Sheng-hua Zhong
From References to Insights: Collaborative Knowledge Minigraph Agents for Automating Scholarly Literature Review
Nov 09, 2024Abstract:Literature reviews play a crucial role in scientific research for understanding the current state of research, identifying gaps, and guiding future studies on specific topics. However, the process of conducting a comprehensive literature review is yet time-consuming. This paper proposes a novel framework, collaborative knowledge minigraph agents (CKMAs), to automate scholarly literature reviews. A novel prompt-based algorithm, the knowledge minigraph construction agent (KMCA), is designed to identify relationships between information pieces from academic literature and automatically constructs knowledge minigraphs. By leveraging the capabilities of large language models on constructed knowledge minigraphs, the multiple path summarization agent (MPSA) efficiently organizes information pieces and relationships from different viewpoints to generate literature review paragraphs. We evaluate CKMAs on three benchmark datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed techniques generate informative, complete, consistent, and insightful summaries for different research problems, promoting the use of LLMs in more professional fields.
EasyECR: A Library for Easy Implementation and Evaluation of Event Coreference Resolution Models
Jun 20, 2024



Abstract:Event Coreference Resolution (ECR) is the task of clustering event mentions that refer to the same real-world event. Despite significant advancements, ECR research faces two main challenges: limited generalizability across domains due to narrow dataset evaluations, and difficulties in comparing models within diverse ECR pipelines. To address these issues, we develop EasyECR, the first open-source library designed to standardize data structures and abstract ECR pipelines for easy implementation and fair evaluation. More specifically, EasyECR integrates seven representative pipelines and ten popular benchmark datasets, enabling model evaluations on various datasets and promoting the development of robust ECR pipelines. By conducting extensive evaluation via our EasyECR, we find that, \lowercase\expandafter{\romannumeral1}) the representative ECR pipelines cannot generalize across multiple datasets, hence evaluating ECR pipelines on multiple datasets is necessary, \lowercase\expandafter{\romannumeral2}) all models in ECR pipelines have a great effect on pipeline performance, therefore, when one model in ECR pipelines are compared, it is essential to ensure that the other models remain consistent. Additionally, reproducing ECR results is not trivial, and the developed library can help reduce this discrepancy. The experimental results provide valuable baselines for future research.
GLA-GCN: Global-local Adaptive Graph Convolutional Network for 3D Human Pose Estimation from Monocular Video
Jul 22, 2023



Abstract:3D human pose estimation has been researched for decades with promising fruits. 3D human pose lifting is one of the promising research directions toward the task where both estimated pose and ground truth pose data are used for training. Existing pose lifting works mainly focus on improving the performance of estimated pose, but they usually underperform when testing on the ground truth pose data. We observe that the performance of the estimated pose can be easily improved by preparing good quality 2D pose, such as fine-tuning the 2D pose or using advanced 2D pose detectors. As such, we concentrate on improving the 3D human pose lifting via ground truth data for the future improvement of more quality estimated pose data. Towards this goal, a simple yet effective model called Global-local Adaptive Graph Convolutional Network (GLA-GCN) is proposed in this work. Our GLA-GCN globally models the spatiotemporal structure via a graph representation and backtraces local joint features for 3D human pose estimation via individually connected layers. To validate our model design, we conduct extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets: Human3.6M, HumanEva-I, and MPI-INF-3DHP. Experimental results show that our GLA-GCN implemented with ground truth 2D poses significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods (e.g., up to around 3%, 17%, and 14% error reductions on Human3.6M, HumanEva-I, and MPI-INF-3DHP, respectively). GitHub: https://github.com/bruceyo/GLA-GCN.
Modeling User Repeat Consumption Behavior for Online Novel Recommendation
Sep 05, 2022
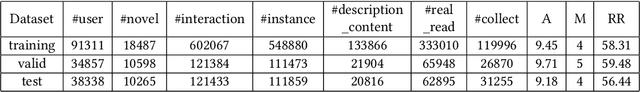
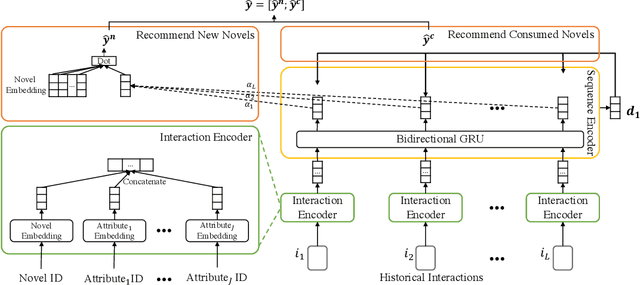
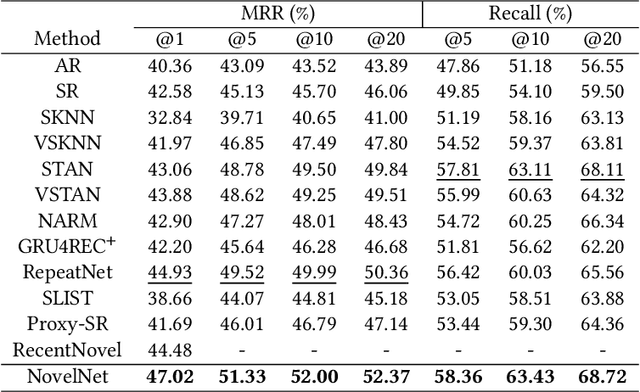
Abstract:Given a user's historical interaction sequence, online novel recommendation suggests the next novel the user may be interested in. Online novel recommendation is important but underexplored. In this paper, we concentrate on recommending online novels to new users of an online novel reading platform, whose first visits to the platform occurred in the last seven days. We have two observations about online novel recommendation for new users. First, repeat novel consumption of new users is a common phenomenon. Second, interactions between users and novels are informative. To accurately predict whether a user will reconsume a novel, it is crucial to characterize each interaction at a fine-grained level. Based on these two observations, we propose a neural network for online novel recommendation, called NovelNet. NovelNet can recommend the next novel from both the user's consumed novels and new novels simultaneously. Specifically, an interaction encoder is used to obtain accurate interaction representation considering fine-grained attributes of interaction, and a pointer network with a pointwise loss is incorporated into NovelNet to recommend previously-consumed novels. Moreover, an online novel recommendation dataset is built from a well-known online novel reading platform and is released for public use as a benchmark. Experimental results on the dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of NovelNet.
Aspect-Sentiment-Multiple-Opinion Triplet Extraction
Oct 14, 2021
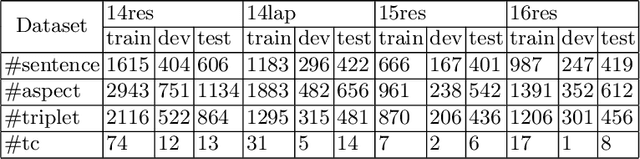
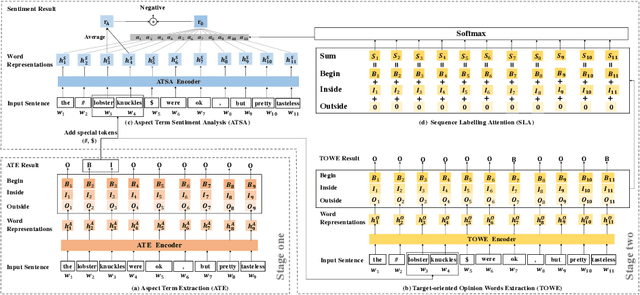
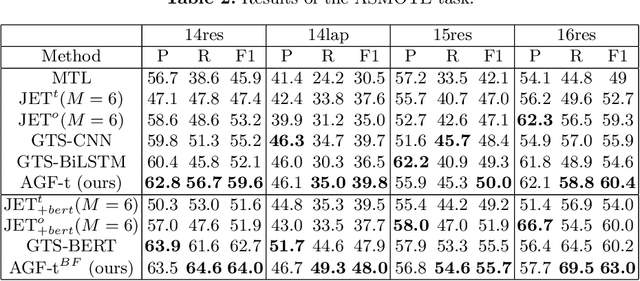
Abstract:Aspect Sentiment Triplet Extraction (ASTE) aims to extract aspect term (aspect), sentiment and opinion term (opinion) triplets from sentences and can tell a complete story, i.e., the discussed aspect, the sentiment toward the aspect, and the cause of the sentiment. ASTE is a charming task, however, one triplet extracted by ASTE only includes one opinion of the aspect, but an aspect in a sentence may have multiple corresponding opinions and one opinion only provides part of the reason why the aspect has this sentiment, as a consequence, some triplets extracted by ASTE are hard to understand, and provide erroneous information for downstream tasks. In this paper, we introduce a new task, named Aspect Sentiment Multiple Opinions Triplet Extraction (ASMOTE). ASMOTE aims to extract aspect, sentiment and multiple opinions triplets. Specifically, one triplet extracted by ASMOTE contains all opinions about the aspect and can tell the exact reason that the aspect has the sentiment. We propose an Aspect-Guided Framework (AGF) to address this task. AGF first extracts aspects, then predicts their opinions and sentiments. Moreover, with the help of the proposed Sequence Labeling Attention(SLA), AGF improves the performance of the sentiment classification using the extracted opinions. Experimental results on multiple datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
GANSER: A Self-supervised Data Augmentation Framework for EEG-based Emotion Recognition
Sep 08, 2021



Abstract:The data scarcity problem in Electroencephalography (EEG) based affective computing results into difficulty in building an effective model with high accuracy and stability using machine learning algorithms especially deep learning models. Data augmentation has recently achieved considerable performance improvement for deep learning models: increased accuracy, stability, and reduced over-fitting. In this paper, we propose a novel data augmentation framework, namely Generative Adversarial Network-based Self-supervised Data Augmentation (GANSER). As the first to combine adversarial training with self-supervised learning for EEG-based emotion recognition, the proposed framework can generate high-quality and high-diversity simulated EEG samples. In particular, we utilize adversarial training to learn an EEG generator and force the generated EEG signals to approximate the distribution of real samples, ensuring the quality of augmented samples. A transformation function is employed to mask parts of EEG signals and force the generator to synthesize potential EEG signals based on the remaining parts, to produce a wide variety of samples. The masking possibility during transformation is introduced as prior knowledge to guide to extract distinguishable features for simulated EEG signals and generalize the classifier to the augmented sample space. Finally, extensive experiments demonstrate our proposed method can help emotion recognition for performance gain and achieve state-of-the-art results.
A More Fine-Grained Aspect-Sentiment-Opinion Triplet Extraction Task
Apr 16, 2021



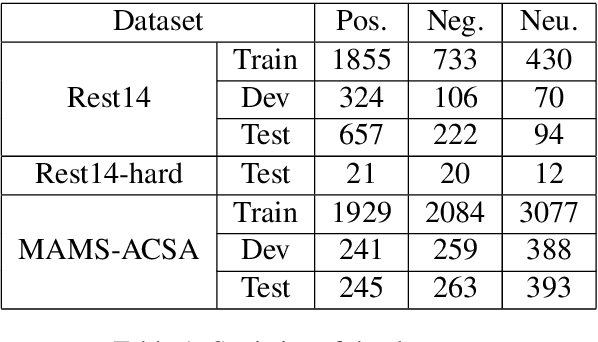
Abstract:Aspect Sentiment Triplet Extraction (ASTE) aims to extract aspect term, sentiment and opinion term triplets from sentences and tries to provide a complete solution for aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA). However, some triplets extracted by ASTE are confusing, since the sentiment in a triplet extracted by ASTE is the sentiment that the sentence expresses toward the aspect term rather than the sentiment of the aspect term and opinion term pair. In this paper, we introduce a more fine-grained Aspect-Sentiment-Opinion Triplet Extraction (ASOTE) Task. ASOTE also extracts aspect term, sentiment and opinion term triplets. However, the sentiment in a triplet extracted by ASOTE is the sentiment of the aspect term and opinion term pair. We build four datasets for ASOTE based on several popular ABSA benchmarks. We propose two methods for ASOTE. The first method extracts the opinion terms of an aspect term and predicts the sentiments of the aspect term and opinion term pairs jointly with a unified tag schema. The second method is based on multiple instance learning, which is trained on ASTE datasets, but can also perform the ASOTE task. Experimental results on the four datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods.
Multi-Instance Multi-Label Learning Networks for Aspect-Category Sentiment Analysis
Oct 06, 2020
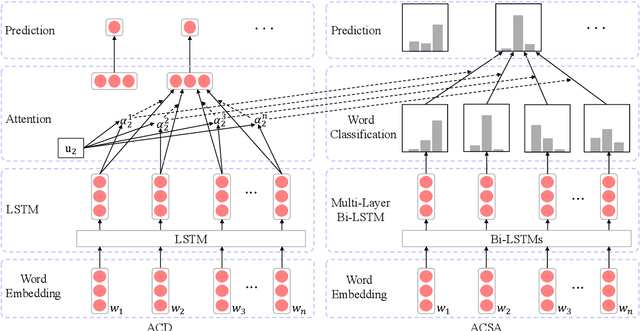
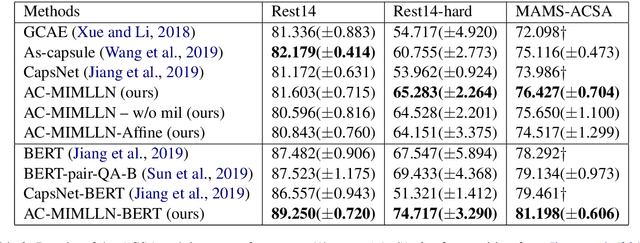
Abstract:Aspect-category sentiment analysis (ACSA) aims to predict sentiment polarities of sentences with respect to given aspect categories. To detect the sentiment toward a particular aspect category in a sentence, most previous methods first generate an aspect category-specific sentence representation for the aspect category, then predict the sentiment polarity based on the representation. These methods ignore the fact that the sentiment of an aspect category mentioned in a sentence is an aggregation of the sentiments of the words indicating the aspect category in the sentence, which leads to suboptimal performance. In this paper, we propose a Multi-Instance Multi-Label Learning Network for Aspect-Category sentiment analysis (AC-MIMLLN), which treats sentences as bags, words as instances, and the words indicating an aspect category as the key instances of the aspect category. Given a sentence and the aspect categories mentioned in the sentence, AC-MIMLLN first predicts the sentiments of the instances, then finds the key instances for the aspect categories, finally obtains the sentiments of the sentence toward the aspect categories by aggregating the key instance sentiments. Experimental results on three public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of AC-MIMLLN.
Sentence Constituent-Aware Aspect-Category Sentiment Analysis with Graph Attention Networks
Oct 04, 2020
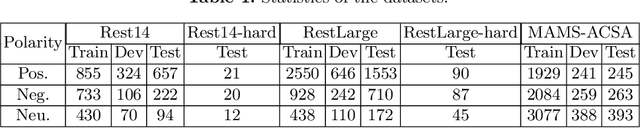
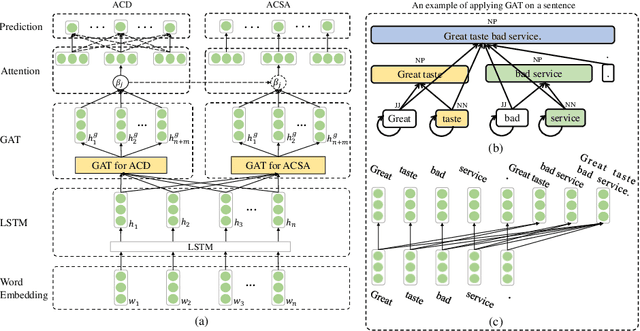
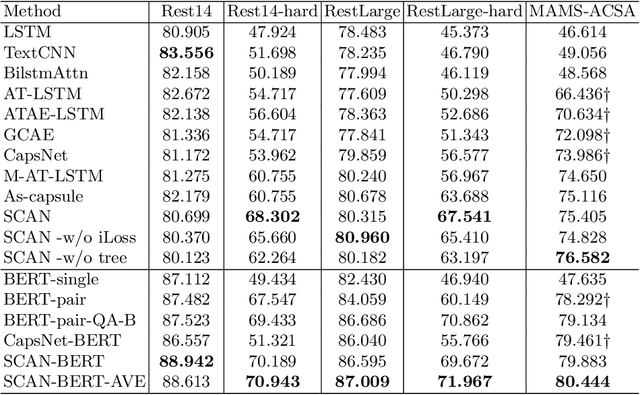
Abstract:Aspect category sentiment analysis (ACSA) aims to predict the sentiment polarities of the aspect categories discussed in sentences. Since a sentence usually discusses one or more aspect categories and expresses different sentiments toward them, various attention-based methods have been developed to allocate the appropriate sentiment words for the given aspect category and obtain promising results. However, most of these methods directly use the given aspect category to find the aspect category-related sentiment words, which may cause mismatching between the sentiment words and the aspect categories when an unrelated sentiment word is semantically meaningful for the given aspect category. To mitigate this problem, we propose a Sentence Constituent-Aware Network (SCAN) for aspect-category sentiment analysis. SCAN contains two graph attention modules and an interactive loss function. The graph attention modules generate representations of the nodes in sentence constituency parse trees for the aspect category detection (ACD) task and the ACSA task, respectively. ACD aims to detect aspect categories discussed in sentences and is a auxiliary task. For a given aspect category, the interactive loss function helps the ACD task to find the nodes which can predict the aspect category but can't predict other aspect categories. The sentiment words in the nodes then are used to predict the sentiment polarity of the aspect category by the ACSA task. The experimental results on five public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of SCAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge