Sangwoo Cho
Lessons from the Field: An Adaptable Lifecycle Approach to Applied Dialogue Summarization
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Summarization of multi-party dialogues is a critical capability in industry, enhancing knowledge transfer and operational effectiveness across many domains. However, automatically generating high-quality summaries is challenging, as the ideal summary must satisfy a set of complex, multi-faceted requirements. While summarization has received immense attention in research, prior work has primarily utilized static datasets and benchmarks, a condition rare in practical scenarios where requirements inevitably evolve. In this work, we present an industry case study on developing an agentic system to summarize multi-party interactions. We share practical insights spanning the full development lifecycle to guide practitioners in building reliable, adaptable summarization systems, as well as to inform future research, covering: 1) robust methods for evaluation despite evolving requirements and task subjectivity, 2) component-wise optimization enabled by the task decomposition inherent in an agentic architecture, 3) the impact of upstream data bottlenecks, and 4) the realities of vendor lock-in due to the poor transferability of LLM prompts.
Leveraging Parameter Space Symmetries for Reasoning Skill Transfer in LLMs
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Task arithmetic is a powerful technique for transferring skills between Large Language Models (LLMs), but it often suffers from negative interference when models have diverged during training. We address this limitation by first aligning the models' parameter spaces, leveraging the inherent permutation, rotation, and scaling symmetries of Transformer architectures. We adapt parameter space alignment for modern Grouped-Query Attention (GQA) and SwiGLU layers, exploring both weight-based and activation-based approaches. Using this alignment-first strategy, we successfully transfer advanced reasoning skills to a non-reasoning model. Experiments on challenging reasoning benchmarks show that our method consistently outperforms standard task arithmetic. This work provides an effective approach for merging and transferring specialized skills across evolving LLM families, reducing redundant fine-tuning and enhancing model adaptability.
Skills Regularized Task Decomposition for Multi-task Offline Reinforcement Learning
Aug 28, 2024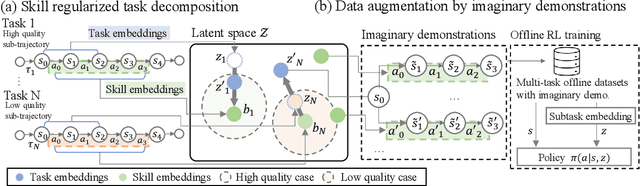
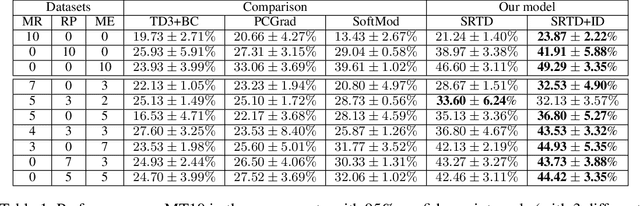
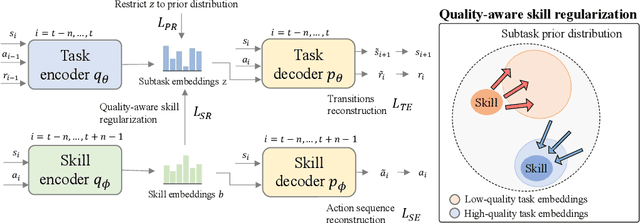
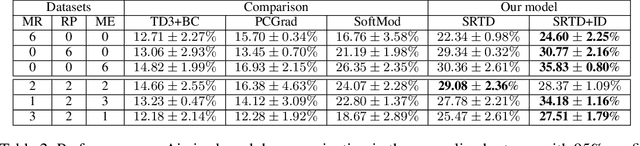
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) with diverse offline datasets can have the advantage of leveraging the relation of multiple tasks and the common skills learned across those tasks, hence allowing us to deal with real-world complex problems efficiently in a data-driven way. In offline RL where only offline data is used and online interaction with the environment is restricted, it is yet difficult to achieve the optimal policy for multiple tasks, especially when the data quality varies for the tasks. In this paper, we present a skill-based multi-task RL technique on heterogeneous datasets that are generated by behavior policies of different quality. To learn the shareable knowledge across those datasets effectively, we employ a task decomposition method for which common skills are jointly learned and used as guidance to reformulate a task in shared and achievable subtasks. In this joint learning, we use Wasserstein auto-encoder (WAE) to represent both skills and tasks on the same latent space and use the quality-weighted loss as a regularization term to induce tasks to be decomposed into subtasks that are more consistent with high-quality skills than others. To improve the performance of offline RL agents learned on the latent space, we also augment datasets with imaginary trajectories relevant to high-quality skills for each task. Through experiments, we show that our multi-task offline RL approach is robust to the mixed configurations of different-quality datasets and it outperforms other state-of-the-art algorithms for several robotic manipulation tasks and drone navigation tasks.
When Reasoning Meets Information Aggregation: A Case Study with Sports Narratives
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Reasoning is most powerful when an LLM accurately aggregates relevant information. We examine the critical role of information aggregation in reasoning by requiring the LLM to analyze sports narratives. To succeed at this task, an LLM must infer points from actions, identify related entities, attribute points accurately to players and teams, and compile key statistics to draw conclusions. We conduct comprehensive experiments with real NBA basketball data and present SportsGen, a new method to synthesize game narratives. By synthesizing data, we can rigorously evaluate LLMs' reasoning capabilities under complex scenarios with varying narrative lengths and density of information. Our findings show that most models, including GPT-4o, often fail to accurately aggregate basketball scores due to frequent scoring patterns. Open-source models like Llama-3 further suffer from significant score hallucinations. Finally, the effectiveness of reasoning is influenced by narrative complexity, information density, and domain-specific terms, highlighting the challenges in analytical reasoning tasks.
Polarity Calibration for Opinion Summarization
Apr 02, 2024



Abstract:Opinion summarization is automatically generating summaries from a variety of subjective information, such as product reviews or political opinions. The challenge of opinions summarization lies in presenting divergent or even conflicting opinions. We conduct an analysis of previous summarization models, which reveals their inclination to amplify the polarity bias, emphasizing the majority opinions while ignoring the minority opinions. To address this issue and make the summarizer express both sides of opinions, we introduce the concept of polarity calibration, which aims to align the polarity of output summary with that of input text. Specifically, we develop a reinforcement training approach for polarity calibration. This approach feeds the polarity distance between output summary and input text as reward into the summarizer, and also balance polarity calibration with content preservation and language naturality. We evaluate our Polarity Calibration model (PoCa) on two types of opinions summarization tasks: summarizing product reviews and political opinions articles. Automatic and human evaluation demonstrate that our approach can mitigate the polarity mismatch between output summary and input text, as well as maintain the content semantic and language quality.
Can Large Language Models do Analytical Reasoning?
Mar 06, 2024



Abstract:This paper explores the cutting-edge Large Language Model with analytical reasoning on sports. Our analytical reasoning embodies the tasks of letting large language models count how many points each team scores in a quarter in the NBA and NFL games. Our major discoveries are in two folds. Firstly, we find among all the models we employed, GPT-4 stands out in effectiveness, followed by Claude-2.1, with GPT-3.5, Gemini-Pro, and Llama-2-70b lagging behind. Specifically, we compare three different prompting techniques and a divide-and-conquer approach, we find that the latter was the most effective. Our divide-and-conquer approach breaks down play-by-play data into smaller, more manageable segments, solves each piece individually, and then aggregates them together. Besides the divide-and-conquer approach, we also explore the Chain of Thought (CoT) strategy, which markedly improves outcomes for certain models, notably GPT-4 and Claude-2.1, with their accuracy rates increasing significantly. However, the CoT strategy has negligible or even detrimental effects on the performance of other models like GPT-3.5 and Gemini-Pro. Secondly, to our surprise, we observe that most models, including GPT-4, struggle to accurately count the total scores for NBA quarters despite showing strong performance in counting NFL quarter scores. This leads us to further investigate the factors that impact the complexity of analytical reasoning tasks with extensive experiments, through which we conclude that task complexity depends on the length of context, the information density, and the presence of related information. Our research provides valuable insights into the complexity of analytical reasoning tasks and potential directions for developing future large language models.
SportsMetrics: Blending Text and Numerical Data to Understand Information Fusion in LLMs
Feb 15, 2024Abstract:Large language models hold significant potential for integrating various data types, such as text documents and database records, for advanced analytics. However, blending text and numerical data presents substantial challenges. LLMs need to process and cross-reference entities and numbers, handle data inconsistencies and redundancies, and develop planning capabilities such as building a working memory for managing complex data queries. In this paper, we introduce four novel tasks centered around sports data analytics to evaluate the numerical reasoning and information fusion capabilities of LLMs. These tasks involve providing LLMs with detailed, play-by-play sports game descriptions, then challenging them with adversarial scenarios such as new game rules, longer durations, scrambled narratives, and analyzing key statistics in game summaries. We conduct extensive experiments on NBA and NFL games to assess the performance of LLMs on these tasks. Our benchmark, SportsMetrics, introduces a new mechanism for assessing LLMs' numerical reasoning and fusion skills.
SPECTRUM: Speaker-Enhanced Pre-Training for Long Dialogue Summarization
Jan 31, 2024Abstract:Multi-turn dialogues are characterized by their extended length and the presence of turn-taking conversations. Traditional language models often overlook the distinct features of these dialogues by treating them as regular text. In this paper, we propose a speaker-enhanced pre-training method for long dialogue summarization, which leverages the inherent structure of multiple-turn dialogues. To support our study, we curate a diverse dataset that includes transcripts from real-world scenarios, movie or TV show transcripts, and dialogues generated by a Large Language Model. We then perform a pre-training, which encompasses the detection of speaker changes, and masked utterance generation. Experimental results of fine-tuned models demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on downstream benchmarks with long context, surpassing baseline models and highlighting the effectiveness of our approach. Our findings highlight the importance of curating pre-training datasets that exhibit diversity and variations in length distribution to ensure effective alignment with downstream datasets.
InFoBench: Evaluating Instruction Following Ability in Large Language Models
Jan 07, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces the Decomposed Requirements Following Ratio (DRFR), a new metric for evaluating Large Language Models' (LLMs) ability to follow instructions. Addressing a gap in current methodologies, DRFR breaks down complex instructions into simpler criteria, facilitating a detailed analysis of LLMs' compliance with various aspects of tasks. Alongside this metric, we present InFoBench, a benchmark comprising 500 diverse instructions and 2,250 decomposed questions across multiple constraint categories. Our experiments compare DRFR with traditional scoring methods and explore annotation sources, including human experts, crowd-sourced workers, and GPT-4. The findings demonstrate DRFR's higher reliability and the effectiveness of using GPT-4 as a cost-efficient annotator. The evaluation of several advanced LLMs using this framework reveals their strengths and areas needing improvement, particularly in complex instruction-following. This study contributes a novel metric and benchmark, offering insights for future LLM development and evaluation.
Zebra: Extending Context Window with Layerwise Grouped Local-Global Attention
Dec 14, 2023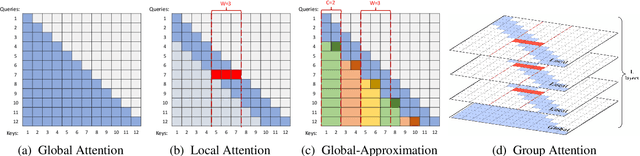


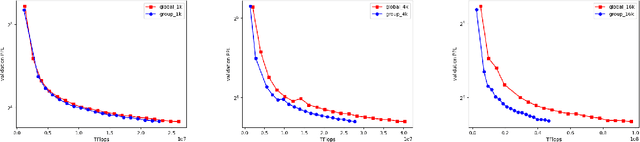
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel approach to enhance the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in processing and understanding extensive text sequences, a critical aspect in applications requiring deep comprehension and synthesis of large volumes of information. Recognizing the inherent challenges in extending the context window for LLMs, primarily built on Transformer architecture, we propose a new model architecture, referred to as Zebra. This architecture efficiently manages the quadratic time and memory complexity issues associated with full attention in the Transformer by employing grouped local-global attention layers. Our model, akin to a zebra's alternating stripes, balances local and global attention layers, significantly reducing computational requirements and memory consumption. Comprehensive experiments, including pretraining from scratch, continuation of long context adaptation training, and long instruction tuning, are conducted to evaluate the Zebra's performance. The results show that Zebra achieves comparable or superior performance on both short and long sequence benchmarks, while also enhancing training and inference efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge