Cunxiang Yin
Aiming at the Target: Filter Collaborative Information for Cross-Domain Recommendation
Mar 29, 2024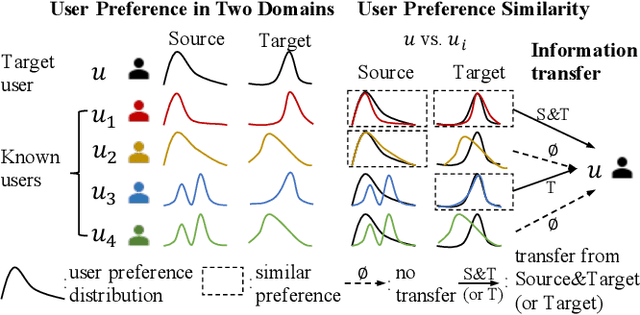
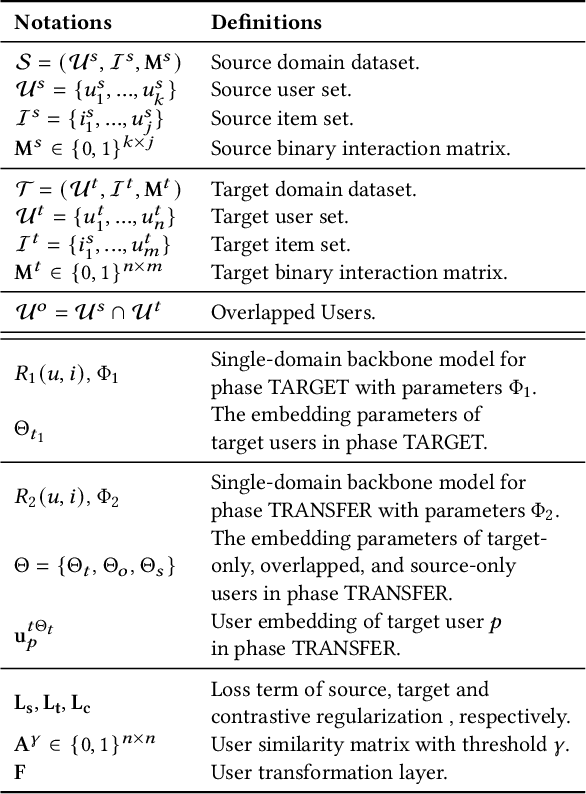
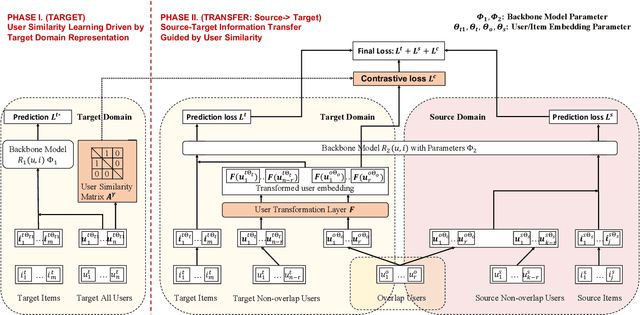
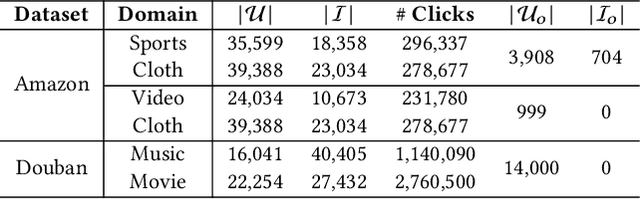
Abstract:Cross-domain recommender (CDR) systems aim to enhance the performance of the target domain by utilizing data from other related domains. However, irrelevant information from the source domain may instead degrade target domain performance, which is known as the negative transfer problem. There have been some attempts to address this problem, mostly by designing adaptive representations for overlapped users. Whereas, representation adaptions solely rely on the expressive capacity of the CDR model, lacking explicit constraint to filter the irrelevant source-domain collaborative information for the target domain. In this paper, we propose a novel Collaborative information regularized User Transformation (CUT) framework to tackle the negative transfer problem by directly filtering users' collaborative information. In CUT, user similarity in the target domain is adopted as a constraint for user transformation learning to filter the user collaborative information from the source domain. CUT first learns user similarity relationships from the target domain. Then, source-target information transfer is guided by the user similarity, where we design a user transformation layer to learn target-domain user representations and a contrastive loss to supervise the user collaborative information transferred. The results show significant performance improvement of CUT compared with SOTA single and cross-domain methods. Further analysis of the target-domain results illustrates that CUT can effectively alleviate the negative transfer problem.
Modeling User Repeat Consumption Behavior for Online Novel Recommendation
Sep 05, 2022
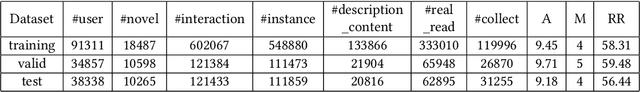
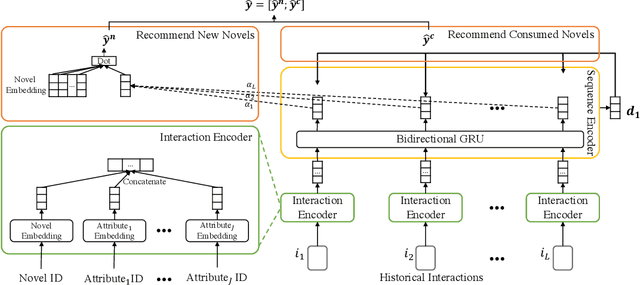
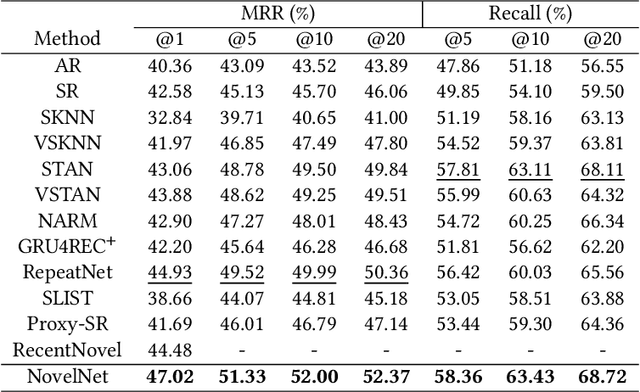
Abstract:Given a user's historical interaction sequence, online novel recommendation suggests the next novel the user may be interested in. Online novel recommendation is important but underexplored. In this paper, we concentrate on recommending online novels to new users of an online novel reading platform, whose first visits to the platform occurred in the last seven days. We have two observations about online novel recommendation for new users. First, repeat novel consumption of new users is a common phenomenon. Second, interactions between users and novels are informative. To accurately predict whether a user will reconsume a novel, it is crucial to characterize each interaction at a fine-grained level. Based on these two observations, we propose a neural network for online novel recommendation, called NovelNet. NovelNet can recommend the next novel from both the user's consumed novels and new novels simultaneously. Specifically, an interaction encoder is used to obtain accurate interaction representation considering fine-grained attributes of interaction, and a pointer network with a pointwise loss is incorporated into NovelNet to recommend previously-consumed novels. Moreover, an online novel recommendation dataset is built from a well-known online novel reading platform and is released for public use as a benchmark. Experimental results on the dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of NovelNet.
Aspect-Sentiment-Multiple-Opinion Triplet Extraction
Oct 14, 2021
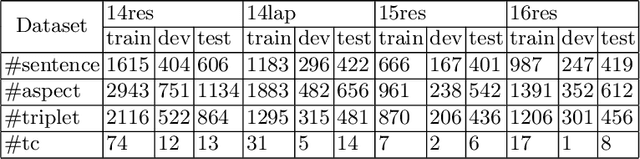
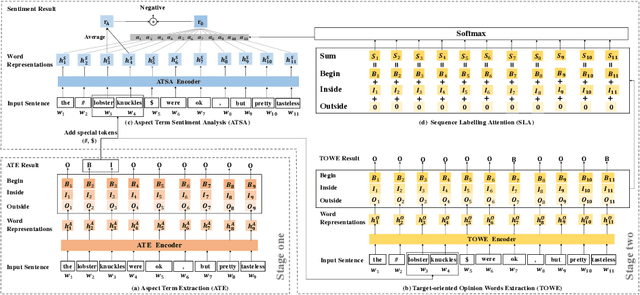
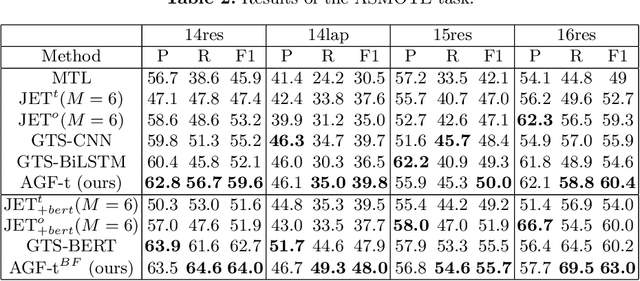
Abstract:Aspect Sentiment Triplet Extraction (ASTE) aims to extract aspect term (aspect), sentiment and opinion term (opinion) triplets from sentences and can tell a complete story, i.e., the discussed aspect, the sentiment toward the aspect, and the cause of the sentiment. ASTE is a charming task, however, one triplet extracted by ASTE only includes one opinion of the aspect, but an aspect in a sentence may have multiple corresponding opinions and one opinion only provides part of the reason why the aspect has this sentiment, as a consequence, some triplets extracted by ASTE are hard to understand, and provide erroneous information for downstream tasks. In this paper, we introduce a new task, named Aspect Sentiment Multiple Opinions Triplet Extraction (ASMOTE). ASMOTE aims to extract aspect, sentiment and multiple opinions triplets. Specifically, one triplet extracted by ASMOTE contains all opinions about the aspect and can tell the exact reason that the aspect has the sentiment. We propose an Aspect-Guided Framework (AGF) to address this task. AGF first extracts aspects, then predicts their opinions and sentiments. Moreover, with the help of the proposed Sequence Labeling Attention(SLA), AGF improves the performance of the sentiment classification using the extracted opinions. Experimental results on multiple datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
Multi-Instance Multi-Label Learning Networks for Aspect-Category Sentiment Analysis
Oct 06, 2020
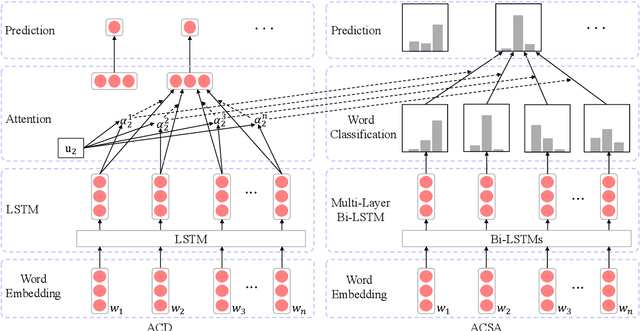
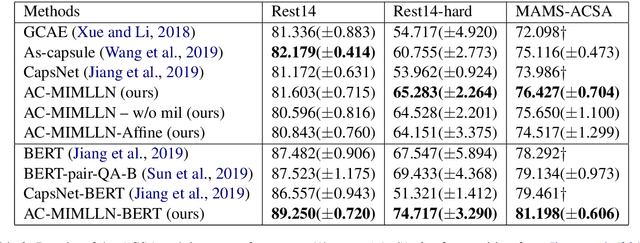
Abstract:Aspect-category sentiment analysis (ACSA) aims to predict sentiment polarities of sentences with respect to given aspect categories. To detect the sentiment toward a particular aspect category in a sentence, most previous methods first generate an aspect category-specific sentence representation for the aspect category, then predict the sentiment polarity based on the representation. These methods ignore the fact that the sentiment of an aspect category mentioned in a sentence is an aggregation of the sentiments of the words indicating the aspect category in the sentence, which leads to suboptimal performance. In this paper, we propose a Multi-Instance Multi-Label Learning Network for Aspect-Category sentiment analysis (AC-MIMLLN), which treats sentences as bags, words as instances, and the words indicating an aspect category as the key instances of the aspect category. Given a sentence and the aspect categories mentioned in the sentence, AC-MIMLLN first predicts the sentiments of the instances, then finds the key instances for the aspect categories, finally obtains the sentiments of the sentence toward the aspect categories by aggregating the key instance sentiments. Experimental results on three public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of AC-MIMLLN.
Sentence Constituent-Aware Aspect-Category Sentiment Analysis with Graph Attention Networks
Oct 04, 2020
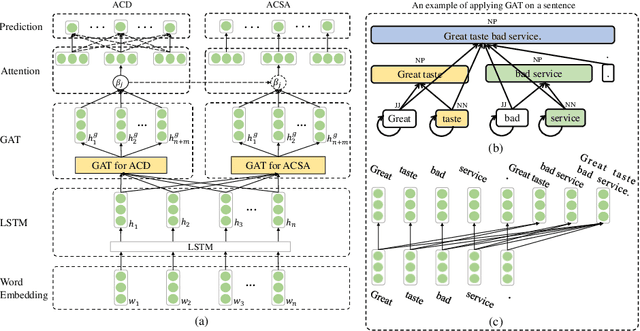
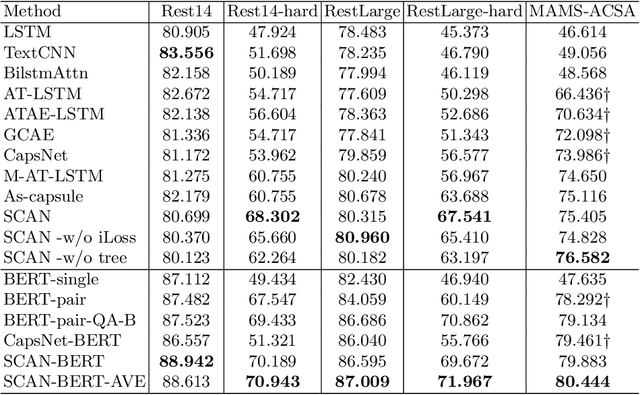
Abstract:Aspect category sentiment analysis (ACSA) aims to predict the sentiment polarities of the aspect categories discussed in sentences. Since a sentence usually discusses one or more aspect categories and expresses different sentiments toward them, various attention-based methods have been developed to allocate the appropriate sentiment words for the given aspect category and obtain promising results. However, most of these methods directly use the given aspect category to find the aspect category-related sentiment words, which may cause mismatching between the sentiment words and the aspect categories when an unrelated sentiment word is semantically meaningful for the given aspect category. To mitigate this problem, we propose a Sentence Constituent-Aware Network (SCAN) for aspect-category sentiment analysis. SCAN contains two graph attention modules and an interactive loss function. The graph attention modules generate representations of the nodes in sentence constituency parse trees for the aspect category detection (ACD) task and the ACSA task, respectively. ACD aims to detect aspect categories discussed in sentences and is a auxiliary task. For a given aspect category, the interactive loss function helps the ACD task to find the nodes which can predict the aspect category but can't predict other aspect categories. The sentiment words in the nodes then are used to predict the sentiment polarity of the aspect category by the ACSA task. The experimental results on five public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of SCAN.
AirRL: A Reinforcement Learning Approach to Urban Air Quality Inference
Mar 27, 2020



Abstract:Urban air pollution has become a major environmental problem that threatens public health. It has become increasingly important to infer fine-grained urban air quality based on existing monitoring stations. One of the challenges is how to effectively select some relevant stations for air quality inference. In this paper, we propose a novel model based on reinforcement learning for urban air quality inference. The model consists of two modules: a station selector and an air quality regressor. The station selector dynamically selects the most relevant monitoring stations when inferring air quality. The air quality regressor takes in the selected stations and makes air quality inference with deep neural network. We conduct experiments on a real-world air quality dataset and our approach achieves the highest performance compared with several popular solutions, and the experiments show significant effectiveness of proposed model in tackling problems of air quality inference.
A Joint Model for Aspect-Category Sentiment Analysis with Contextualized Aspect Embedding
Aug 29, 2019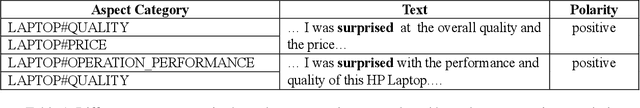

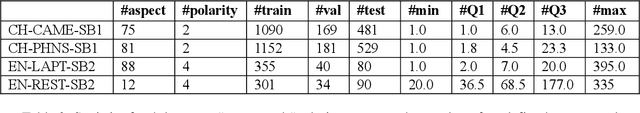
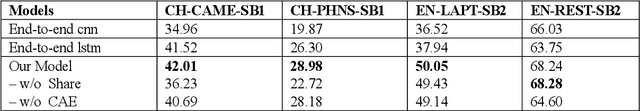
Abstract:Aspect-category sentiment analysis (ACSA) aims to identify all the aspect categories mentioned in the text and their corresponding sentiment polarities. Some joint models have been proposed to address this task. However, these joint models do not solve the following two problems well: mismatching between the aspect categories and the sentiment words, and data deficiency of some aspect categories. To solve them, we propose a novel joint model which contains a contextualized aspect embedding layer and a shared sentiment prediction layer. The contextualized aspect embedding layer extracts the aspect category related information, which is used to generate aspect-specific representations for sentiment classification like traditional context-independent aspect embedding (CIAE) and is therefore called contextualized aspect embedding (CAE). The CAE can mitigate the mismatching problem because it is semantically more related to sentiment words than CIAE. The shared sentiment prediction layer transfers sentiment knowledge between aspect categories and alleviates the problem caused by data deficiency. Experiments conducted on SemEval 2016 Datasets show that our proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge