps towards commercial data-minimalistic applications.
Analyzing Hypersensitive AI: Instability in Corporate-Scale Machine Learning
Jul 17, 2018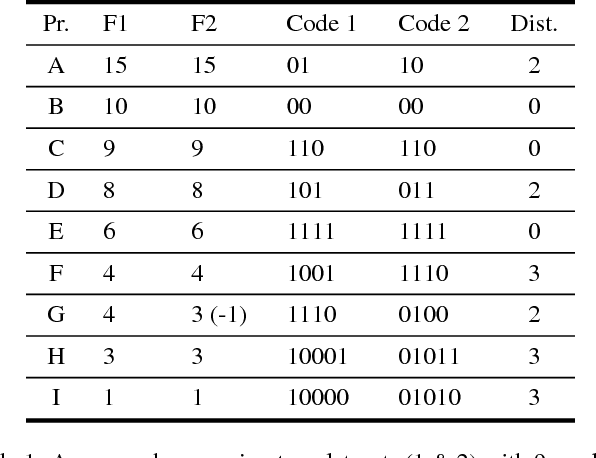
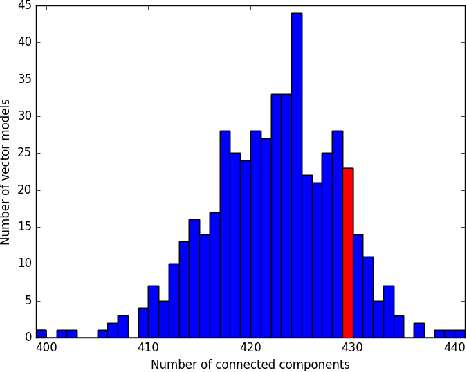
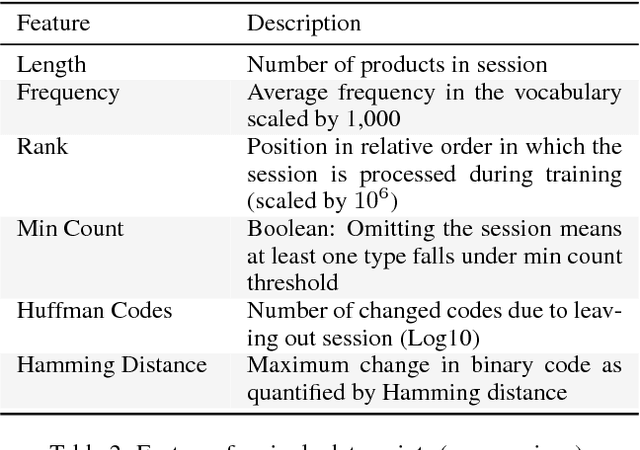
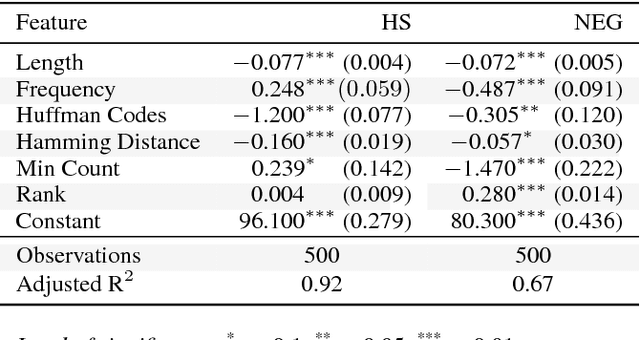
Abstract:Predictive geometric models deliver excellent results for many Machine Learning use cases. Despite their undoubted performance, neural predictive algorithms can show unexpected degrees of instability and variance, particularly when applied to large datasets. We present an approach to measure changes in geometric models with respect to both output consistency and topological stability. Considering the example of a recommender system using word2vec, we analyze the influence of single data points, approximation methods and parameter settings. Our findings can help to stabilize models where needed and to detect differences in informational value of data points on a large scale.
* 7 pages, presented as poster at IJCAI-ECAI Workshop on Explainable AI
Recognizing Fine-Grained and Composite Activities using Hand-Centric Features and Script Data
Oct 15, 2015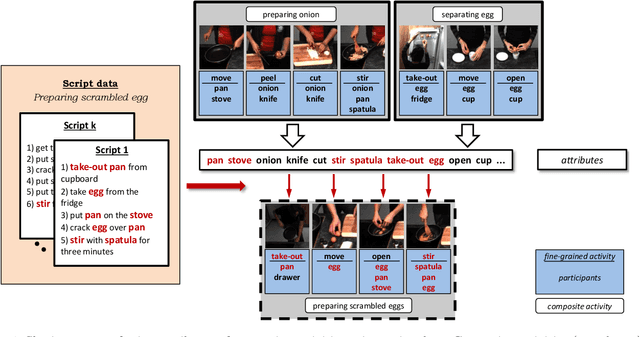
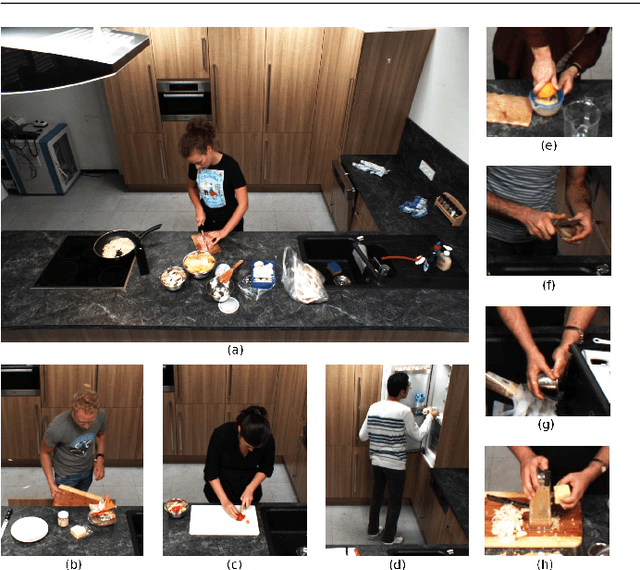
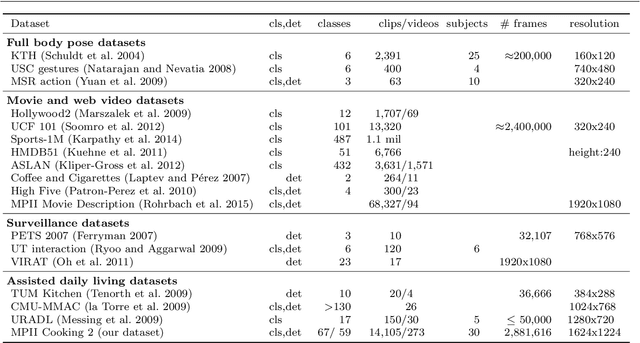

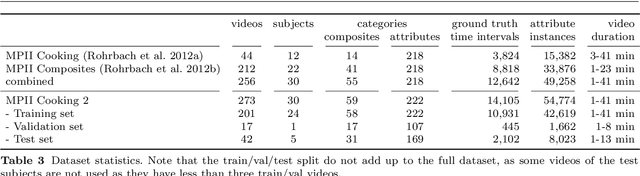
Abstract:Activity recognition has shown impressive progress in recent years. However, the challenges of detecting fine-grained activities and understanding how they are combined into composite activities have been largely overlooked. In this work we approach both tasks and present a dataset which provides detailed annotations to address them. The first challenge is to detect fine-grained activities, which are defined by low inter-class variability and are typically characterized by fine-grained body motions. We explore how human pose and hands can help to approach this challenge by comparing two pose-based and two hand-centric features with state-of-the-art holistic features. To attack the second challenge, recognizing composite activities, we leverage the fact that these activities are compositional and that the essential components of the activities can be obtained from textual descriptions or scripts. We show the benefits of our hand-centric approach for fine-grained activity classification and detection. For composite activity recognition we find that decomposition into attributes allows sharing information across composites and is essential to attack this hard task. Using script data we can recognize novel composites without having training data for them.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge