Sibaji Gaj
OpenKBP-Opt: An international and reproducible evaluation of 76 knowledge-based planning pipelines
Feb 16, 2022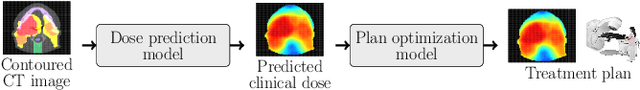

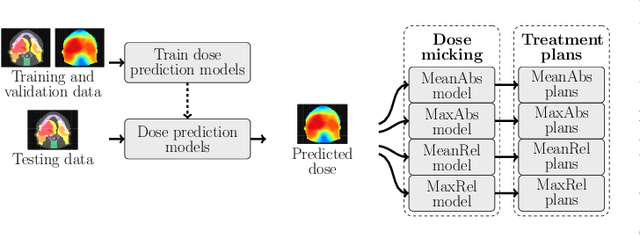
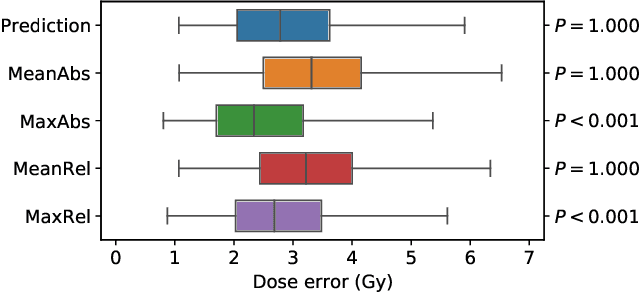
Abstract:We establish an open framework for developing plan optimization models for knowledge-based planning (KBP) in radiotherapy. Our framework includes reference plans for 100 patients with head-and-neck cancer and high-quality dose predictions from 19 KBP models that were developed by different research groups during the OpenKBP Grand Challenge. The dose predictions were input to four optimization models to form 76 unique KBP pipelines that generated 7600 plans. The predictions and plans were compared to the reference plans via: dose score, which is the average mean absolute voxel-by-voxel difference in dose a model achieved; the deviation in dose-volume histogram (DVH) criterion; and the frequency of clinical planning criteria satisfaction. We also performed a theoretical investigation to justify our dose mimicking models. The range in rank order correlation of the dose score between predictions and their KBP pipelines was 0.50 to 0.62, which indicates that the quality of the predictions is generally positively correlated with the quality of the plans. Additionally, compared to the input predictions, the KBP-generated plans performed significantly better (P<0.05; one-sided Wilcoxon test) on 18 of 23 DVH criteria. Similarly, each optimization model generated plans that satisfied a higher percentage of criteria than the reference plans. Lastly, our theoretical investigation demonstrated that the dose mimicking models generated plans that are also optimal for a conventional planning model. This was the largest international effort to date for evaluating the combination of KBP prediction and optimization models. In the interest of reproducibility, our data and code is freely available at https://github.com/ababier/open-kbp-opt.
Knee Osteoarthritis Severity Prediction using an Attentive Multi-Scale Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Jun 27, 2021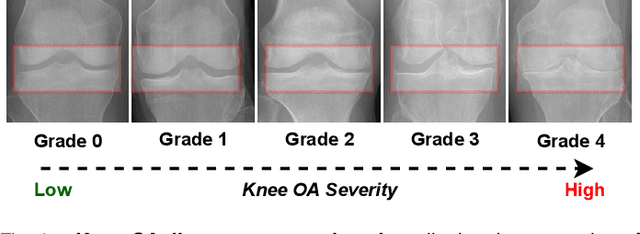
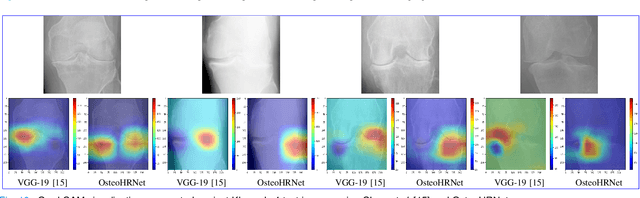
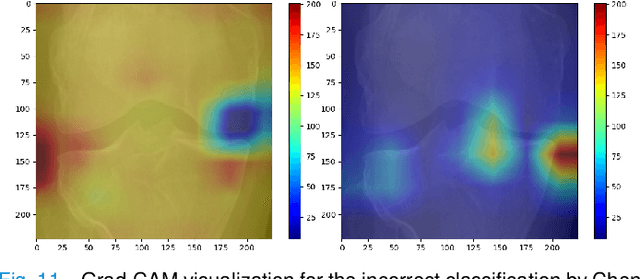
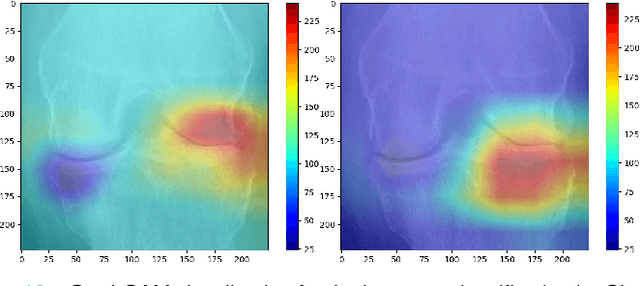
Abstract:Knee Osteoarthritis (OA) is a destructive joint disease identified by joint stiffness, pain, and functional disability concerning millions of lives across the globe. It is generally assessed by evaluating physical symptoms, medical history, and other joint screening tests like radiographs, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), and Computed Tomography (CT) scans. Unfortunately, the conventional methods are very subjective, which forms a barrier in detecting the disease progression at an early stage. This paper presents a deep learning-based framework, namely OsteoHRNet, that automatically assesses the Knee OA severity in terms of Kellgren and Lawrence (KL) grade classification from X-rays. As a primary novelty, the proposed approach is built upon one of the most recent deep models, called the High-Resolution Network (HRNet), to capture the multi-scale features of knee X-rays. In addition, we have also incorporated an attention mechanism to filter out the counterproductive features and boost the performance further. Our proposed model has achieved the best multiclass accuracy of 71.74% and MAE of 0.311 on the baseline cohort of the OAI dataset, which is a remarkable gain over the existing best-published works. We have also employed the Gradient-based Class Activation Maps (Grad-CAMs) visualization to justify the proposed network learning.
The International Workshop on Osteoarthritis Imaging Knee MRI Segmentation Challenge: A Multi-Institute Evaluation and Analysis Framework on a Standardized Dataset
May 26, 2020
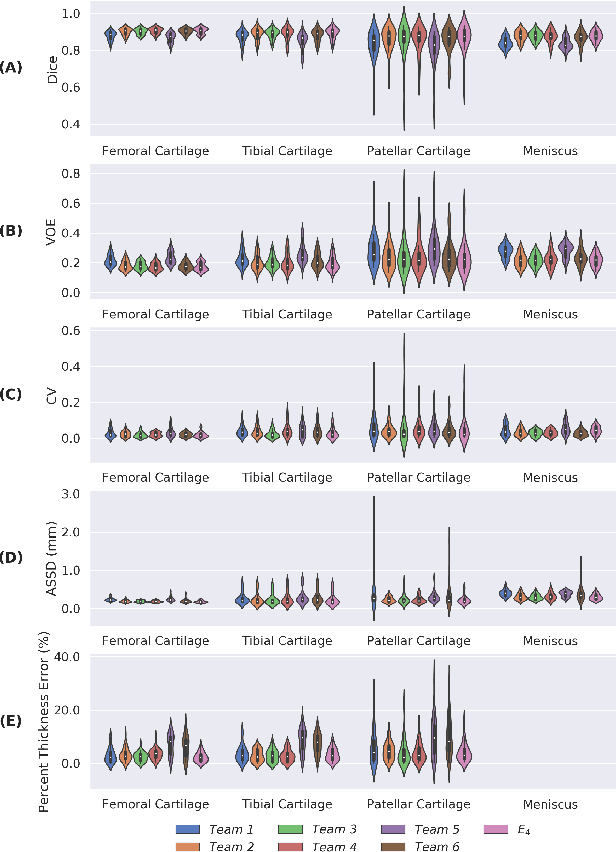
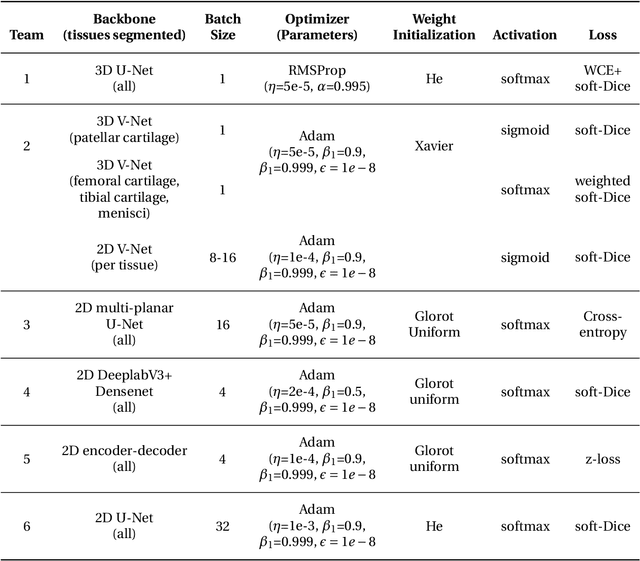
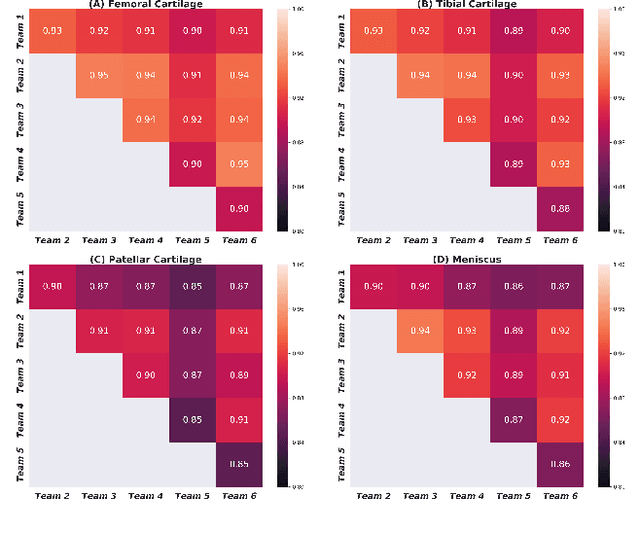
Abstract:Purpose: To organize a knee MRI segmentation challenge for characterizing the semantic and clinical efficacy of automatic segmentation methods relevant for monitoring osteoarthritis progression. Methods: A dataset partition consisting of 3D knee MRI from 88 subjects at two timepoints with ground-truth articular (femoral, tibial, patellar) cartilage and meniscus segmentations was standardized. Challenge submissions and a majority-vote ensemble were evaluated using Dice score, average symmetric surface distance, volumetric overlap error, and coefficient of variation on a hold-out test set. Similarities in network segmentations were evaluated using pairwise Dice correlations. Articular cartilage thickness was computed per-scan and longitudinally. Correlation between thickness error and segmentation metrics was measured using Pearson's coefficient. Two empirical upper bounds for ensemble performance were computed using combinations of model outputs that consolidated true positives and true negatives. Results: Six teams (T1-T6) submitted entries for the challenge. No significant differences were observed across all segmentation metrics for all tissues (p=1.0) among the four top-performing networks (T2, T3, T4, T6). Dice correlations between network pairs were high (>0.85). Per-scan thickness errors were negligible among T1-T4 (p=0.99) and longitudinal changes showed minimal bias (<0.03mm). Low correlations (<0.41) were observed between segmentation metrics and thickness error. The majority-vote ensemble was comparable to top performing networks (p=1.0). Empirical upper bound performances were similar for both combinations (p=1.0). Conclusion: Diverse networks learned to segment the knee similarly where high segmentation accuracy did not correlate to cartilage thickness accuracy. Voting ensembles did not outperform individual networks but may help regularize individual models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge