Sarthak Jain
University of Illinois Urbana Champaign and Cisco
Mitigating Bad Ground Truth in Supervised Machine Learning based Crop Classification: A Multi-Level Framework with Sentinel-2 Images
Mar 14, 2025
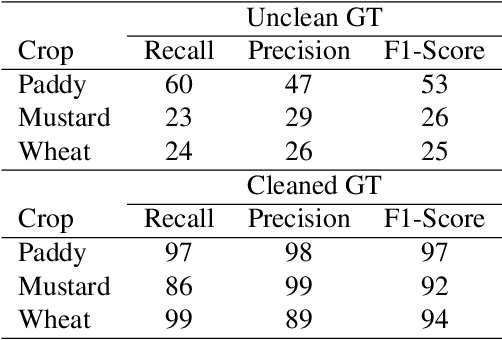
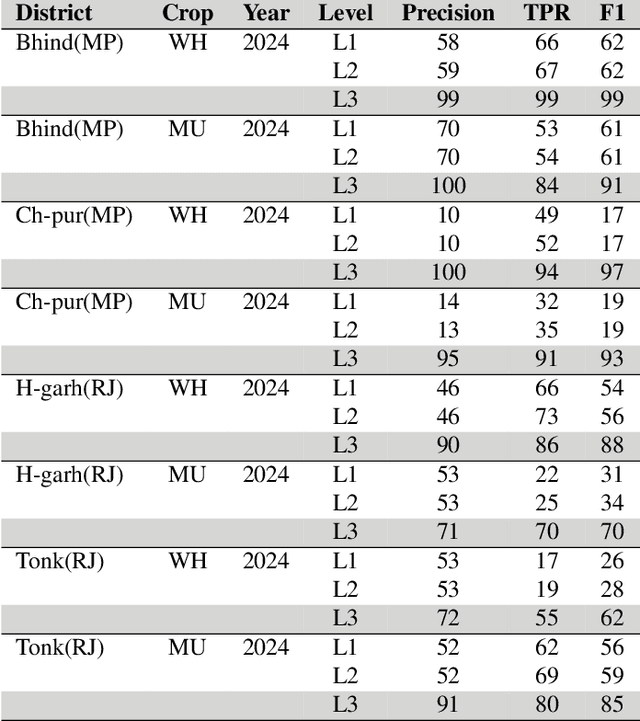
Abstract:In agricultural management, precise Ground Truth (GT) data is crucial for accurate Machine Learning (ML) based crop classification. Yet, issues like crop mislabeling and incorrect land identification are common. We propose a multi-level GT cleaning framework while utilizing multi-temporal Sentinel-2 data to address these issues. Specifically, this framework utilizes generating embeddings for farmland, clustering similar crop profiles, and identification of outliers indicating GT errors. We validated clusters with False Colour Composite (FCC) checks and used distance-based metrics to scale and automate this verification process. The importance of cleaning the GT data became apparent when the models were trained on the clean and unclean data. For instance, when we trained a Random Forest model with the clean GT data, we achieved upto 70\% absolute percentage points higher for the F1 score metric. This approach advances crop classification methodologies, with potential for applications towards improving loan underwriting and agricultural decision-making.
Self-supervised Analogical Learning using Language Models
Feb 03, 2025
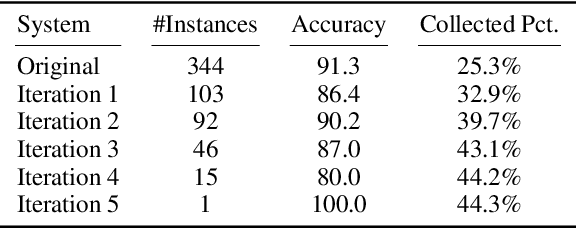
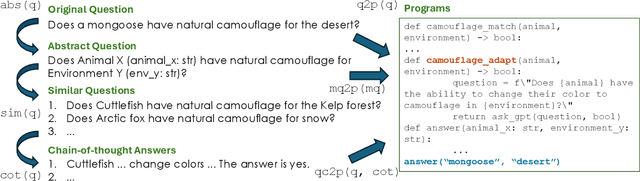

Abstract:Large language models have been shown to suffer from reasoning inconsistency issues. That is, they fail more in situations unfamiliar to the training data, even though exact or very similar reasoning paths exist in more common cases that they can successfully solve. Such observations motivate us to propose methods that encourage models to understand the high-level and abstract reasoning processes during training instead of only the final answer. This way, models can transfer the exact solution to similar cases, regardless of their relevance to the pre-training data distribution. In this work, we propose SAL, a self-supervised analogical learning framework. SAL mimics the human analogy process and trains models to explicitly transfer high-quality symbolic solutions from cases that they know how to solve to other rare cases in which they tend to fail more. We show that the resulting models after SAL learning outperform base language models on a wide range of reasoning benchmarks, such as StrategyQA, GSM8K, and HotpotQA, by 2% to 20%. At the same time, we show that our model is more generalizable and controllable through analytical studies.
ViBe: A Text-to-Video Benchmark for Evaluating Hallucination in Large Multimodal Models
Nov 16, 2024



Abstract:Latest developments in Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have broadened their capabilities to include video understanding. Specifically, Text-to-video (T2V) models have made significant progress in quality, comprehension, and duration, excelling at creating videos from simple textual prompts. Yet, they still frequently produce hallucinated content that clearly signals the video is AI-generated. We introduce ViBe: a large-scale Text-to-Video Benchmark of hallucinated videos from T2V models. We identify five major types of hallucination: Vanishing Subject, Numeric Variability, Temporal Dysmorphia, Omission Error, and Physical Incongruity. Using 10 open-source T2V models, we developed the first large-scale dataset of hallucinated videos, comprising 3,782 videos annotated by humans into these five categories. ViBe offers a unique resource for evaluating the reliability of T2V models and provides a foundation for improving hallucination detection and mitigation in video generation. We establish classification as a baseline and present various ensemble classifier configurations, with the TimeSFormer + CNN combination yielding the best performance, achieving 0.345 accuracy and 0.342 F1 score. This benchmark aims to drive the development of robust T2V models that produce videos more accurately aligned with input prompts.
SeQuiFi: Mitigating Catastrophic Forgetting in Speech Emotion Recognition with Sequential Class-Finetuning
Oct 16, 2024

Abstract:In this work, we introduce SeQuiFi, a novel approach for mitigating catastrophic forgetting (CF) in speech emotion recognition (SER). SeQuiFi adopts a sequential class-finetuning strategy, where the model is fine-tuned incrementally on one emotion class at a time, preserving and enhancing retention for each class. While various state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, such as regularization-based, memory-based, and weight-averaging techniques, have been proposed to address CF, it still remains a challenge, particularly with diverse and multilingual datasets. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that SeQuiFi significantly outperforms both vanilla fine-tuning and SOTA continual learning techniques in terms of accuracy and F1 scores on multiple benchmark SER datasets, including CREMA-D, RAVDESS, Emo-DB, MESD, and SHEMO, covering different languages.
Are Music Foundation Models Better at Singing Voice Deepfake Detection? Far-Better Fuse them with Speech Foundation Models
Sep 21, 2024



Abstract:In this study, for the first time, we extensively investigate whether music foundation models (MFMs) or speech foundation models (SFMs) work better for singing voice deepfake detection (SVDD), which has recently attracted attention in the research community. For this, we perform a comprehensive comparative study of state-of-the-art (SOTA) MFMs (MERT variants and music2vec) and SFMs (pre-trained for general speech representation learning as well as speaker recognition). We show that speaker recognition SFM representations perform the best amongst all the foundation models (FMs), and this performance can be attributed to its higher efficacy in capturing the pitch, tone, intensity, etc, characteristics present in singing voices. To our end, we also explore the fusion of FMs for exploiting their complementary behavior for improved SVDD, and we propose a novel framework, FIONA for the same. With FIONA, through the synchronization of x-vector (speaker recognition SFM) and MERT-v1-330M (MFM), we report the best performance with the lowest Equal Error Rate (EER) of 13.74 %, beating all the individual FMs as well as baseline FM fusions and achieving SOTA results.
LLM Agents Improve Semantic Code Search
Aug 05, 2024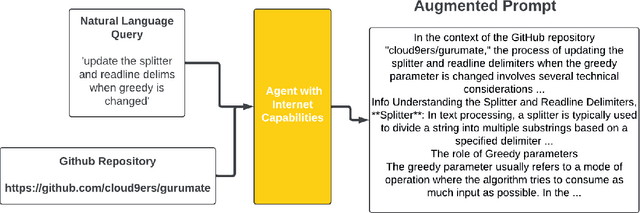

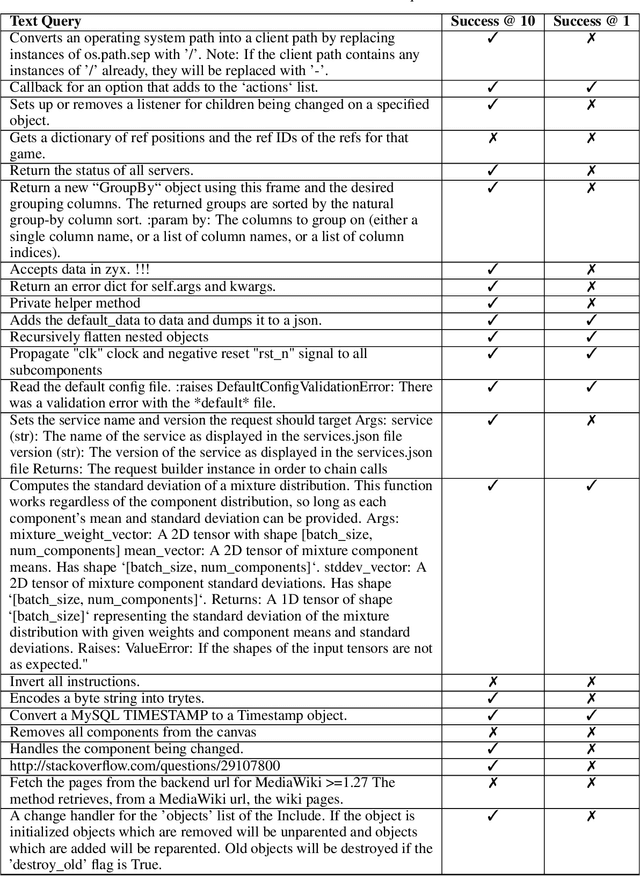
Abstract:Code Search is a key task that many programmers often have to perform while developing solutions to problems. Current methodologies suffer from an inability to perform accurately on prompts that contain some ambiguity or ones that require additional context relative to a code-base. We introduce the approach of using Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) powered agents to inject information into user prompts allowing for better inputs into embedding models. By utilizing RAG, agents enhance user queries with relevant details from GitHub repositories, making them more informative and contextually aligned. Additionally, we introduce a multi-stream ensemble approach which when paired with agentic workflow can obtain improved retrieval accuracy, which we deploy on application called repo-rift.com. Experimental results on the CodeSearchNet dataset demonstrate that RepoRift significantly outperforms existing methods, achieving an 78.2% success rate at Success@10 and a 34.6% success rate at Success@1. This research presents a substantial advancement in semantic code search, highlighting the potential of agentic LLMs and RAG to enhance code retrieval systems.
PERSONA: An Application for Emotion Recognition, Gender Recognition and Age Estimation
Jun 10, 2024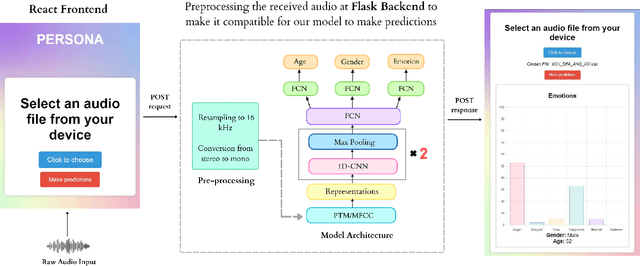
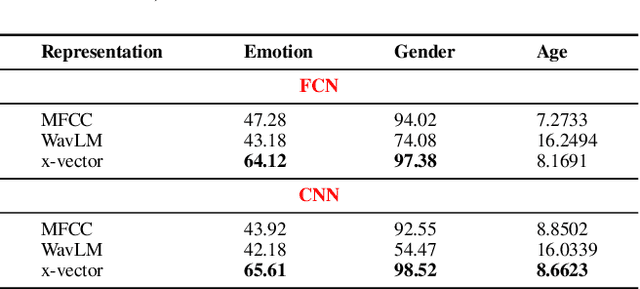
Abstract:Emotion Recognition (ER), Gender Recognition (GR), and Age Estimation (AE) constitute paralinguistic tasks that rely not on the spoken content but primarily on speech characteristics such as pitch and tone. While previous research has made significant strides in developing models for each task individually, there has been comparatively less emphasis on concurrently learning these tasks, despite their inherent interconnectedness. As such in this demonstration, we present PERSONA, an application for predicting ER, GR, and AE with a single model in the backend. One notable point is we show that representations from speaker recognition pre-trained model (PTM) is better suited for such a multi-task learning format than the state-of-the-art (SOTA) self-supervised (SSL) PTM by carrying out a comparative study. Our methodology obviates the need for deploying separate models for each task and can potentially conserve resources and time during the training and deployment phases.
The Reasonable Effectiveness of Speaker Embeddings for Violence Detection
Jun 10, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we focus on audio violence detection (AVD). AVD is necessary for several reasons, especially in the context of maintaining safety, preventing harm, and ensuring security in various environments. This calls for accurate AVD systems. Like many related applications in audio processing, the most common approach for improving the performance, would be by leveraging self-supervised (SSL) pre-trained models (PTMs). However, as these SSL models are very large models with million of parameters and this can hinder real-world deployment especially in compute-constraint environment. To resolve this, we propose the usage of speaker recognition models which are much smaller compared to the SSL models. Experimentation with speaker recognition model embeddings with SVM & Random Forest as classifiers, we show that speaker recognition model embeddings perform the best in comparison to state-of-the-art (SOTA) SSL models and achieve SOTA results.
ComFeAT: Combination of Neural and Spectral Features for Improved Depression Detection
Jun 10, 2024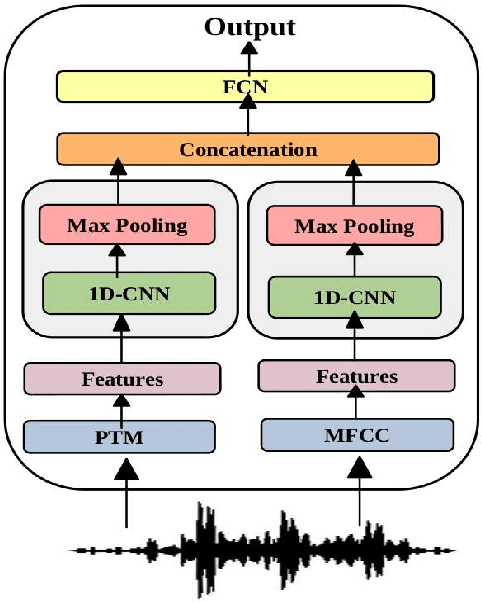
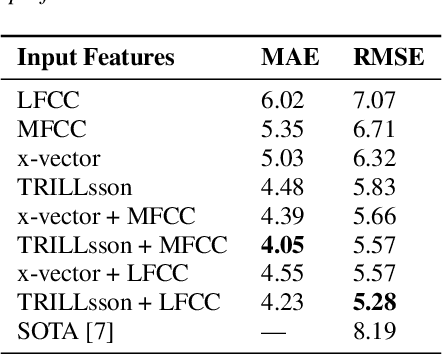
Abstract:In this work, we focus on the detection of depression through speech analysis. Previous research has widely explored features extracted from pre-trained models (PTMs) primarily trained for paralinguistic tasks. Although these features have led to sufficient advances in speech-based depression detection, their performance declines in real-world settings. To address this, in this paper, we introduce ComFeAT, an application that employs a CNN model trained on a combination of features extracted from PTMs, a.k.a. neural features and spectral features to enhance depression detection. Spectral features are robust to domain variations, but, they are not as good as neural features in performance, suprisingly, combining them shows complementary behavior and improves over both neural and spectral features individually. The proposed method also improves over previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) works on E-DAIC benchmark.
From Instructions to Constraints: Language Model Alignment with Automatic Constraint Verification
Mar 10, 2024Abstract:User alignment is crucial for adapting general-purpose language models (LMs) to downstream tasks, but human annotations are often not available for all types of instructions, especially those with customized constraints. We observe that user instructions typically contain constraints. While assessing response quality in terms of the whole instruction is often costly, efficiently evaluating the satisfaction rate of constraints is feasible. We investigate common constraints in NLP tasks, categorize them into three classes based on the types of their arguments, and propose a unified framework, ACT (Aligning to ConsTraints), to automatically produce supervision signals for user alignment with constraints. Specifically, ACT uses constraint verifiers, which are typically easy to implement in practice, to compute constraint satisfaction rate (CSR) of each response. It samples multiple responses for each prompt and collect preference labels based on their CSR automatically. Subsequently, ACT adapts the LM to the target task through a ranking-based learning process. Experiments on fine-grained entity typing, abstractive summarization, and temporal question answering show that ACT is able to enhance LMs' capability to adhere to different classes of constraints, thereby improving task performance. Further experiments show that the constraint-following capabilities are transferable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge