Shang Wang
Elastic Architecture Search for Efficient Language Models
Oct 30, 2025



Abstract:As large pre-trained language models become increasingly critical to natural language understanding (NLU) tasks, their substantial computational and memory requirements have raised significant economic and environmental concerns. Addressing these challenges, this paper introduces the Elastic Language Model (ELM), a novel neural architecture search (NAS) method optimized for compact language models. ELM extends existing NAS approaches by introducing a flexible search space with efficient transformer blocks and dynamic modules for dimension and head number adjustment. These innovations enhance the efficiency and flexibility of the search process, which facilitates more thorough and effective exploration of model architectures. We also introduce novel knowledge distillation losses that preserve the unique characteristics of each block, in order to improve the discrimination between architectural choices during the search process. Experiments on masked language modeling and causal language modeling tasks demonstrate that models discovered by ELM significantly outperform existing methods.
The Demon is in Ambiguity: Revisiting Situation Recognition with Single Positive Multi-Label Learning
Aug 29, 2025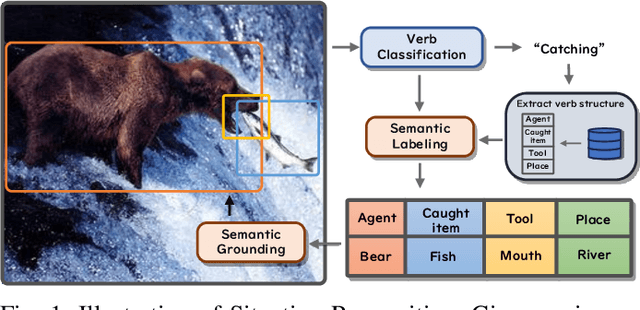
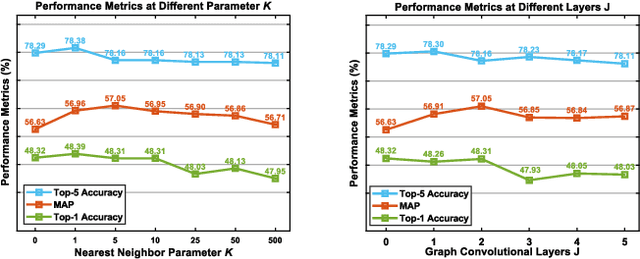
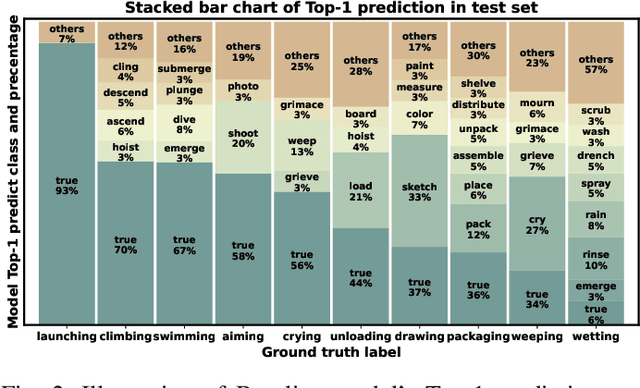
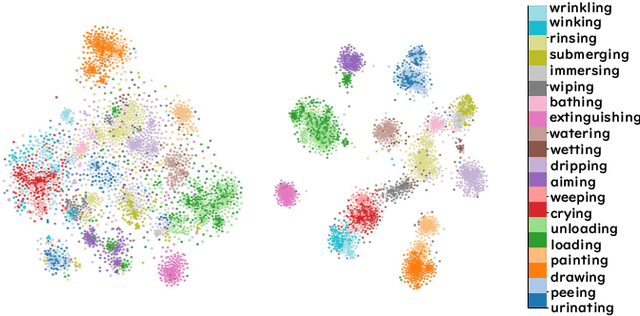
Abstract:Context recognition (SR) is a fundamental task in computer vision that aims to extract structured semantic summaries from images by identifying key events and their associated entities. Specifically, given an input image, the model must first classify the main visual events (verb classification), then identify the participating entities and their semantic roles (semantic role labeling), and finally localize these entities in the image (semantic role localization). Existing methods treat verb classification as a single-label problem, but we show through a comprehensive analysis that this formulation fails to address the inherent ambiguity in visual event recognition, as multiple verb categories may reasonably describe the same image. This paper makes three key contributions: First, we reveal through empirical analysis that verb classification is inherently a multi-label problem due to the ubiquitous semantic overlap between verb categories. Second, given the impracticality of fully annotating large-scale datasets with multiple labels, we propose to reformulate verb classification as a single positive multi-label learning (SPMLL) problem - a novel perspective in SR research. Third, we design a comprehensive multi-label evaluation benchmark for SR that is carefully designed to fairly evaluate model performance in a multi-label setting. To address the challenges of SPMLL, we futher develop the Graph Enhanced Verb Multilayer Perceptron (GE-VerbMLP), which combines graph neural networks to capture label correlations and adversarial training to optimize decision boundaries. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets show that our approach achieves more than 3\% MAP improvement while remaining competitive on traditional top-1 and top-5 accuracy metrics.
A Transformer-based Neural Architecture Search Method
May 02, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a neural architecture search method based on Transformer architecture, searching cross multihead attention computation ways for different number of encoder and decoder combinations. In order to search for neural network structures with better translation results, we considered perplexity as an auxiliary evaluation metric for the algorithm in addition to BLEU scores and iteratively improved each individual neural network within the population by a multi-objective genetic algorithm. Experimental results show that the neural network structures searched by the algorithm outperform all the baseline models, and that the introduction of the auxiliary evaluation metric can find better models than considering only the BLEU score as an evaluation metric.
A Neural Architecture Search Method using Auxiliary Evaluation Metric based on ResNet Architecture
May 02, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a neural architecture search space using ResNet as a framework, with search objectives including parameters for convolution, pooling, fully connected layers, and connectivity of the residual network. In addition to recognition accuracy, this paper uses the loss value on the validation set as a secondary objective for optimization. The experimental results demonstrate that the search space of this paper together with the optimisation approach can find competitive network architectures on the MNIST, Fashion-MNIST and CIFAR100 datasets.
W-PCA Based Gradient-Free Proxy for Efficient Search of Lightweight Language Models
Apr 22, 2025



Abstract:The demand for efficient natural language processing (NLP) systems has led to the development of lightweight language models. Previous work in this area has primarily focused on manual design or training-based neural architecture search (NAS) methods. Recently, zero-shot NAS methods have been proposed for evaluating language models without the need for training. However, prevailing approaches to zero-shot NAS often face challenges such as biased evaluation metrics and computational inefficiencies. In this paper, we introduce weight-weighted PCA (W-PCA), a novel zero-shot NAS method specifically tailored for lightweight language models. Our approach utilizes two evaluation proxies: the parameter count and the number of principal components with cumulative contribution exceeding $\eta$ in the feed-forward neural (FFN) layer. Additionally, by eliminating the need for gradient computations, we optimize the evaluation time, thus enhancing the efficiency of designing and evaluating lightweight language models. We conduct a comparative analysis on the GLUE and SQuAD datasets to evaluate our approach. The results demonstrate that our method significantly reduces training time compared to one-shot NAS methods and achieves higher scores in the testing phase compared to previous state-of-the-art training-based methods. Furthermore, we perform ranking evaluations on a dataset sampled from the FlexiBERT search space. Our approach exhibits superior ranking correlation and further reduces solving time compared to other zero-shot NAS methods that require gradient computation.
Data-Free Model-Related Attacks: Unleashing the Potential of Generative AI
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:Generative AI technology has become increasingly integrated into our daily lives, offering powerful capabilities to enhance productivity. However, these same capabilities can be exploited by adversaries for malicious purposes. While existing research on adversarial applications of generative AI predominantly focuses on cyberattacks, less attention has been given to attacks targeting deep learning models. In this paper, we introduce the use of generative AI for facilitating model-related attacks, including model extraction, membership inference, and model inversion. Our study reveals that adversaries can launch a variety of model-related attacks against both image and text models in a data-free and black-box manner, achieving comparable performance to baseline methods that have access to the target models' training data and parameters in a white-box manner. This research serves as an important early warning to the community about the potential risks associated with generative AI-powered attacks on deep learning models.
Creating a Cooperative AI Policymaking Platform through Open Source Collaboration
Dec 09, 2024

Abstract:Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) present significant risks and opportunities, requiring improved governance to mitigate societal harms and promote equitable benefits. Current incentive structures and regulatory delays may hinder responsible AI development and deployment, particularly in light of the transformative potential of large language models (LLMs). To address these challenges, we propose developing the following three contributions: (1) a large multimodal text and economic-timeseries foundation model that integrates economic and natural language policy data for enhanced forecasting and decision-making, (2) algorithmic mechanisms for eliciting diverse and representative perspectives, enabling the creation of data-driven public policy recommendations, and (3) an AI-driven web platform for supporting transparent, inclusive, and data-driven policymaking.
When Machine Unlearning Meets Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Keep Secret or Forget Knowledge?
Oct 20, 2024



Abstract:The deployment of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and Gemini has shown their powerful natural language generation capabilities. However, these models can inadvertently learn and retain sensitive information and harmful content during training, raising significant ethical and legal concerns. To address these issues, machine unlearning has been introduced as a potential solution. While existing unlearning methods take into account the specific characteristics of LLMs, they often suffer from high computational demands, limited applicability, or the risk of catastrophic forgetting. To address these limitations, we propose a lightweight unlearning framework based on Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology. By modifying the external knowledge base of RAG, we simulate the effects of forgetting without directly interacting with the unlearned LLM. We approach the construction of unlearned knowledge as a constrained optimization problem, deriving two key components that underpin the effectiveness of RAG-based unlearning. This RAG-based approach is particularly effective for closed-source LLMs, where existing unlearning methods often fail. We evaluate our framework through extensive experiments on both open-source and closed-source models, including ChatGPT, Gemini, Llama-2-7b-chat-hf, and PaLM 2. The results demonstrate that our approach meets five key unlearning criteria: effectiveness, universality, harmlessness, simplicity, and robustness. Meanwhile, this approach can extend to multimodal large language models and LLM-based agents.
FPGA Divide-and-Conquer Placement using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Apr 11, 2024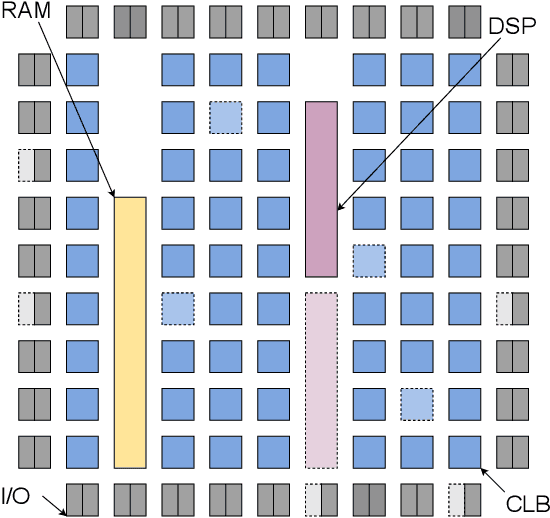
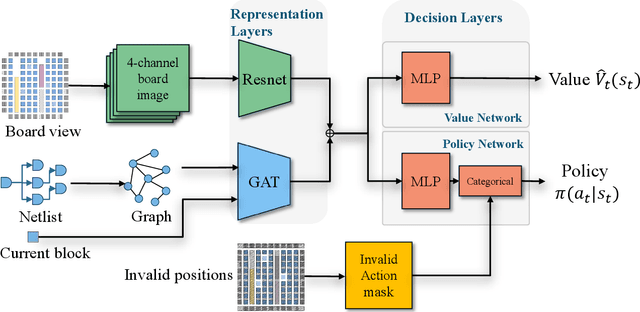
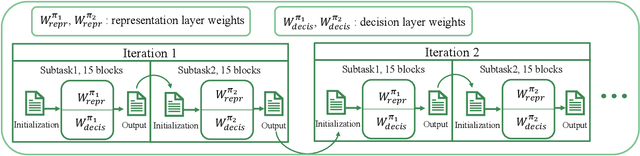
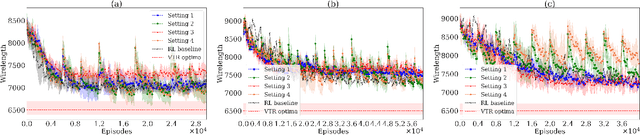
Abstract:This paper introduces the problem of learning to place logic blocks in Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) and a learning-based method. In contrast to previous search-based placement algorithms, we instead employ Reinforcement Learning (RL) with the goal of minimizing wirelength. In addition to our preliminary learning results, we also evaluated a novel decomposition to address the nature of large search space when placing many blocks on a chipboard. Empirical experiments evaluate the effectiveness of the learning and decomposition paradigms on FPGA placement tasks.
Horizontal Class Backdoor to Deep Learning
Oct 01, 2023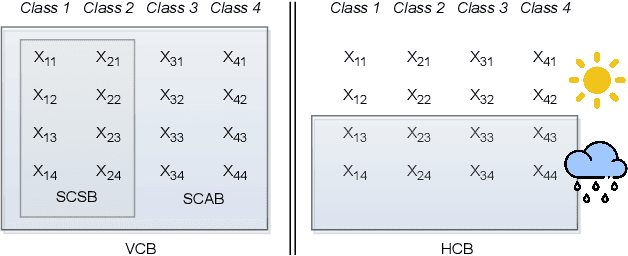
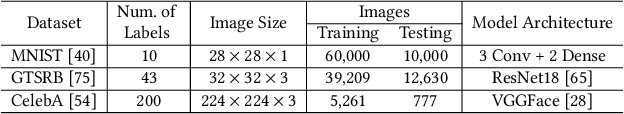

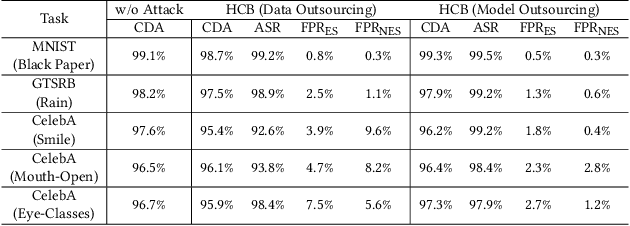
Abstract:All existing backdoor attacks to deep learning (DL) models belong to the vertical class backdoor (VCB). That is, any sample from a class will activate the implanted backdoor in the presence of the secret trigger, regardless of source-class-agnostic or source-class-specific backdoor. Current trends of existing defenses are overwhelmingly devised for VCB attacks especially the source-class-agnostic backdoor, which essentially neglects other potential simple but general backdoor types, thus giving false security implications. It is thus urgent to discover unknown backdoor types. This work reveals a new, simple, and general horizontal class backdoor (HCB) attack. We show that the backdoor can be naturally bounded with innocuous natural features that are common and pervasive in the real world. Note that an innocuous feature (e.g., expression) is irrelevant to the main task of the model (e.g., recognizing a person from one to another). The innocuous feature spans across classes horizontally but is exhibited by partial samples per class -- satisfying the horizontal class (HC) property. Only when the trigger is concurrently presented with the HC innocuous feature, can the backdoor be effectively activated. Extensive experiments on attacking performance in terms of high attack success rates with tasks of 1) MNIST, 2) facial recognition, 3) traffic sign recognition, and 4) object detection demonstrate that the HCB is highly efficient and effective. We extensively evaluate the HCB evasiveness against a (chronologically) series of 9 influential countermeasures of Fine-Pruning (RAID 18'), STRIP (ACSAC 19'), Neural Cleanse (Oakland 19'), ABS (CCS 19'), Februus (ACSAC 20'), MNTD (Oakland 21'), SCAn (USENIX SEC 21'), MOTH (Oakland 22'), and Beatrix (NDSS 23'), where none of them can succeed even when a simplest trigger is used.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge