Sahal Shaji Mullappilly
A Benchmark and Agentic Framework for Omni-Modal Reasoning and Tool Use in Long Videos
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Long-form multimodal video understanding requires integrating vision, speech, and ambient audio with coherent long-range reasoning. Existing benchmarks emphasize either temporal length or multimodal richness, but rarely both and while some incorporate open-ended questions and advanced metrics, they mostly rely on single-score accuracy, obscuring failure modes. We introduce LongShOTBench, a diagnostic benchmark with open-ended, intent-driven questions; single- and multi-turn dialogues; and tasks requiring multimodal reasoning and agentic tool use across video, audio, and speech. Each item includes a reference answer and graded rubric for interpretable, and traceable evaluation. LongShOTBench is produced via a scalable, human-validated pipeline to ensure coverage and reproducibility. All samples in our LongShOTBench are human-verified and corrected. Furthermore, we present LongShOTAgent, an agentic system that analyzes long videos via preprocessing, search, and iterative refinement. On LongShOTBench, state-of-the-art MLLMs show large gaps: Gemini-2.5-Flash achieves 52.95%, open-source models remain below 30%, and LongShOTAgent attains 44.66%. These results underscore the difficulty of real-world long-form video understanding. LongShOTBench provides a practical, reproducible foundation for evaluating and improving MLLMs. All resources are available on GitHub: https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/longshot.
LLMVoX: Autoregressive Streaming Text-to-Speech Model for Any LLM
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in speech-to-speech dialogue systems leverage LLMs for multimodal interactions, yet they remain hindered by fine-tuning requirements, high computational overhead, and text-speech misalignment. Existing speech-enabled LLMs often degrade conversational quality by modifying the LLM, thereby compromising its linguistic capabilities. In contrast, we propose LLMVoX, a lightweight 30M-parameter, LLM-agnostic, autoregressive streaming TTS system that generates high-quality speech with low latency, while fully preserving the capabilities of the base LLM. Our approach achieves a significantly lower Word Error Rate compared to speech-enabled LLMs, while operating at comparable latency and UTMOS score. By decoupling speech synthesis from LLM processing via a multi-queue token streaming system, LLMVoX supports seamless, infinite-length dialogues. Its plug-and-play design also facilitates extension to various tasks with different backbones. Furthermore, LLMVoX generalizes to new languages with only dataset adaptation, attaining a low Character Error Rate on an Arabic speech task. Additionally, we have integrated LLMVoX with a Vision-Language Model to create an omni-model with speech, text, and vision capabilities, without requiring additional multimodal training. Our code base and project page is available at https://mbzuai-oryx.github.io/LLMVoX .
BiMediX2: Bio-Medical EXpert LMM for Diverse Medical Modalities
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces BiMediX2, a bilingual (Arabic-English) Bio-Medical EXpert Large Multimodal Model (LMM) with a unified architecture that integrates text and visual modalities, enabling advanced image understanding and medical applications. BiMediX2 leverages the Llama3.1 architecture and integrates text and visual capabilities to facilitate seamless interactions in both English and Arabic, supporting text-based inputs and multi-turn conversations involving medical images. The model is trained on an extensive bilingual healthcare dataset consisting of 1.6M samples of diverse medical interactions for both text and image modalities, mixed in Arabic and English. We also propose the first bilingual GPT-4o based medical LMM benchmark named BiMed-MBench. BiMediX2 is benchmarked on both text-based and image-based tasks, achieving state-of-the-art performance across several medical benchmarks. It outperforms recent state-of-the-art models in medical LLM evaluation benchmarks. Our model also sets a new benchmark in multimodal medical evaluations with over 9% improvement in English and over 20% in Arabic evaluations. Additionally, it surpasses GPT-4 by around 9% in UPHILL factual accuracy evaluations and excels in various medical Visual Question Answering, Report Generation, and Report Summarization tasks. The project page including source code and the trained model, is available at https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/BiMediX2.
Semi-supervised Open-World Object Detection
Feb 25, 2024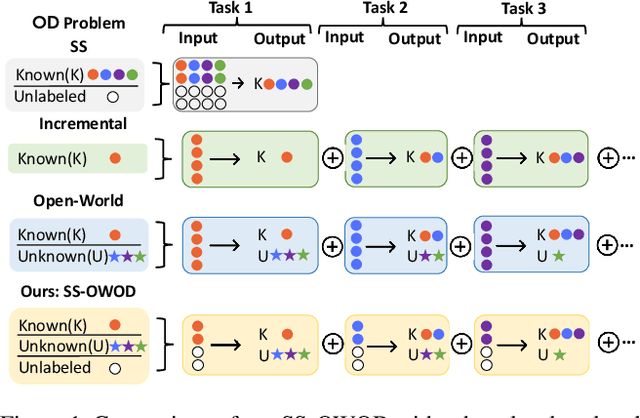
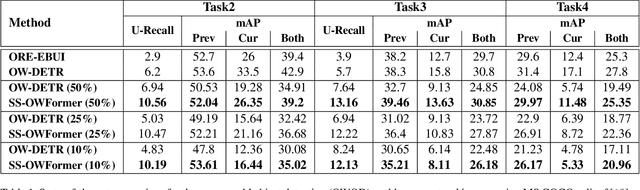
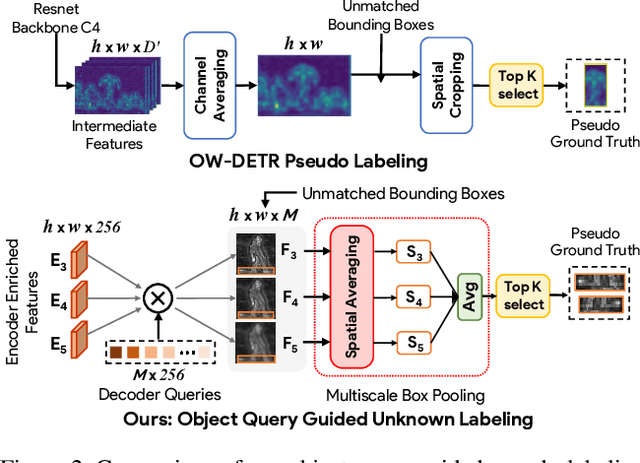
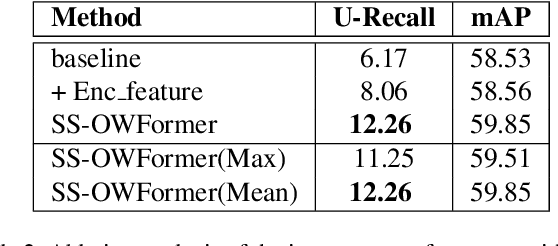
Abstract:Conventional open-world object detection (OWOD) problem setting first distinguishes known and unknown classes and then later incrementally learns the unknown objects when introduced with labels in the subsequent tasks. However, the current OWOD formulation heavily relies on the external human oracle for knowledge input during the incremental learning stages. Such reliance on run-time makes this formulation less realistic in a real-world deployment. To address this, we introduce a more realistic formulation, named semi-supervised open-world detection (SS-OWOD), that reduces the annotation cost by casting the incremental learning stages of OWOD in a semi-supervised manner. We demonstrate that the performance of the state-of-the-art OWOD detector dramatically deteriorates in the proposed SS-OWOD setting. Therefore, we introduce a novel SS-OWOD detector, named SS-OWFormer, that utilizes a feature-alignment scheme to better align the object query representations between the original and augmented images to leverage the large unlabeled and few labeled data. We further introduce a pseudo-labeling scheme for unknown detection that exploits the inherent capability of decoder object queries to capture object-specific information. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our SS-OWOD problem setting and approach for remote sensing object detection, proposing carefully curated splits and baseline performance evaluations. Our experiments on 4 datasets including MS COCO, PASCAL, Objects365 and DOTA demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Our source code, models and splits are available here - https://github.com/sahalshajim/SS-OWFormer
BiMediX: Bilingual Medical Mixture of Experts LLM
Feb 20, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce BiMediX, the first bilingual medical mixture of experts LLM designed for seamless interaction in both English and Arabic. Our model facilitates a wide range of medical interactions in English and Arabic, including multi-turn chats to inquire about additional details such as patient symptoms and medical history, multiple-choice question answering, and open-ended question answering. We propose a semi-automated English-to-Arabic translation pipeline with human refinement to ensure high-quality translations. We also introduce a comprehensive evaluation benchmark for Arabic medical LLMs. Furthermore, we introduce BiMed1.3M, an extensive Arabic-English bilingual instruction set covering 1.3 Million diverse medical interactions, resulting in over 632 million healthcare specialized tokens for instruction tuning. Our BiMed1.3M dataset includes 250k synthesized multi-turn doctor-patient chats and maintains a 1:2 Arabic-to-English ratio. Our model outperforms state-of-the-art Med42 and Meditron by average absolute gains of 2.5% and 4.1%, respectively, computed across multiple medical evaluation benchmarks in English, while operating at 8-times faster inference. Moreover, our BiMediX outperforms the generic Arabic-English bilingual LLM, Jais-30B, by average absolute gains of 10% on our Arabic medical benchmark and 15% on bilingual evaluations across multiple datasets. Our project page with source code and trained model is available at https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/BiMediX .
Arabic Mini-ClimateGPT : A Climate Change and Sustainability Tailored Arabic LLM
Dec 14, 2023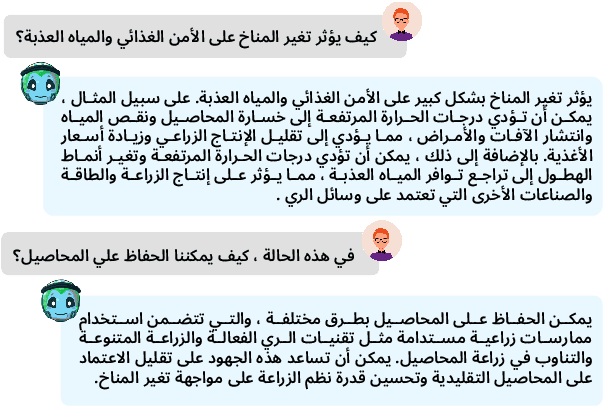
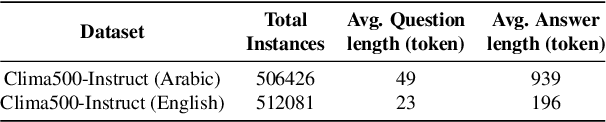
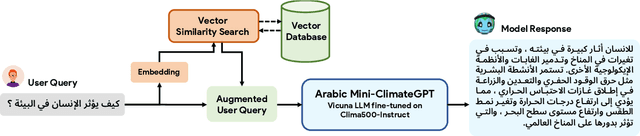
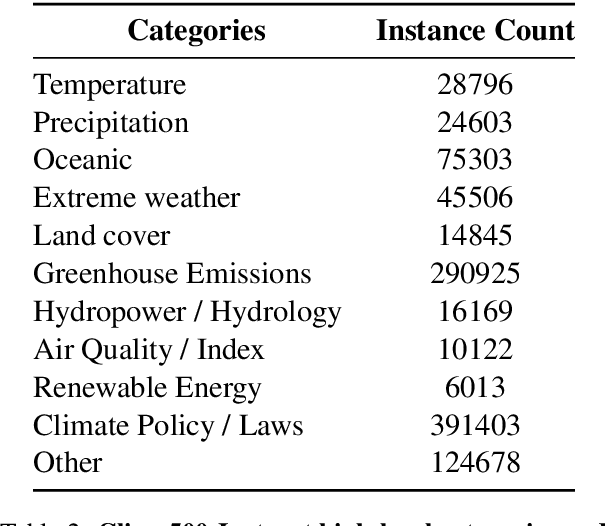
Abstract:Climate change is one of the most significant challenges we face together as a society. Creating awareness and educating policy makers the wide-ranging impact of climate change is an essential step towards a sustainable future. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and Bard have shown impressive conversational abilities and excel in a wide variety of NLP tasks. While these models are close-source, recently alternative open-source LLMs such as Stanford Alpaca and Vicuna have shown promising results. However, these open-source models are not specifically tailored for climate related domain specific information and also struggle to generate meaningful responses in other languages such as, Arabic. To this end, we propose a light-weight Arabic Mini-ClimateGPT that is built on an open-source LLM and is specifically fine-tuned on a conversational-style instruction tuning curated Arabic dataset Clima500-Instruct with over 500k instructions about climate change and sustainability. Further, our model also utilizes a vector embedding based retrieval mechanism during inference. We validate our proposed model through quantitative and qualitative evaluations on climate-related queries. Our model surpasses the baseline LLM in 88.3% of cases during ChatGPT-based evaluation. Furthermore, our human expert evaluation reveals an 81.6% preference for our model's responses over multiple popular open-source models. Our open-source demos, code-base and models are available here https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/ClimateGPT.
* Accepted to EMNLP 2023 (Findings)
XrayGPT: Chest Radiographs Summarization using Medical Vision-Language Models
Jun 13, 2023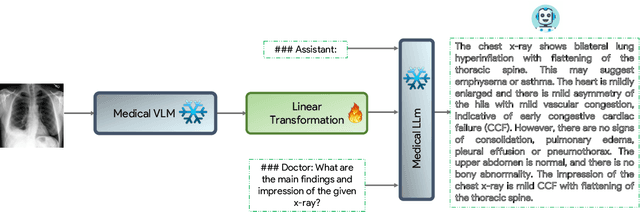
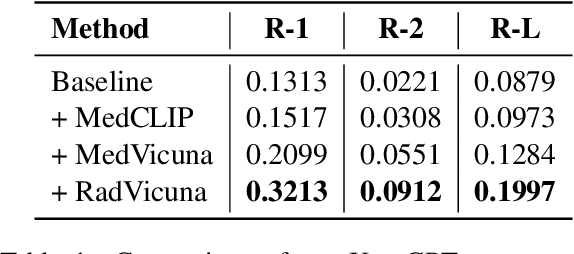


Abstract:The latest breakthroughs in large vision-language models, such as Bard and GPT-4, have showcased extraordinary abilities in performing a wide range of tasks. Such models are trained on massive datasets comprising billions of public image-text pairs with diverse tasks. However, their performance on task-specific domains, such as radiology, is still under-investigated and potentially limited due to a lack of sophistication in understanding biomedical images. On the other hand, conversational medical models have exhibited remarkable success but have mainly focused on text-based analysis. In this paper, we introduce XrayGPT, a novel conversational medical vision-language model that can analyze and answer open-ended questions about chest radiographs. Specifically, we align both medical visual encoder (MedClip) with a fine-tuned large language model (Vicuna), using a simple linear transformation. This alignment enables our model to possess exceptional visual conversation abilities, grounded in a deep understanding of radiographs and medical domain knowledge. To enhance the performance of LLMs in the medical context, we generate ~217k interactive and high-quality summaries from free-text radiology reports. These summaries serve to enhance the performance of LLMs through the fine-tuning process. Our approach opens up new avenues the research for advancing the automated analysis of chest radiographs. Our open-source demos, models, and instruction sets are available at: https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/XrayGPT.
An Empirical Study Of Self-supervised Learning Approaches For Object Detection With Transformers
May 11, 2022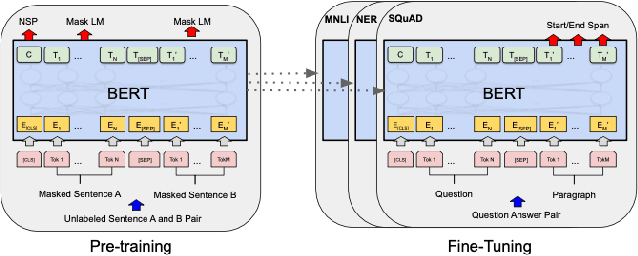
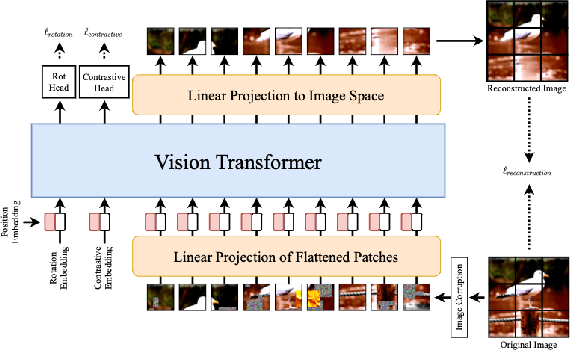
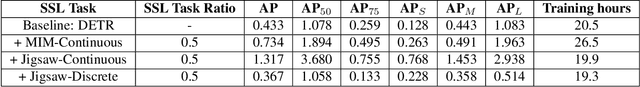
Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) methods such as masked language modeling have shown massive performance gains by pretraining transformer models for a variety of natural language processing tasks. The follow-up research adapted similar methods like masked image modeling in vision transformer and demonstrated improvements in the image classification task. Such simple self-supervised methods are not exhaustively studied for object detection transformers (DETR, Deformable DETR) as their transformer encoder modules take input in the convolutional neural network (CNN) extracted feature space rather than the image space as in general vision transformers. However, the CNN feature maps still maintain the spatial relationship and we utilize this property to design self-supervised learning approaches to train the encoder of object detection transformers in pretraining and multi-task learning settings. We explore common self-supervised methods based on image reconstruction, masked image modeling and jigsaw. Preliminary experiments in the iSAID dataset demonstrate faster convergence of DETR in the initial epochs in both pretraining and multi-task learning settings; nonetheless, similar improvement is not observed in the case of multi-task learning with Deformable DETR. The code for our experiments with DETR and Deformable DETR are available at https://github.com/gokulkarthik/detr and https://github.com/gokulkarthik/Deformable-DETR respectively.
MuCoT: Multilingual Contrastive Training for Question-Answering in Low-resource Languages
Apr 12, 2022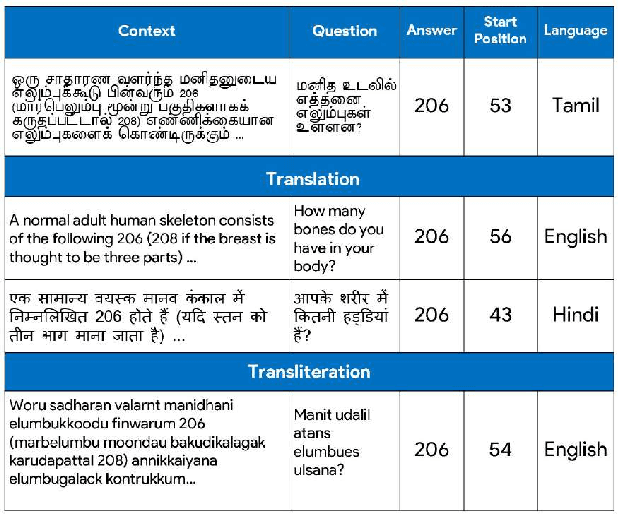
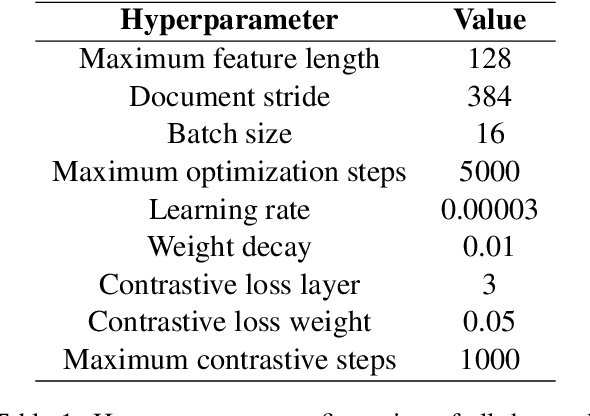
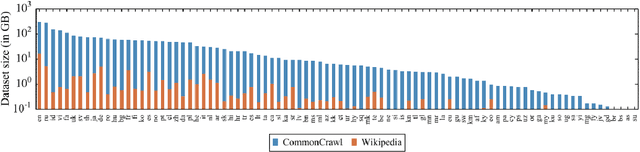
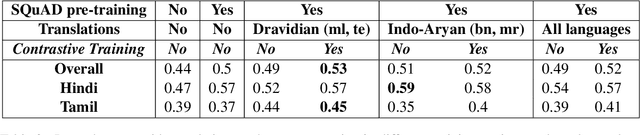
Abstract:Accuracy of English-language Question Answering (QA) systems has improved significantly in recent years with the advent of Transformer-based models (e.g., BERT). These models are pre-trained in a self-supervised fashion with a large English text corpus and further fine-tuned with a massive English QA dataset (e.g., SQuAD). However, QA datasets on such a scale are not available for most of the other languages. Multi-lingual BERT-based models (mBERT) are often used to transfer knowledge from high-resource languages to low-resource languages. Since these models are pre-trained with huge text corpora containing multiple languages, they typically learn language-agnostic embeddings for tokens from different languages. However, directly training an mBERT-based QA system for low-resource languages is challenging due to the paucity of training data. In this work, we augment the QA samples of the target language using translation and transliteration into other languages and use the augmented data to fine-tune an mBERT-based QA model, which is already pre-trained in English. Experiments on the Google ChAII dataset show that fine-tuning the mBERT model with translations from the same language family boosts the question-answering performance, whereas the performance degrades in the case of cross-language families. We further show that introducing a contrastive loss between the translated question-context feature pairs during the fine-tuning process, prevents such degradation with cross-lingual family translations and leads to marginal improvement. The code for this work is available at https://github.com/gokulkarthik/mucot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge