Shijia Liao
Fish-Speech: Leveraging Large Language Models for Advanced Multilingual Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Nov 02, 2024



Abstract:Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems face ongoing challenges in processing complex linguistic features, handling polyphonic expressions, and producing natural-sounding multilingual speech - capabilities that are crucial for future AI applications. In this paper, we present Fish-Speech, a novel framework that implements a serial fast-slow Dual Autoregressive (Dual-AR) architecture to enhance the stability of Grouped Finite Scalar Vector Quantization (GFSQ) in sequence generation tasks. This architecture improves codebook processing efficiency while maintaining high-fidelity outputs, making it particularly effective for AI interactions and voice cloning. Fish-Speech leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) for linguistic feature extraction, eliminating the need for traditional grapheme-to-phoneme (G2P) conversion and thereby streamlining the synthesis pipeline and enhancing multilingual support. Additionally, we developed FF-GAN through GFSQ to achieve superior compression ratios and near 100\% codebook utilization. Our approach addresses key limitations of current TTS systems while providing a foundation for more sophisticated, context-aware speech synthesis. Experimental results show that Fish-Speech significantly outperforms baseline models in handling complex linguistic scenarios and voice cloning tasks, demonstrating its potential to advance TTS technology in AI applications. The implementation is open source at \href{https://github.com/fishaudio/fish-speech}{https://github.com/fishaudio/fish-speech}.
Eagle: Exploring The Design Space for Multimodal LLMs with Mixture of Encoders
Aug 28, 2024



Abstract:The ability to accurately interpret complex visual information is a crucial topic of multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Recent work indicates that enhanced visual perception significantly reduces hallucinations and improves performance on resolution-sensitive tasks, such as optical character recognition and document analysis. A number of recent MLLMs achieve this goal using a mixture of vision encoders. Despite their success, there is a lack of systematic comparisons and detailed ablation studies addressing critical aspects, such as expert selection and the integration of multiple vision experts. This study provides an extensive exploration of the design space for MLLMs using a mixture of vision encoders and resolutions. Our findings reveal several underlying principles common to various existing strategies, leading to a streamlined yet effective design approach. We discover that simply concatenating visual tokens from a set of complementary vision encoders is as effective as more complex mixing architectures or strategies. We additionally introduce Pre-Alignment to bridge the gap between vision-focused encoders and language tokens, enhancing model coherence. The resulting family of MLLMs, Eagle, surpasses other leading open-source models on major MLLM benchmarks. Models and code: https://github.com/NVlabs/Eagle
LITA: Language Instructed Temporal-Localization Assistant
Mar 27, 2024
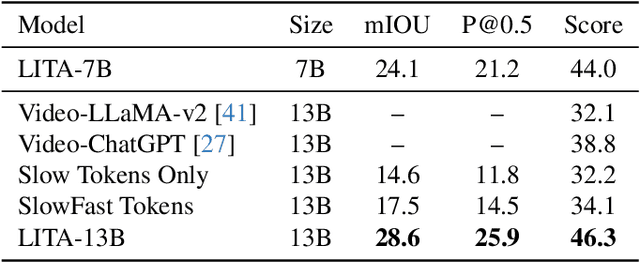
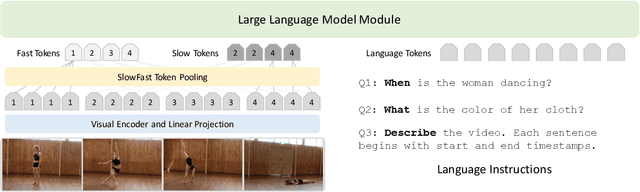
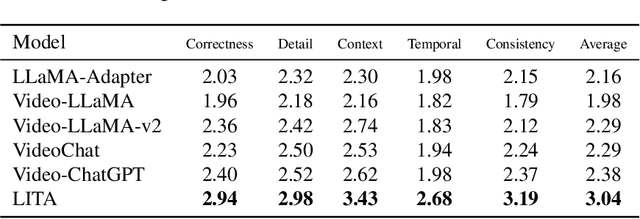
Abstract:There has been tremendous progress in multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs). Recent works have extended these models to video input with promising instruction following capabilities. However, an important missing piece is temporal localization. These models cannot accurately answer the "When?" questions. We identify three key aspects that limit their temporal localization capabilities: (i) time representation, (ii) architecture, and (iii) data. We address these shortcomings by proposing Language Instructed Temporal-Localization Assistant (LITA) with the following features: (1) We introduce time tokens that encode timestamps relative to the video length to better represent time in videos. (2) We introduce SlowFast tokens in the architecture to capture temporal information at fine temporal resolution. (3) We emphasize temporal localization data for LITA. In addition to leveraging existing video datasets with timestamps, we propose a new task, Reasoning Temporal Localization (RTL), along with the dataset, ActivityNet-RTL, for learning and evaluating this task. Reasoning temporal localization requires both the reasoning and temporal localization of Video LLMs. LITA demonstrates strong performance on this challenging task, nearly doubling the temporal mean intersection-over-union (mIoU) of baselines. In addition, we show that our emphasis on temporal localization also substantially improves video-based text generation compared to existing Video LLMs, including a 36% relative improvement of Temporal Understanding. Code is available at: https://github.com/NVlabs/LITA
EVA-GAN: Enhanced Various Audio Generation via Scalable Generative Adversarial Networks
Jan 31, 2024Abstract:The advent of Large Models marks a new era in machine learning, significantly outperforming smaller models by leveraging vast datasets to capture and synthesize complex patterns. Despite these advancements, the exploration into scaling, especially in the audio generation domain, remains limited, with previous efforts didn't extend into the high-fidelity (HiFi) 44.1kHz domain and suffering from both spectral discontinuities and blurriness in the high-frequency domain, alongside a lack of robustness against out-of-domain data. These limitations restrict the applicability of models to diverse use cases, including music and singing generation. Our work introduces Enhanced Various Audio Generation via Scalable Generative Adversarial Networks (EVA-GAN), yields significant improvements over previous state-of-the-art in spectral and high-frequency reconstruction and robustness in out-of-domain data performance, enabling the generation of HiFi audios by employing an extensive dataset of 36,000 hours of 44.1kHz audio, a context-aware module, a Human-In-The-Loop artifact measurement toolkit, and expands the model to approximately 200 million parameters. Demonstrations of our work are available at https://double-blind-eva-gan.cc.
SHARE: Single-view Human Adversarial REconstruction
Dec 30, 2023Abstract:The accuracy of 3D Human Pose and Shape reconstruction (HPS) from an image is progressively improving. Yet, no known method is robust across all image distortion. To address issues due to variations of camera poses, we introduce SHARE, a novel fine-tuning method that utilizes adversarial data augmentation to enhance the robustness of existing HPS techniques. We perform a comprehensive analysis on the impact of camera poses on HPS reconstruction outcomes. We first generated large-scale image datasets captured systematically from diverse camera perspectives. We then established a mapping between camera poses and reconstruction errors as a continuous function that characterizes the relationship between camera poses and HPS quality. Leveraging this representation, we introduce RoME (Regions of Maximal Error), a novel sampling technique for our adversarial fine-tuning method. The SHARE framework is generalizable across various single-view HPS methods and we demonstrate its performance on HMR, SPIN, PARE, CLIFF and ExPose. Our results illustrate a reduction in mean joint errors across single-view HPS techniques, for images captured from multiple camera positions without compromising their baseline performance. In many challenging cases, our method surpasses the performance of existing models, highlighting its practical significance for diverse real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge