Saber Zerhoudi
OwlerLite: Scope- and Freshness-Aware Web Retrieval for LLM Assistants
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Browser-based language models often use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) but typically rely on fixed, outdated indices that give users no control over which sources are consulted. This can lead to answers that mix trusted and untrusted content or draw on stale information. We present OwlerLite, a browser-based RAG system that makes user-defined scopes and data freshness central to retrieval. Users define reusable scopes-sets of web pages or sources-and select them when querying. A freshness-aware crawler monitors live pages, uses a semantic change detector to identify meaningful updates, and selectively re-indexes changed content. OwlerLite integrates text relevance, scope choice, and recency into a unified retrieval model. Implemented as a browser extension, it represents a step toward more controllable and trustworthy web assistants.
From SERPs to Agents: A Platform for Comparative Studies of Information Interaction
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:The diversification of information access systems, from RAG to autonomous agents, creates a critical need for comparative user studies. However, the technical overhead to deploy and manage these distinct systems is a major barrier. We present UXLab, an open-source system for web-based user studies that addresses this challenge. Its core is a web-based dashboard enabling the complete, no-code configuration of complex experimental designs. Researchers can visually manage the full study, from recruitment to comparing backends like traditional search, vector databases, and LLMs. We demonstrate UXLab's value via a micro case study comparing user behavior with RAG versus an autonomous agent. UXLab allows researchers to focus on experimental design and analysis, supporting future multi-modal interaction research.
In-Browser Agents for Search Assistance
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:A fundamental tension exists between the demand for sophisticated AI assistance in web search and the need for user data privacy. Current centralized models require users to transmit sensitive browsing data to external services, which limits user control. In this paper, we present a browser extension that provides a viable in-browser alternative. We introduce a hybrid architecture that functions entirely on the client side, combining two components: (1) an adaptive probabilistic model that learns a user's behavioral policy from direct feedback, and (2) a Small Language Model (SLM), running in the browser, which is grounded by the probabilistic model to generate context-aware suggestions. To evaluate this approach, we conducted a three-week longitudinal user study with 18 participants. Our results show that this privacy-preserving approach is highly effective at adapting to individual user behavior, leading to measurably improved search efficiency. This work demonstrates that sophisticated AI assistance is achievable without compromising user privacy or data control.
Variations in Relevance Judgments and the Shelf Life of Test Collections
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:The fundamental property of Cranfield-style evaluations, that system rankings are stable even when assessors disagree on individual relevance decisions, was validated on traditional test collections. However, the paradigm shift towards neural retrieval models affected the characteristics of modern test collections, e.g., documents are short, judged with four grades of relevance, and information needs have no descriptions or narratives. Under these changes, it is unclear whether assessor disagreement remains negligible for system comparisons. We investigate this aspect under the additional condition that the few modern test collections are heavily re-used. Given more possible query interpretations due to less formalized information needs, an ''expiration date'' for test collections might be needed if top-effectiveness requires overfitting to a single interpretation of relevance. We run a reproducibility study and re-annotate the relevance judgments of the 2019 TREC Deep Learning track. We can reproduce prior work in the neural retrieval setting, showing that assessor disagreement does not affect system rankings. However, we observe that some models substantially degrade with our new relevance judgments, and some have already reached the effectiveness of humans as rankers, providing evidence that test collections can expire.
Report on the Workshop on Simulations for Information Access (Sim4IA 2024) at SIGIR 2024
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:This paper is a report of the Workshop on Simulations for Information Access (Sim4IA) workshop at SIGIR 2024. The workshop had two keynotes, a panel discussion, nine lightning talks, and two breakout sessions. Key takeaways were user simulation's importance in academia and industry, the possible bridging of online and offline evaluation, and the issues of organizing a companion shared task around user simulations for information access. We report on how we organized the workshop, provide a brief overview of what happened at the workshop, and summarize the main topics and findings of the workshop and future work.
PersonaRAG: Enhancing Retrieval-Augmented Generation Systems with User-Centric Agents
Jul 12, 2024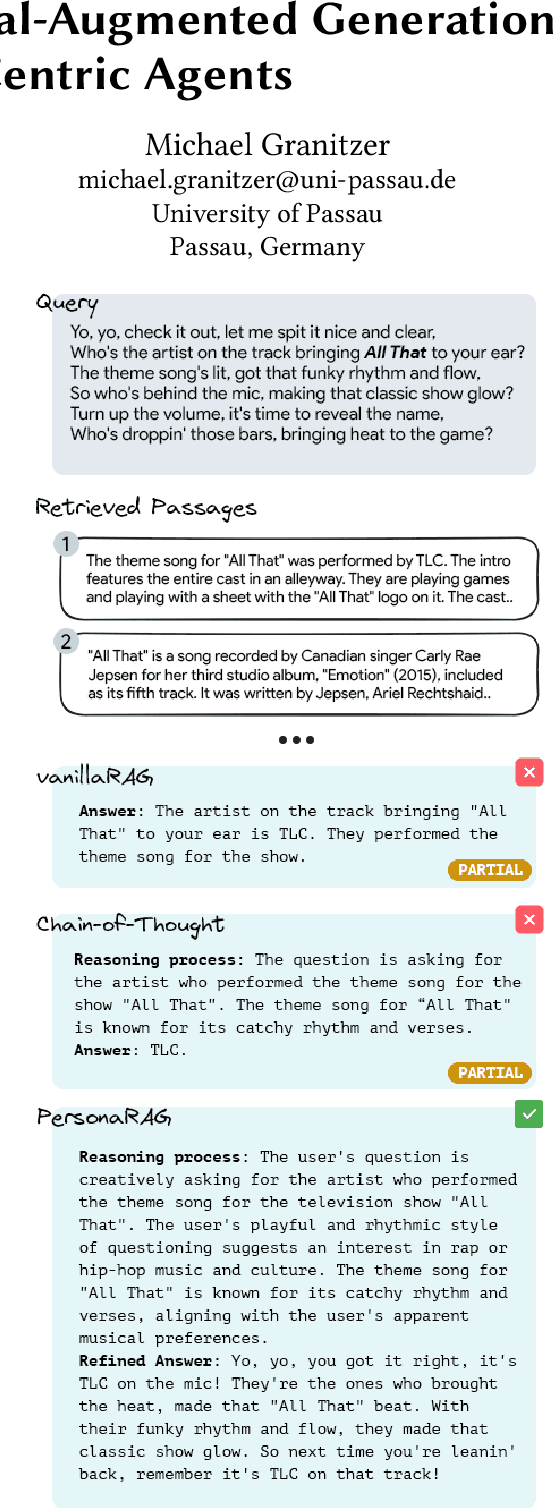
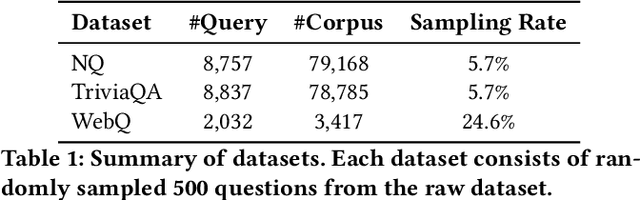
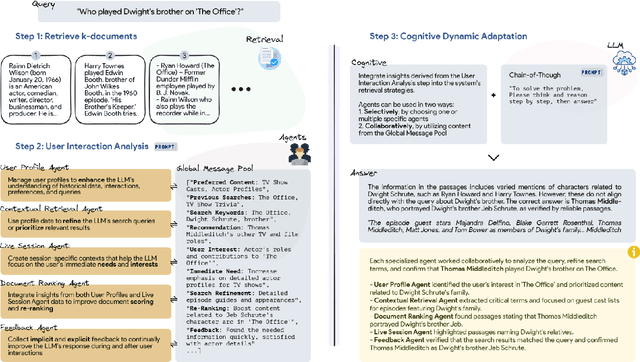
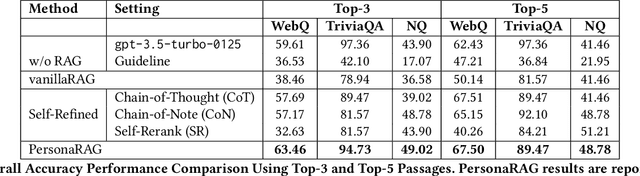
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle with generating reliable outputs due to outdated knowledge and hallucinations. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) models address this by enhancing LLMs with external knowledge, but often fail to personalize the retrieval process. This paper introduces PersonaRAG, a novel framework incorporating user-centric agents to adapt retrieval and generation based on real-time user data and interactions. Evaluated across various question answering datasets, PersonaRAG demonstrates superiority over baseline models, providing tailored answers to user needs. The results suggest promising directions for user-adapted information retrieval systems.
Beyond Benchmarks: Evaluating Embedding Model Similarity for Retrieval Augmented Generation Systems
Jul 11, 2024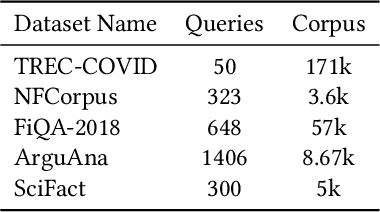
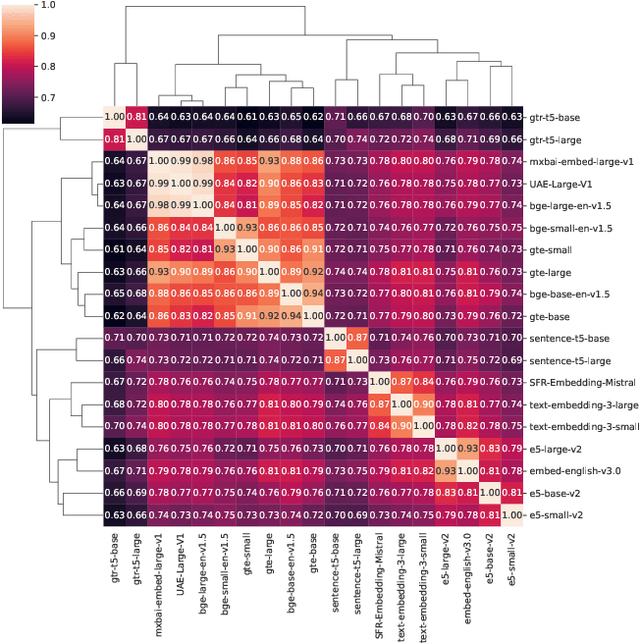
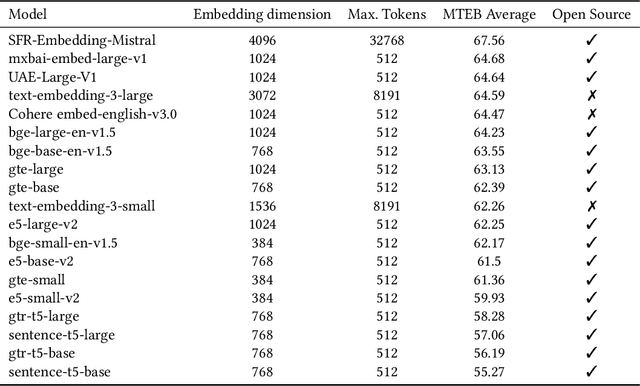
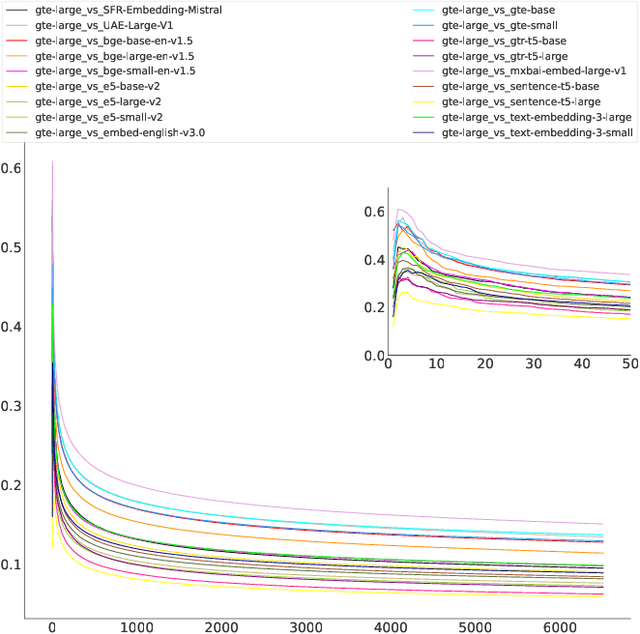
Abstract:The choice of embedding model is a crucial step in the design of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. Given the sheer volume of available options, identifying clusters of similar models streamlines this model selection process. Relying solely on benchmark performance scores only allows for a weak assessment of model similarity. Thus, in this study, we evaluate the similarity of embedding models within the context of RAG systems. Our assessment is two-fold: We use Centered Kernel Alignment to compare embeddings on a pair-wise level. Additionally, as it is especially pertinent to RAG systems, we evaluate the similarity of retrieval results between these models using Jaccard and rank similarity. We compare different families of embedding models, including proprietary ones, across five datasets from the popular Benchmark Information Retrieval (BEIR). Through our experiments we identify clusters of models corresponding to model families, but interestingly, also some inter-family clusters. Furthermore, our analysis of top-k retrieval similarity reveals high-variance at low k values. We also identify possible open-source alternatives to proprietary models, with Mistral exhibiting the highest similarity to OpenAI models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge